|
Binding Neuron
A binding neuron (BN) is an abstract concept of processing of input impulses in a generic neuron based on their temporal coherence and the level of neuronal inhibition. Mathematically, the concept may be implemented by most neuronal models including the well-known leaky integrate-and-fire model. The BN concept originated in 1996 and 1998 papers by A. K. Vidybida, Description of the concept For a generic neuron the stimuli are excitatory impulses. Normally, more than single input impulse is necessary for exciting neuron up to the level when it fires and emits an output impulse. Let the neuron receives n input impulses at consecutive moments of time t_1,t_2,\dots,t_n. In the BN concept the temporal coherence tc between input impulses is defined as follows tc = \frac\,. The high degree of temporal coherence between input impulses suggests that in external media all n impulses can be created by a single complex event. Correspondingly, if BN is stimulated by a highly coherent se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Neuron Model
Biological neuron models, also known as spiking neuron models, are mathematical descriptions of the conduction of electrical signals in neurons. Neurons (or nerve cells) are electrically excitable cells within the nervous system, able to fire electric signals, called action potentials, across a neural network. These mathematical models describe the role of the biophysical and geometrical characteristics of neurons on the conduction of electrical activity. Central to these models is the description of how the membrane potential (that is, the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell) across the cell membrane changes over time. In an experimental setting, stimulating neurons with an electrical current generates an action potential (or spike), that propagates down the neuron's axon. This axon can branch out and connect to a large number of downstream neurons at sites called synapses. At these synapses, the spike can cause the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme Eng
Scheme or schemer may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''The Scheme'', a BBC Scotland documentary TV series * The Scheme (band), an English pop band * ''The Scheme'', an action role-playing video game for the PC-8801, made by Quest Corporation * Schemer (comics), Richard Fisk, a Marvel Comics villain turned antihero * Horace Schemer, a fictional character in the TV series ''Shining Time Station'' * ''Schemers'' (film), a Scottish film Computing * Scheme (programming language), a minimalist dialect of Lisp * Scheme (URI), the front part of a web link, like "http" or "ftp" * Google Schemer, a former service allowing its users to share plans and interests Other uses * Classification scheme (information science), eg a thesaurus, a taxonomy, a data model or an ontology * Scheme (mathematics), a concept in algebraic geometry * Scheme (rhetoric), a figure of speech that changes a sentence's structure * Scam, an attempt to swindle or cheat people through deception * Scheme, a type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
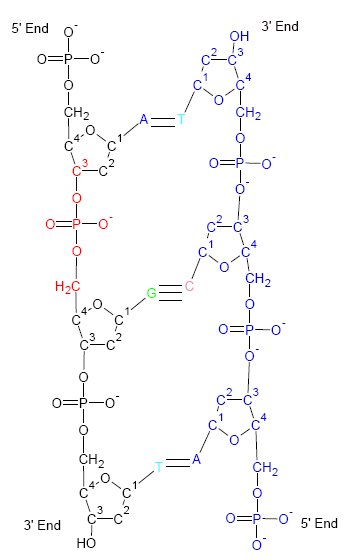
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid double helix, helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular geometry, molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term "central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Problem
The unity of consciousness and (cognitive) binding problem is the problem of how objects, background, and abstract or emotional features are combined into a single experience. The binding problem refers to the overall encoding of our brain circuits for the combination of decisions, actions, and perception. It is considered a "problem" because no complete model exists. The binding problem can be subdivided into the four areas of perception, neuroscience, cognitive science, and the philosophy of mind. It includes general considerations on coordination, the subjective unity of perception, and variable binding. General considerations on coordination Summary of problem Attention is crucial in determining which phenomena appear to be bound together, noticed, and remembered. This specific binding problem is generally referred to as temporal synchrony. At the most basic level, all neural firing and its adaptation depends on specific consideration to timing (Feldman, 2010). At a much la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin–Huxley Model
The Hodgkin–Huxley model, or conductance-based model, is a mathematical model that describes how action potentials in neurons are initiated and propagated. It is a set of nonlinear differential equations that approximates the electrical engineering characteristics of excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells. It is a continuous-time dynamical system. Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley described the model in 1952 to explain the ionic mechanisms underlying the initiation and propagation of action potentials in the squid giant axon. They received the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this work. Basic components The typical Hodgkin–Huxley model treats each component of an excitable cell as an electrical element (as shown in the figure). The lipid bilayer is represented as a capacitance (Cm). Voltage-gated ion channels are represented by electrical conductances (''g''''n'', where ''n'' is the specific ion channel) that depend on both voltage and time. Leak chann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of Membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and myocyte, muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell interaction, cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward axon terminal, synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of ''negative'' ions into the cell or positive ions ''out'' of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC). EPSPs, like IPSPs, are graded (i.e. they have an additive effect). When multiple EPSPs occur on a single patch of postsynaptic membrane, their combined effect is the sum of the individual EPSPs. Larger EPSPs result in greater membra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step Ukr
Step(s) or STEP may refer to: Common meanings * Steps, making a staircase * Walking * Dance move * Military step, or march ** Marching Arts Films and television * ''Steps'' (TV series), Hong Kong * ''Step'' (film), US, 2017 Literature * ''Steps'' (novel), by Jerzy Kosinski * Systematic Training for Effective Parenting, a book series Music * Step (music), pitch change * Steps (pop group), UK * ''Step'' (Kara album), 2011, South Korea ** "Step" (Kara song) * ''Step'' (Meg album), 2007, Japan * "Step" (Vampire Weekend song) * "Step" (ClariS song) Organizations * STEP (company), Belgium * Society of Trust and Estate Practitioners, international professional body for advisers who specialise in inheritance and succession planning * Board on Science, Technology, and Economic Policy of the U.S. National Academies * Solving the E-waste Problem, a UN organization Science, technology, and mathematics * Step (software), a physics simulator in KDE * Step function, in mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892. Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living organisms including molecular biology, cell biology, chemical biology, and bioche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |