|
Bombing Of Hamburg In World War II
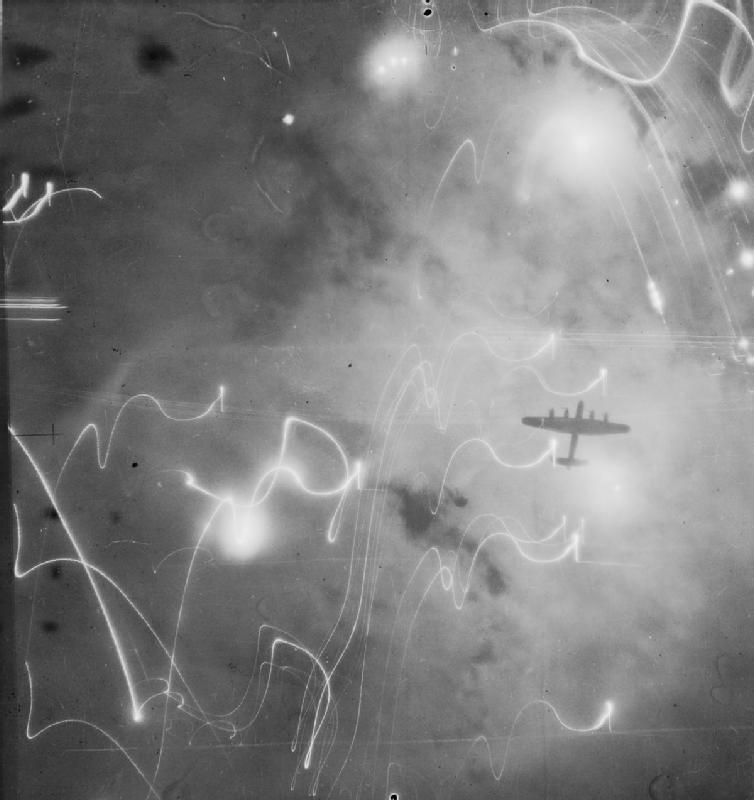
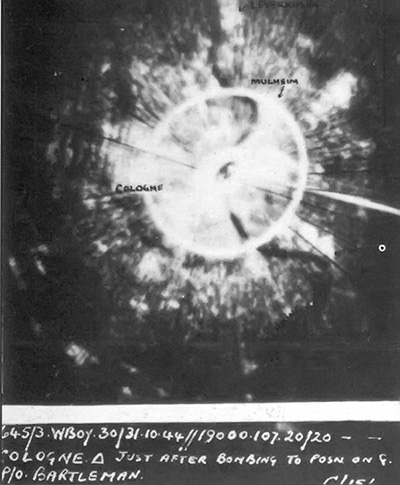
The Allied bombing of Hamburg during World War II included numerous attacks on civilians and civic infrastructure. As a large city and industrial centre, Hamburg's shipyards, U-boat pens, and the Hamburg-Harburg area oil refineries were attacked throughout the war. As part of a sustained campaign of strategic bombing during World War II, the attack during the last week of July 1943, code named Operation Gomorrah, created one of the largest firestorms raised by the Royal Air Force and United States Army Air Forces in World War II, killing an estimated 37,000 people in Hamburg, wounding 180,000 more, and destroying 60% of the city's houses. Hamburg was selected as a target because it was considered particularly susceptible to attack with incendiaries, which, from the experience of the Blitz, were known to inflict more damage than just high explosive bombs. Hamburg also contained a high number of targets supporting the German war effort and was relatively easy for navigators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H2S Radar
H2S was the first airborne radar system, airborne, Airborne ground surveillance, ground scanning radar system. It was developed for the Royal Air Force's RAF Bomber Command, Bomber Command during World War II to identify targets on the ground for night and all-weather bombing. This allowed attacks outside the range of the various radio navigation aids like Gee (navigation), Gee or Oboe (navigation), Oboe, which were limited to about of range from various base stations. It was also widely used as a general navigation system, allowing landmarks to be identified at long range. In March 1941, experiments with an early aircraft interception radar based on the 9.1 cm wavelength, S band, (3 GHz) cavity magnetron revealed that different objects have very different radar signatures; water, open land and built-up areas of cities and towns all produced distinct returns. In January 1942, a new team was set up to combine the magnetron with a new scanning antenna and plan position indic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, during the Second World War) and again from 1951 to 1955. For some 62 of the years between 1900 and 1964, he was a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), member of parliament (MP) and represented a total of five Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, constituencies over that time. Ideologically an adherent to economic liberalism and imperialism, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924. Of mixed English and American parentage, Churchill was born in Oxfordshire into the wealthy, aristocratic Spencer family. He joined the British Army in 1895 and saw action in British R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin D
Franklin may refer to: People and characters * Franklin (given name), including list of people and characters with the name * Franklin (surname), including list of people and characters with the name * Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class Places * Franklin (crater), a lunar impact crater * Franklin County (other), in a number of countries * Mount Franklin (other), including Franklin Mountain Australia * Franklin, Tasmania, a township * Division of Franklin, federal electoral division in Tasmania * Division of Franklin (state), state electoral division in Tasmania * Franklin, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Gungahlin * Franklin River, river of Tasmania * Franklin Sound, waterway of Tasmania Canada * District of Franklin, a former district of the Northwest Territories * Franklin, Quebec, a municipality in the Montérégie region * Rural Municipality of Franklin, Manitoba * Franklin, Manitoba, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth Air Force
The Eighth Air Force (Air Forces Strategic) is a numbered air force (NAF) of the United States Air Force's Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). It is headquartered at Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana. The command serves as Air Forces Strategic – Global Strike, one of the air components of United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). The Eighth Air Force includes the heart of America's heavy bomber force: the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit stealth bomber, the Rockwell B-1 Lancer supersonic bomber, and the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress heavy bomber aircraft. VIII Bomber Command of the United States Army Air Forces was established early in 1942. The first combat units arrived in the United Kingdom in June and combat operations began in July with first heavy bomber operations in August. Its bomber units were deployed in the UK, chiefly around East Anglia. From June 1943 it was the daylight bombing part of the Combined Bomber Offensive against Germany. VIII Bomber Command was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the Strategic bombing during World War II#Europe, strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bombing campaign against Germany became Area bombing directive, less restrictive and increasingly targeted industrial sites and the civilian manpower base essential for German war production. In total 501,536 operational sorties were flown, of bombs were dropped and 8,325 aircraft lost in action. Bomber Command crews also suffered a high casualty rate: 55,573 were killed out of a total of 125,000 aircrew, a 44.4% death rate. A further 8,403 men were wounded in action, and 9,838 became prisoners of war. Bomber Command stood at the peak of its post-war Armed forces, military power in the 1960s, the V bombers holding the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent and a supplemental force of English Electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Harris
Marshal of the Royal Air Force Sir Arthur Travers Harris, 1st Baronet, (13 April 1892 – 5 April 1984), commonly known as "Bomber" Harris by the press and often within the RAF as "Butcher" or "Butch" Harris, was Air Officer Commanding, Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief (AOC-in-C) RAF Bomber Command during the height of the Anglo-American strategic bombing campaign against Nazi Germany in the Second World War. Born in Gloucestershire, Harris emigrated to Rhodesia (region), Rhodesia in 1910, aged 17. He joined the Rhodesia Regiment, 1st Rhodesia Regiment at the outbreak of the First World War and saw action in South Africa and South West Africa campaign, South West Africa. In 1915, Harris returned to England to fight in the Western Front (World War I), European theatre of the war. He joined the Royal Flying Corps, with which he remained until the formation of the Royal Air Force in 1918. Harris remained in the Air Force through the 1920s and 1930s, serving in British India, India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area Bombing
In military aviation, area bombardment or area bombing is a type of aerial bombardment in which bombs are dropped over the general area of a target. The term "area bombing" came into prominence during World War II. Area bombing is a form of strategic bombing. It can serve several intertwined purposes: to disrupt the production of military materiel, to disrupt lines of communications, to divert the enemy's industrial and military resources from the primary battlefield to air defence and infrastructure repair, and to demoralise the enemy's population (See terror bombing). "Carpet bombing",An early example of this use of "carpet bombing" is from 1942: also known as "saturation bombing", and "obliteration bombing", refers to a type of area bombing that aims to effect complete destruction of the target area by exploding bombs in every part of it. Area bombing is contrasted with precision bombing. The latter is directed at a selected target – not necessarily a small, and not nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total War
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all (including civilian-associated) resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilises all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare over non-combatant needs. The term has been defined as "A war that is unrestricted in terms of the weapons used, the Territory (country subdivision), territory or combatants involved, or the objectives pursued, especially one in which the law of war, laws of war are disregarded." In the mid-19th century, scholars identified what later became known as total war as a separate class of warfare. In a total war, the differentiation between combatants and non-combatants diminishes due to the capacity of opposing sides to consider nearly every human, including non-combatants, as resources that are used in the war effort. Characteristics Total war is a concept that has been extensively studied by scholars of conflict and war. One of the most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill War Ministry
The Churchill war ministry was the United Kingdom's unity coalition government for most of the Second World War from 10 May 1940 to 23 May 1945. It was led by Winston Churchill, who was appointed prime minister of the United Kingdom by King George VI following the resignation of Neville Chamberlain in the aftermath of the Norway Debate. At the outset, Churchill formed a five-man war cabinet which included Chamberlain as Lord President of the Council, Clement Attlee as Lord Privy Seal and later as Deputy Prime Minister, Viscount Halifax as Foreign Secretary, and Arthur Greenwood as a minister without portfolio. Although the original war cabinet was limited to five members, in practice they were augmented by the service chiefs and ministers who attended the majority of meetings. The cabinet changed in size and membership as the war progressed but there were significant additions later in 1940 when it was increased to eight after Churchill, Attlee, and Greenwood were joined b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire And Brimstone
Fire and brimstone ( ''gofrīt wāʾēš''; ) is an idiomatic expression referring to God's wrath found in both the Old and New Testaments. In the Bible, it often appears in reference to the fate of the unfaithful. Brimstone, an archaic term for sulfur, evokes the acrid odor of sulfur dioxide, which is stated to be given off by lightning strikes. The association of sulfur with divine retribution is common in the Bible. The English translation "fire and brimstone" is found in the 1611 Christian King James Version of the Old Testament and also in the 1917 translation of the Jewish Publication Society. The 1857 Leeser translation of the Tanakh inconsistently uses both "sulfur" and "brimstone" to translate גָּפְרִ֣ית וָאֵ֑שׁ. The translation used by the 1985 New JPS is "sulfurous fire" while the 1978 Christian New International Version translation uses "burning sulfur." Used as an adjective, fire-and-brimstone often refers to a style of Christian preaching th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |