|
Bloom–Richardson–Elston Grading System
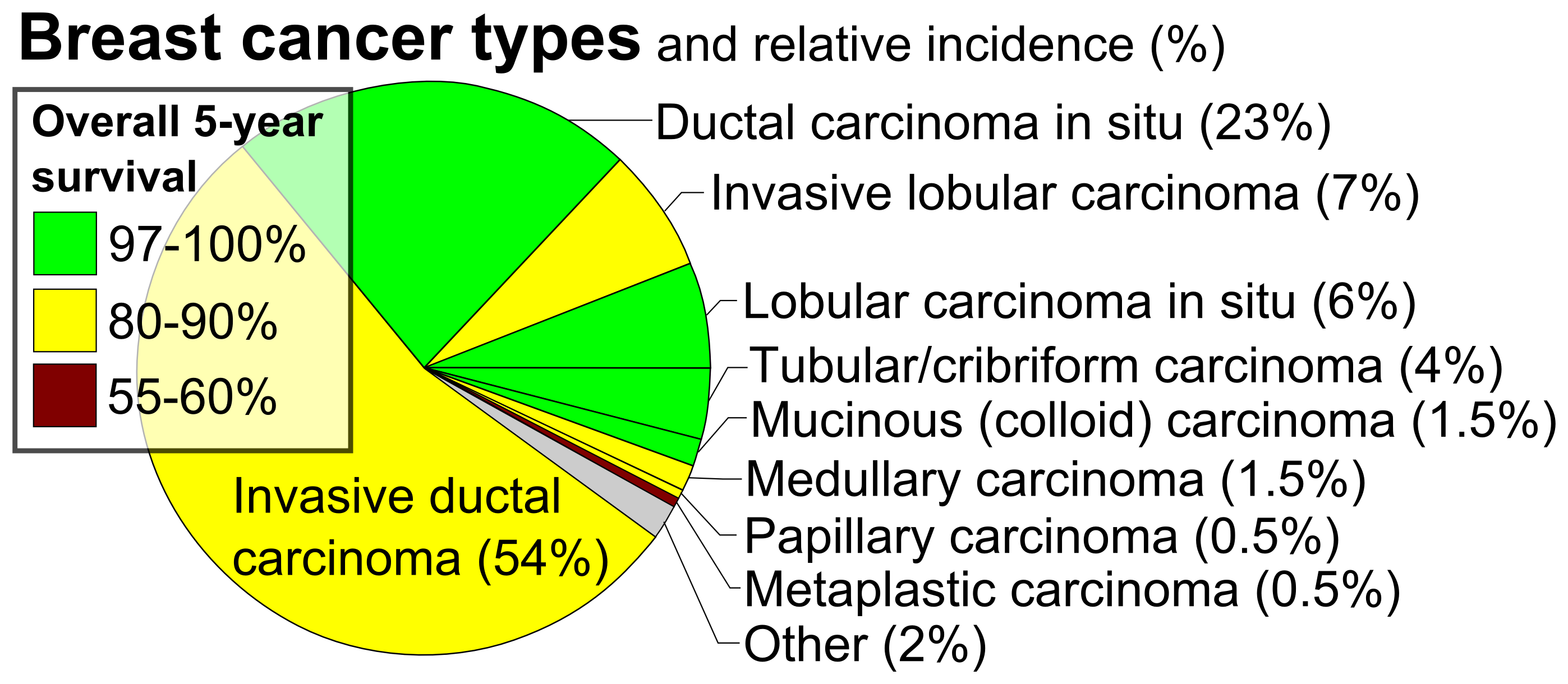
Breast cancer classification divides breast cancer into categories according to different schemes criteria and serving a different purpose. The major categories are the histopathological type, the grade of the tumor, the stage of the tumor, and the expression of proteins and genes. As knowledge of cancer cell biology develops these classifications are updated. The purpose of classification is to select the best treatment. The effectiveness of a specific treatment is demonstrated for a specific breast cancer (usually by randomized, controlled trials). That treatment may not be effective in a different breast cancer. Some breast cancers are aggressive and life-threatening, and must be treated with aggressive treatments that have major adverse effects. Other breast cancers are less aggressive and can be treated with less aggressive treatments, such as lumpectomy. Treatment algorithms rely on breast cancer classification to define specific subgroups that are each treated according to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Status
Receptor may refer to: *Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse *Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a neurotransmitter, or other substance **Cell surface receptor, a receptor on the outer surface of a cell membrane, that takes part in communication between the cell and the outside world **Nuclear receptor, a receptor found within cells that is responsible for sensing steroid and thyroid hormones and certain other molecules **Immune receptor, a receptor that occurs on the surface of immunocytes and binds to antigens *Receiver (radio), a device for the reception of electromagnetic signals. {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and Signal_transduction, transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses, such as a change in the electrophysiology, electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptor, GABA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand (biochemistry), ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Cell surface receptors, also known as transmembrane receptors, include ligand-gated ion channels, G prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; there is no stage after IV. Metastases can occur several years after the primary breast cancer, although it is sometimes diagnosed at the same time as the primary breast cancer or, rarely, before the primary breast cancer has been diagnosed. Metastatic breast cancer cells frequently differ from the preceding primary breast cancer in properties such as receptor status. The cells have often developed resistance to several lines of previous treatment and have acquired special properties that permit them to metastasize to distant sites. Metastatic breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but it cannot be cured. Distant metastases are the cause of about 90% of deaths du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump that can be felt, typically being detected through screening mammography. It has been diagnosed in a significant percentage of men (see male breast cancer). In DCIS, abnormal cells are found in the lining of one or more milk ducts in the breast. ''In situ'' means "in place" and refers to the fact that the abnormal cells have not moved out of the mammary duct and into any of the surrounding tissues in the breast ("pre-cancerous" indicates that it has not yet become an invasive cancer). In some cases, DCIS may become invasive and spread to other tissues, but there is no way of determining which lesions will remain stable without treatment, and which will go on to become invasive. DCIS encompasses a wide spectrum of diseases rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paget's Disease Of The Nipple
Paget's disease of the breast (also known as mammary Paget's disease) is a rare skin change at the nipple nearly always associated with underlying breast cancer. Paget's disease of the breast was first described by Sir James Paget in 1874. The condition is an uncommon disease accounting for 1 to 4% of all breast cancers cases. 92% to 100% of patients with Paget's disease of the breast have an underlying breast cancer. The condition in itself often appears innocuous, limited to a surface appearance and it is sometimes dismissed, although it is actually indicative of underlying breast cancer. Signs and symptoms Paget's disease of the breast can affect the nipple and areola: the nipple is typically affected first and then the skin changes spread to the areola. It is common for symptoms to wax and wane. Symptoms typically only affect one breast and may include: * ''Skin:'' The first symptom is usually an eczema-like rash. The skin of the nipple and areola may be red, itchy, or tingl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B cell, B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system, a lymph node is a Lymphatic system#Secondary lymphoid organs, secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial Pharyngitis, throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to gland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staging
Staging may refer to: Computing * Staging (cloud computing), a process used to assemble, test, and review a new solution before it is moved into production and the existing solution is decommissioned * Staging (data), intermediately storing data between the sources of information and a data warehouse (DW) * Disk staging, using disks as an additional, temporary stage of backup process before finally storing backup * Staging site, a website used to assemble, test, and review its newer versions before it is moved into production Other uses * Staging (cooking), a chef works briefly and without pay in another chef's kitchen to learn new techniques and cuisines * Staging (rocketry), the use of multiple engines and propellant to launch a rocket * Staging (stagecoaches), the business of running stagecoaches or the act of journeying in them * Staging (theatre), the process of selecting, designing, adapting to, or modifying the performance space for a play or film * Cancer staging, a descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNM Classification
The TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors (TNM) is a globally recognised standard for classifying the anatomical extent of the spread of malignant tumours (cancer). It has gained wide international acceptance for many solid tumor cancers, but is not applicable to leukaemia or tumors of the central nervous system. Most common tumors have their own TNM classification. The TNM staging system is sometimes referred to as the AJCC/UICC staging system or the UICC/AJCC staging system. Several revisions have been published, the latest being the eighth edition in 2017. TNM was developed and is maintained by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC). It is also used by the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) and the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO). In 1987, the UICC and AJCC staging systems were unified into the single TNM staging system. TNM is a notation system that describes the stage of a cancer, which originates from a solid tumor, using alphanu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphovascular Space Invasion
Lymphovascular invasion (LVI or lymphovascular space invasion) is the invasion of a cancer to the blood vessels and/or lymphatics. Terminology Lymph: A clear or white fluid that travels through vessels, moves within tissues and work to keep all the parts of the body clean. Vascular: The body's network of blood vessels. When cancer spreads to lymph and vascular system, it is thus termed as ''Lymphovascular Invasion.'' Pathology Lymphovascular invasion, especially in carcinomas, usually precedes spread to the lymph nodes that drain the tissue in which the tumour arose. Conversely, cancers with lymph node spread (known as a lymph node metastases), usually have lymphovascular invasion. Lymph node metastases usually precede secondary tumours, i.e. distant metastases. The absence of LVI in the context of proven lymph node metastasis is usually thought to be due to sampling error. Prognostic significance The predictive value and prevalence of lymphovascular invasion is strongly depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |