|
Blockade Of Almeida
In the Blockade of Almeida (14 April – 10 May 1811) a French garrison under Antoine François Brenier de Montmorand was surrounded by approximately 13,000 Anglo-Allied soldiers led by Generals Sir Alexander Campbell, 1st Baronet and Sir William Erskine, 2nd Baronet. After a French relief attempt failed, Brenier and his troops broke out at night after blowing up portions of the fortress. To the fury of the British army commander Arthur Wellesley, Viscount Wellington, most of the French escaped due to their commander's single-minded determination, British fumbling, and remarkably good luck. The action took place during the Peninsular War portion of the Napoleonic Wars. Almeida, Portugal is located near the Spanish border about northeast of Lisbon. The town was originally captured from a Portuguese garrison during the 1810 Siege of Almeida. Background On 11 October 1810, Marshal André Masséna's French army found itself confronted by the elaborately built and well-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Fortress Of Almeida
The Castle/Fortress of Almeida () is a castle situated in the civil parish of Almeida, in the municipality of Almeida in the Portuguese district of Guarda, in the former-northwestern province of Beira Alta. It was constructed in this region due to its significant strategic importance, due to its close proximity to the border between Portugal and Spain. It is classified as a National Monument. The 1810 explosion: the magazine which was the seat of the explosion was in the cathedral adjacent to the castle, not the castle itself as reported in the text. History Portuguese settlements in the north were conveniently constructed on hilltops, providing protection to local populations from raids. During the Roman Iberian invasion/occupation many of these settlements were converted into fortified villages, due to their strategic positions. The first defensive structures were believed to be constructed by these colonists, who worked in the older castros into their fortifications. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Napoleonic Wars , partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars , image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg , caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battles of Battle of Austerlitz, Austerlitz, Fall of Berlin (1806), Berlin, Battle of Friedland, Friedland, Battle of Aspern-Essling, Aspern-Essling, French occupation of Moscow, Moscow, Battle of Leipzig, Leipzig and Battle of Paris (1814), Paris , date = {{start and end dates, 1803, 5, 18, 1815, 11, 20, df=yes({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=05, day1=18, year1=1803, month2=11, day2=20, year2=1815) , place = Atlantic Ocean, Caucasus, Europe, French Guiana, Mediterranean Sea, North Sea, West Indies, Ottoman Egypt, Egypt, East Indies. , result = Coalition victory , combatant1 = Coalition forces of the Napoleonic Wars, Coalition forces:{{flagcountry, United Kingdom of Great Britain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812)
The siege of Ciudad Rodrigo was the successful investment of the French-occupied city of Ciudad Rodrigo by Lord Wellington's Anglo-Portuguese Army from 7-20 January 1812. Wellington's army, which numbered up to 40,000 men, faced a small French garrison of 1,800 troops under the command of Jean Léonard Barrié. After two breaches were blasted in the city's walls by heavy artillery units of the Royal Artillery, Ciudad Rodrigo was successfully stormed by British troops on the evening of 19 January. After overcoming the French defenders, the attacking troops went on a rampage for several hours before order was restored. The Anglo-Portuguese Army suffered casualties of about 1,700 men, including two generals killed. Strategically, the fall of the city opened the northern gateway into French-occupied Spain from Portugal. Background The allied campaign in Spain started with the siege of Ciudad Rodrigo. Preliminary operations As part of his strategy in Spain, Napoleon or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
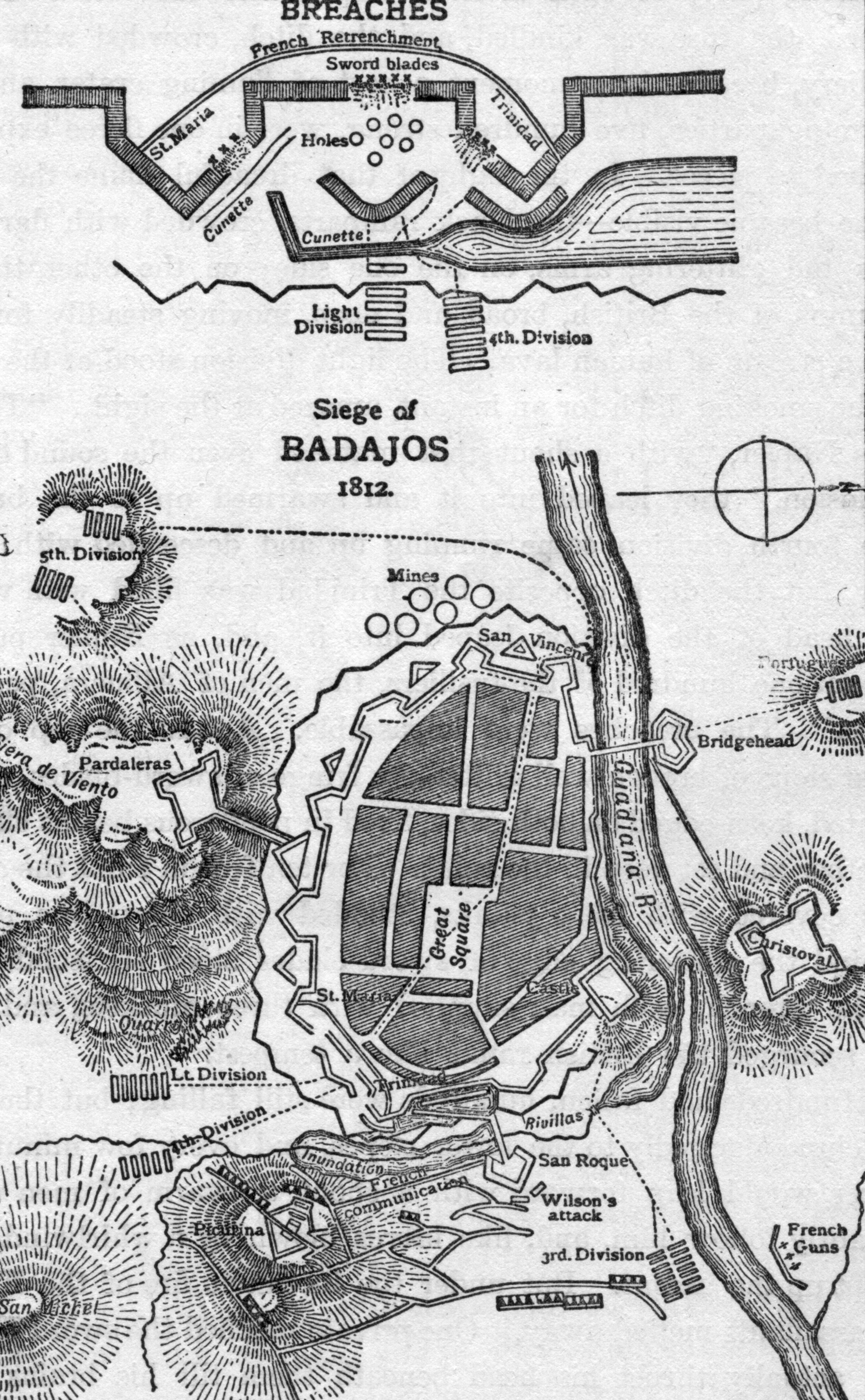
Siege Of Badajoz (1812)
In the siege of Badajoz (16 March – 6 April 1812), also called the third siege of Badajoz, an Anglo-Portuguese Army under the command of the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley, the Earl of Wellington (who was later made Duke of Wellington) besieged Badajoz, Spain, and forced the surrender of the First French Empire, French garrison. The siege was one of the bloodiest in the Napoleonic Wars and was considered a costly victory by the British, with some 4,800 Allied soldiers killed or wounded in a few short hours of intense fighting during the storming of the breaches as the siege drew to an end. Enraged at the huge number of casualties they suffered in seizing the city, the troops broke into houses and stores consuming vast quantities of alcohol with many of them then going on a rampage, threatening their officers and ignoring their commands to desist, and even killing several. It took three days before the men were brought back into order. When ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th (Herefordshire) Regiment Of Foot
The 36th (Herefordshire) Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1701. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment of Foot to form the Worcestershire Regiment in 1881. Its lineage is continued today by the Mercian Regiment. History Formation The unit was raised on the outbreak of the War of the Spanish Succession: on 28 June 1701 William III issued a warrant to William Caulfeild, 2nd Viscount Charlemont to raise a regiment of foot in Ireland. It was the successor to a previous regiment raised by Charlemont in 1694 for Irish service. William died in March 1702 and his successor, Queen Anne, issued a further warrant declaring that Charlemont's Regiment of Foot was to be one of six newly formed regiments to be equipped for "sea service".Cannon 1853, pp. 2–4 Early service: the War of the Spanish Succession The regiment was selected to form part of an Anglo-Dutch force under the command of the Duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass defenses. Failing a military outcome, sieges can often be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force. A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are legal barriers to trade rather than physical barriers. It is also distinct from a siege in that a blockade is usually directed at an entire country or region, rather than a fortress or city and the objective may not always be to conquer the area. A blockading power can seek to cut off all maritime transport from and to the blockaded country, although stopping all land transport to and from an area may also be considered a blockade. Blockades restrict the trading rights of neutrals, who must submit for inspection for contraband, which the blockading power may define narrowly or broadly, sometimes including food and medicine. In the 20th century, air power has also been used to enhance the effectiveness of blockades by halting air traffic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Portuguese Army
The Anglo-Portuguese Army was the combined British and Portuguese army that participated in the Peninsular War, under the command of Arthur Wellesley. The Army is also referred to as the British-Portuguese Army and, in Portuguese, as the ''Exército Anglo-Luso'' or the ''Exército Anglo-Português''. The Anglo-Portuguese Army was established with the British Army deployed to the Iberian Peninsula under the command of General Arthur Wellesley, and the Portuguese Army rebuilt under the leadership of British General William Beresford and the Portuguese War Secretary Miguel Pereira Forjaz. The new Portuguese battalions were supplied with British equipment, trained to British standards and thoroughly re-organised. Incompetent or corrupt officers were cashiered and appropriate replacements were appointed or promoted from amongst promising Non-commissioned officers. On 22 April 1809, Wellesley became Commander-in-Chief of the British Army in the Peninsula, replacing General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Reynier
Divisional general, Divisional-General Jean Louis Ébénézer Reynier (14 January 1771 – 27 February 1814) was a French Army officer who served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He rose in rank to become a general officer during the French Revolutionary Wars and led a division under Napoleon in the French invasion of Egypt and Syria. During the Napoleonic Wars, he continued to hold important combat commands, eventually leading an army corps during the Peninsular War in 1810–1811 and during the War of the Sixth Coalition in 1812–1813. Background and education Reynier was born on 14 January 1771 in Lausanne to a Protestant family, the son of Jacques François Reynier, a physician, and Caroline Chapuis. Through his father he was descended from French Huguenots from the Dauphiné who fled to Switzerland after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes. His brother Jean-Louis-Antoine (1762–1824), a naturalist and archeologist, held government posts in the French adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Of Division
Divisional general is a general officer rank who commands an army division. The rank originates from the French Revolutionary System, and is used by a number of countries. The rank is above a brigade general, and normally below an army corps general. The rank is mostly used in countries where it is used as a modern alternative to a previous older rank of major-general or lieutenant-general. Specific countries Brazil The Brazilian rank ''general-de-divisão'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''major-brigadeiro''(literally "major-brigadier"). The navy equivalent is ''vice-almirante'' (literally, vice-admiral) Chile The Chilean rank ''general de división'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''general de aviación'' (literally "aviation general"). These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |