|
Blue Cheese
Blue cheese is any cheese made with the addition of Microbial food cultures, cultures of edible Mold (fungus), molds, which create blue-green spots or veins through the cheese. Blue cheeses vary in flavor from mild to strong and from slightly sweet to salty or sharp; in colour from pale to dark; and in consistency from liquid to hard. They may have a distinctive smell, either from the mold or from various specially cultivated bacteria such as ''Brevibacterium linens''. Some blue cheeses are injected with spores before the curds form, and others have spores mixed in with the curds after they form. Blue cheeses are typically aged in temperature-controlled environments. History Blue cheese is believed to have been discovered by accident when cheeses were stored in caves with naturally controlled temperature and moisture levels which happened to be favorable environments for varieties of harmless mold. Analysis of paleofeces sampled in the salt mines of Hallstatt , Hallstatt, Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleu Au Lait De Chèvre
Bleu or BLEU may refer to: * ''Three Colors: Blue'', a 1993 film * BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy), a machine translation evaluation metric * Belgium–Luxembourg Economic Union * Blue cheese, a type of cheese * Parti bleu, 19th century political group in Quebec, Canada * ''Doneness, Bleu'' (blue-rare), synonymous with "extra rare", indicating a barely-cooked meat preparation; very red and cold * ''Le Bleu'', a 2001 album by Justin King People * Bleu (musician), a member of the pop group L.E.O. * Corbin Bleu, an American actor, model, dancer and singer * Yung Bleu, an American record producer, rapper and singer also known as "Bleu" * Deis, a character from the ''Breath of Fire'' role-playing video game series known as "Bleu" in the English versions See also * Blue (other) * Lebleu (other) * Les Bleus (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonzola (cheese)
Gorgonzola (, ) is a famously pungent Italian blue cheese made from unskimmed cow's milk; believed to have been created in the 9th century; now with use of its name controlled under the criteria of a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO). Gorgonzola is available in two primary variations: ''Dolce'' with a more delicate flavor and buttery consistency, vs ''Piccante'' with a more pungent flavor and firm, crumbly texture. Either can be quite salty, with a "bite" from their blue veining. More recently, a variation has been marketed widely, featuring a layered block alternating the more assertive Gorgonzola with the more delicate Mascarpone, marketed as ''Gorgonzola e Mascarpone.'' The cheese takes its name from Lombardian town of Gorgonzola, Milan, where the cheese originated and which celebrates an annual September Gorgonzola festival, called the ''Sagra Nazionale del Gorgonzola''. Within the European Union and countries recognizing Protected Designation of Origin (PDO), a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Lactis
''Lactococcus lactis'' is a gram-positive bacterium used extensively in the production of buttermilk and cheese, but has also become famous as the first genetically modified organism to be used alive for the treatment of human disease. ''L. lactis'' cells are cocci that group in pairs and short chains, and, depending on growth conditions, appear ovoid with a typical length of 0.5 - 1.5 μm. ''L. lactis'' does not produce spores ( nonsporulating) and are not motile ( nonmotile). They have a homofermentative metabolism, meaning they produce lactic acid from sugars. They've also been reported to produce exclusive L-(+)-lactic acid. However, reported D-(−)-lactic acid can be produced when cultured at low pH. The capability to produce lactic acid is one of the reasons why ''L. lactis'' is one of the most important microorganisms in the dairy industry. Based on its history in food fermentation, ''L. lactis'' has generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, with few case reports o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starter Culture
A fermentation starter (called simply starter within the corresponding context, sometimes called a mother) is a preparation to assist the beginning of the fermentation process in preparation of various foods and alcoholic drinks. Food groups where they are used include breads, especially sourdough bread, and cheese. A starter culture is a microbiological culture which actually performs fermentation. These starters usually consist of a cultivation medium, such as grains, seeds, or nutrient liquids that have been well colonized by the microorganisms used for the fermentation. These starters are formed using a specific cultivation medium and a specific mix of fungal and bacterial strains.Norman F. Haard, S.A. Odunfa, Cherl-Ho Lee, R. Quintero-Ramírez, Argelia Lorence-Quiñones, Carmen Wacher-Radarte, ''Fermented Cereals: A Global Perspective'', Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, 1999, .Dilip K. Arora, Libero Ajello, K. G. Mukerji, ''Handbook of Applied Mycology: Foods and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteurization
In food processing, pasteurization (American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), also pasteurisation) is a process of food preservation in which packaged foods (e.g., milk and fruit juices) are treated with mild heat, usually to less than , to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life. Pasteurization either destroys or deactivates microorganisms and enzymes that contribute to food spoilage or the risk of disease, including vegetative bacteria, but most Endospore, bacterial spores survive the process. Pasteurization is named after the French microbiologist Louis Pasteur, whose research in the 1860s demonstrated that thermal processing would deactivate unwanted microorganisms in wine. Spoilage enzymes are also inactivated during pasteurization. Today, pasteurization is used widely in the dairy industry and other food processing industries for food preservation and food safety. By the year 1999, most liquid products were heat treated in a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esterase
In biochemistry, an esterase is a class of enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis (and as such, it is a type of hydrolase). A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure, and their biological function. EC classification/list of enzymes * ''EC 3.1.1'': Carboxylic ester hydrolases ** Acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6), splits off acetyl groups *** Cholinesterase **** Acetylcholinesterase, inactivates the neurotransmitter acetylcholine **** Pseudocholinesterase, broad substrate specificity, found in the blood plasma and in the liver ** Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11), clarifies fruit juices * ''EC 3.1.2'': Thiolester hydrolases ** Thioesterase *** Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 * ''EC 3.1.3'': Phosphoric monoester hydrolases ** Phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.x), hydrolyses phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and an alcohol *** Alkaline phosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies and immune-modulating components that milk immunity, strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, Milking, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk Homogenization
Homogenization or homogenisation is any of several processes used to make a mixture of two mutually non-soluble liquids the same throughout. This is achieved by turning one of the liquids into a state consisting of extremely small particles distributed uniformly throughout the other liquid. A typical example is the homogenization of milk, wherein the milk fat globules are reduced in size and dispersed uniformly through the rest of the milk. Definition Homogenization (from ''homogeneous''; Greek, : '','' + '','' ) is the process of converting two immiscible liquids (i.e. liquids that are not soluble, in all proportions, one in another) into an emulsion, a mixture of two or more liquids that are generally immiscible. Sometimes two types of homogenization are distinguished: primary homogenization, when the emulsion is created directly from separate liquids; and secondary homogenization, when the emulsion is created by the reduction in size of droplets in an existing emulsion. Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
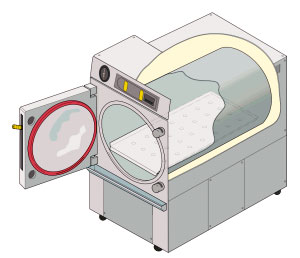
Autoclave (industrial)
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for 30–60 minutes at a gauge pressure of 103 kPa depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclaves are widely used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublimation (phase Transition)
Sublimation is the Phase transition, transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is ''sublime'', or less preferably, ''sublimate''. ''Sublimate'' also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly (for further details, see #False correspondence with vaporization, below) is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition (phase transition), ''deposition'' (also called ''desublimation''), in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase, without passing through the liquid state. Technically, all solids may sublime, though most sublime at extremely low rates that are hardly detectable under usual conditions. At standard condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeze-dried
Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product and lowering pressure, thereby removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by most conventional methods that evaporate water using heat. Because of the low temperature used in processing, the rehydrated product retains many of its original qualities. When solid objects like strawberries are freeze dried the original shape of the product is maintained. If the product to be dried is a liquid, as often seen in pharmaceutical applications, the properties of the final product are optimized by the combination of excipients (i.e., inactive ingredients). Primary applications of freeze drying include biological (e.g., bacteria and yeasts), biomedical (e.g., surgical transplants), food processing (e.g., coffee), and preservation. History The Inca were freeze drying potatoes into chuño since the 13th century. The process i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria Blu 01 WikiCheese Lokal K
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is below the German average. Major cities include Munich (its capital and largest city, which is also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became the independent Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |