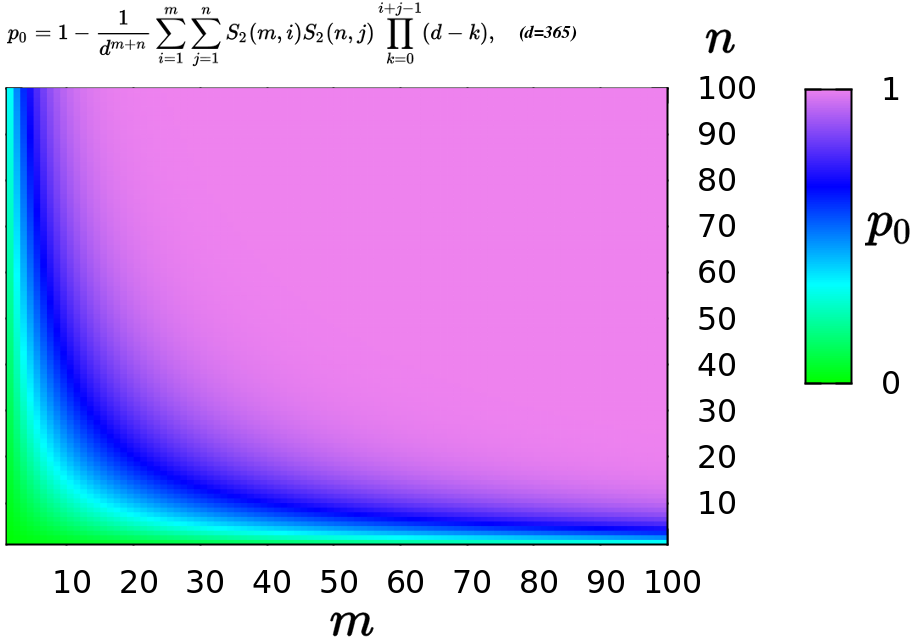
 |
Birthday Problem
In probability theory, the birthday problem asks for the probability that, in a set of randomly chosen people, at least two will share the same birthday. The birthday paradox is the counterintuitive fact that only 23 people are needed for that probability to exceed 50%. The birthday paradox is a veridical paradox: it seems wrong at first glance but is, in fact, true. While it may seem surprising that only 23 individuals are required to reach a 50% probability of a shared birthday, this result is made more intuitive by considering that the birthday comparisons will be made between every possible pair of individuals. With 23 individuals, there are = 253 pairs to consider. Real-world applications for the birthday problem include a cryptographic attack called the birthday attack, which uses this probabilistic model to reduce the complexity of finding a Collision attack, collision for a hash function, as well as calculating the approximate risk of a hash collision existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mutually Exclusive Events
In logic and probability theory, two events (or propositions) are mutually exclusive or disjoint if they cannot both occur at the same time. A clear example is the set of outcomes of a single coin toss, which can result in either heads or tails, but not both. In the coin-tossing example, both outcomes are, in theory, collectively exhaustive, which means that at least one of the outcomes must happen, so these two possibilities together exhaust all the possibilities. However, not all mutually exclusive events are collectively exhaustive. For example, the outcomes 1 and 4 of a single roll of a six-sided die are mutually exclusive (both cannot happen at the same time) but not collectively exhaustive (there are other possible outcomes; 2,3,5,6). Logic In logic, two propositions \phi and \psi are mutually exclusive if it is not logically possible for them to be true at the same time; that is, \lnot (\phi \land \psi) is a tautology. To say that more than two propositions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Poisson Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution () is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event. It can also be used for the number of events in other types of intervals than time, and in dimension greater than 1 (e.g., number of events in a given area or volume). The Poisson distribution is named after French mathematician Siméon Denis Poisson. It plays an important role for discrete-stable distributions. Under a Poisson distribution with the expectation of ''λ'' events in a given interval, the probability of ''k'' events in the same interval is: :\frac . For instance, consider a call center which receives an average of ''λ ='' 3 calls per minute at all times of day. If the calls are independent, receiving one does not change the probability of when the next on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sampling (statistics)
In this statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a population (statistics), statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population, and statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection compared to recording data from the entire population (in many cases, collecting the whole population is impossible, like getting sizes of all stars in the universe), and thus, it can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population. Each observation measures one or more properties (such as weight, location, colour or mass) of independent objects or individuals. In survey sampling, weights can be applied to the data to adjust for the sample design, particularly in stratified samplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Taylor Series
In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the 18th century. The partial sum formed by the first terms of a Taylor series is a polynomial of degree that is called the th Taylor polynomial of the function. Taylor polynomials are approximations of a function, which become generally more accurate as increases. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error introduced by the use of such approximations. If the Taylor series of a function is convergent, its sum is the limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Birthday Paradox Approximation
A birthday is the anniversary of the birth of a person or figuratively of an institution. Birthdays of people are celebrated in numerous cultures, often with birthday gifts, birthday cards, a birthday party, or a rite of passage. Many religions celebrate the birth of their founders or religious figures with special holidays (e.g. Christmas, Mawlid, Buddha's Birthday, Krishna Janmashtami, and Gurpurb). There is a distinction between birth''day'' and birth''date'' (also known as date of birth): the former, except for February 29, occurs each year (e.g. January 15), while the latter is the complete date when a person was born (e.g. January 15, 2001). Coming of age In most legal systems, one becomes a legal adult on a particular birthday when they reach the age of majority (usually between 12 and 21), and reaching age-specific milestones confers particular rights and responsibilities. At certain ages, one may become eligible to leave School leaving age, full-time education, beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
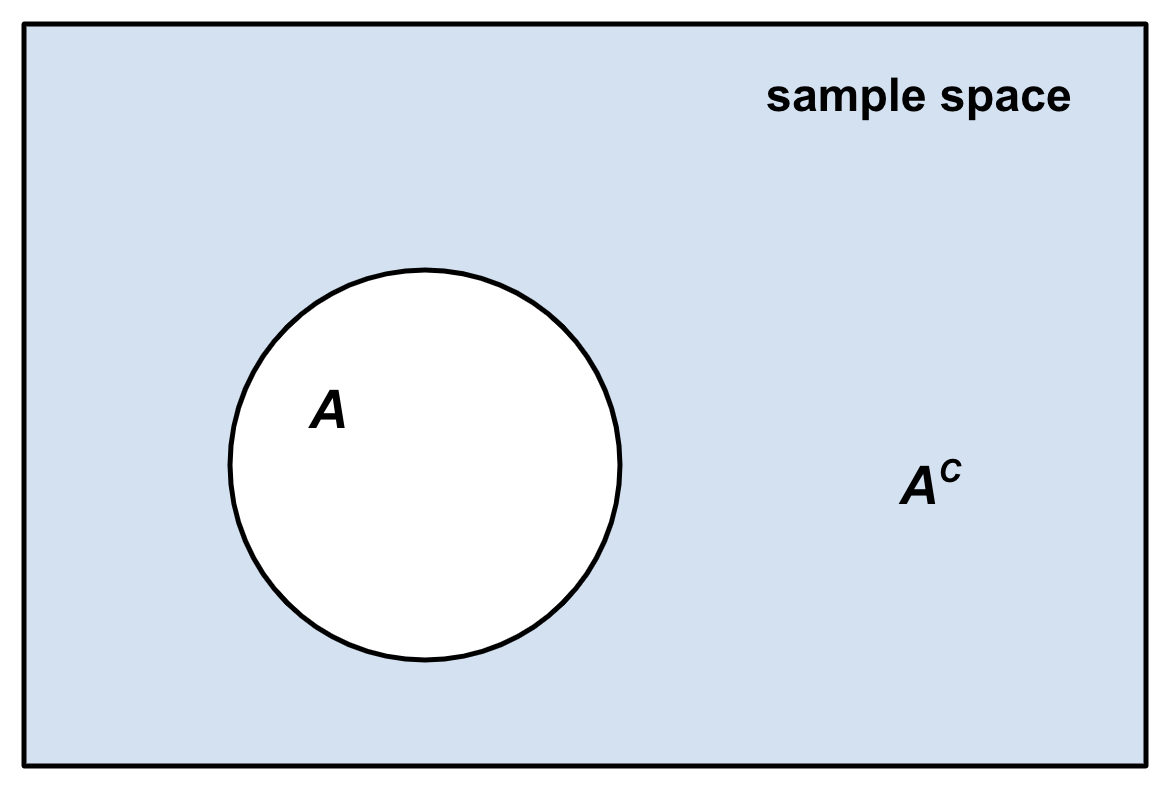 |
Complementary Event
In probability theory, the complement of any event ''A'' is the event ot ''A'' i.e. the event that ''A'' does not occur.Robert R. Johnson, Patricia J. Kuby: ''Elementary Statistics''. Cengage Learning 2007, , p. 229 () The event ''A'' and its complement ot ''A''are mutually exclusive and exhaustive. Generally, there is only one event ''B'' such that ''A'' and ''B'' are both mutually exclusive and exhaustive; that event is the complement of ''A''. The complement of an event ''A'' is usually denoted as ''A′'', ''Ac'', \neg''A'' or '. Given an event, the event and its complementary event define a Bernoulli trial: did the event occur or not? For example, if a typical coin is tossed and one assumes that it cannot land on its edge, then it can either land showing "heads" or "tails." Because these two outcomes are mutually exclusive (i.e. the coin cannot simultaneously show both heads and tails) and collectively exhaustive (i.e. there are no other possible outcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Binomial Coefficient
In mathematics, the binomial coefficients are the positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theorem. Commonly, a binomial coefficient is indexed by a pair of integers and is written \tbinom. It is the coefficient of the term in the polynomial expansion of the binomial power ; this coefficient can be computed by the multiplicative formula : \binom nk = \frac, which using factorial notation can be compactly expressed as : \binom = \frac. For example, the fourth power of is : \begin (1 + x)^4 &= \tbinom x^0 + \tbinom x^1 + \tbinom x^2 + \tbinom x^3 + \tbinom x^4 \\ &= 1 + 4x + 6 x^2 + 4x^3 + x^4, \end and the binomial coefficient \tbinom =\tfrac = \tfrac = 6 is the coefficient of the term. Arranging the numbers \tbinom, \tbinom, \ldots, \tbinom in successive rows for gives a triangular array called Pascal's triangle, satisfying the recurrence relation : \binom = \binom + \binom . The binomial coefficients occur in many areas of mathematics, and espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the Product (mathematics), product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book ''Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |