|
Bloom Syndrome Protein
Bloom syndrome protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BLM'' gene and is not expressed in Bloom syndrome. The Bloom syndrome gene product is related to the RecQ subset of DExH box-containing DNA helicases and has both DNA-stimulated ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase activities. Mutations causing Bloom syndrome delete or alter helicase motifs and may disable the 3' → 5' helicase activity. The normal protein may act to suppress inappropriate homologous recombination. Meiosis Recombination during meiosis is often initiated by a DNA double-strand break (DSB). During recombination, sections of DNA at the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then "invades" the DNA of an homologous chromosome that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways leading to a crossover (CO) or a non-cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage (naturally Occurring)
Natural DNA damage is an alteration in the chemical structure of DNA, such as a break in a strand of DNA, a nucleobase missing from the backbone of DNA, or a chemically changed base such as 8-OHdG. DNA damage can occur naturally or via environmental factors, but is distinctly different from mutation, although both are types of error in DNA. DNA damage is an abnormal chemical structure in DNA, while a mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs. DNA damages cause changes in the structure of the genetic material and prevents the replication mechanism from functioning and performing properly. The DNA damage response (DDR) is a complex signal transduction pathway which recognizes when DNA is damaged and initiates the cellular response to the damage. DNA damage and mutation have different biological consequences. While most DNA damages can undergo DNA repair, such repair is not 100% efficient. Un-repaired DNA damages accumulate in non-replicating cells, such as cells in the brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flap Structure-specific Endonuclease 1
Flap endonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FEN1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene removes 5' overhanging "flaps" (or short sections of single stranded DNA that "hang off" because their nucleotide bases are prevented from binding to their complementary base pair—despite any base pairing downstream) in DNA repair and processes the 5' ends of Okazaki fragments in lagging strand DNA synthesis. Direct physical interaction between this protein and AP endonuclease 1 during long-patch base excision repair provides coordinated loading of the proteins onto the substrate, thus passing the substrate from one enzyme to another. The protein is a member of the XPG/RAD2 endonuclease family and is one of ten proteins essential for cell-free DNA replication. DNA secondary structure can inhibit flap processing at certain trinucleotide repeats in a length-dependent manner by concealing the 5' end of the flap that is necessary for both binding and cleav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FANCM
Fanconi anemia, complementation group M, also known as FANCM is a human gene. It is an emerging target in cancer therapy, in particular cancers with specific genetic deficiencies. Function The protein encoded by this gene, FANCM displays DNA binding against fork structures and an ATPase activity associated with DNA branch migration. It is believed that FANCM in conjunction with other Fanconi anemia- proteins repair DNA at stalled replication forks, and stalled transcription structures called R-loops. The structure of the C-terminus of FANCM (amino acids 1799-2048), bound to a partner protein FAAP24, reveals how the protein complex recognises branched DNA. A structure of amino acids 675-790 of FANCM reveal how the protein binds duplex DNA through a remodeling of the MHF1:MHF2 histone-like protein complex. Disease association Bi-allelic mutations in the FANCM gene were originally associated with Fanconi anemia, although several individuals with FANCM deficiency do not appear to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHEK1
Checkpoint kinase 1, commonly referred to as Chk1, is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that, in humans, is encoded by the ''CHEK1'' gene. Chk1 coordinates the DNA damage response (DDR) and cell cycle checkpoint response. Activation of Chk1 results in the initiation of cell cycle checkpoints, cell cycle arrest, DNA repair and cell death to prevent damaged cells from progressing through the cell cycle. Discovery In 1993, Beach and associates initially identified Chk1 as a serine/threonine kinase which regulates the G2/M phase transition in fission yeast. Constitutive expression of Chk1 in fission yeast was shown to induce cell cycle arrest. The same gene called Rad27 was identified in budding yeast by Carr and associates. In 1997, homologs were identified in more complex organisms including the fruit fly, human and mouse. Through these findings, it is apparent Chk1 is highly conserved from yeast to humans. Structure Human Chk1 is located on chromosome 11 on the cytogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHAF1A
Chromatin assembly factor 1 subunit A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CHAF1A'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Function Chromatin assembly factor I ( CAF-1) is a nuclear complex consisting of p50, p60 ( CHAF1B; MIM 601245), and p150 (CHAF1A) subunits that assembles histone tetramers onto replicating DNA in vitro (Kaufman et al., 1995). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> Interactions CHAF1A has been shown to interact with: * ASF1A, * ASF1B, * BLM, * CBX5, and * MBD1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
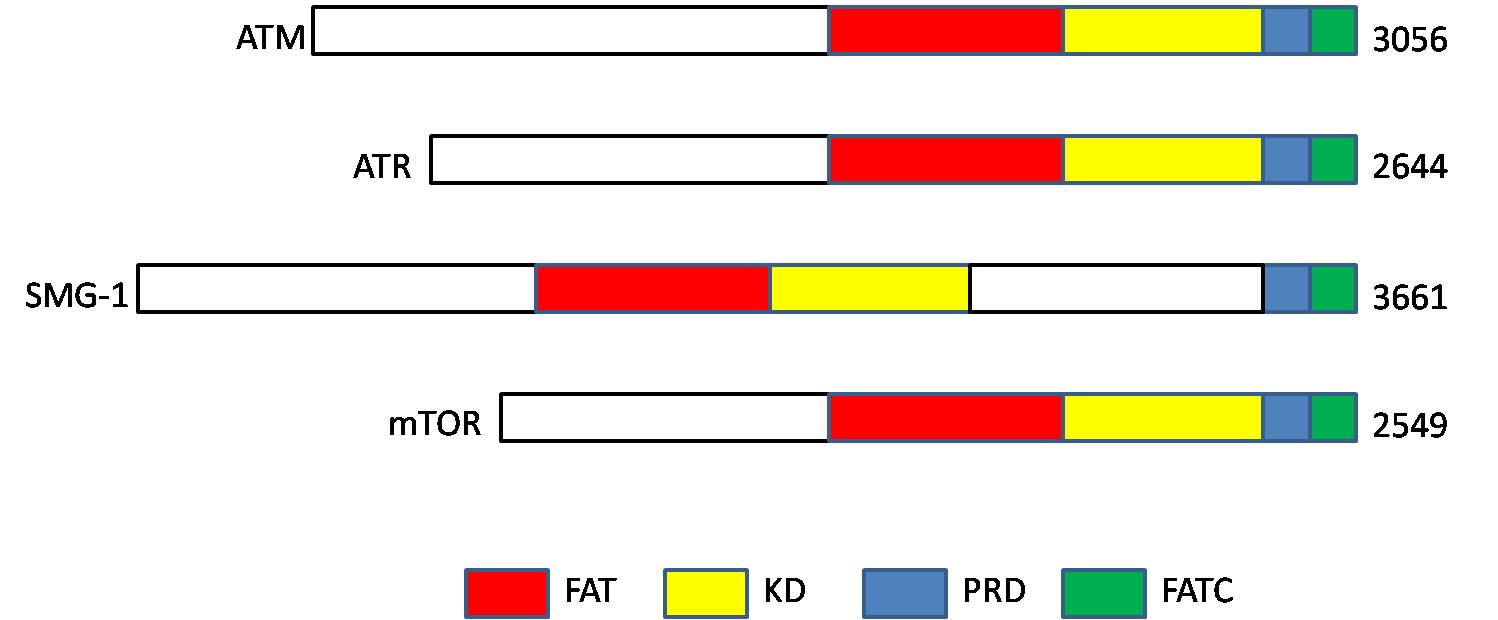
Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA repair#Double-strand breaks, DNA double-strand breaks (Canonical pathway, canonical pathway), oxidative stress, topoisomerase cleavage complexes, splicing intermediates, R-loops and in some cases by DNA repair, single-strand DNA breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage cell cycle checkpoint, checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia#Cause, ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Michael B. Kastan, Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |