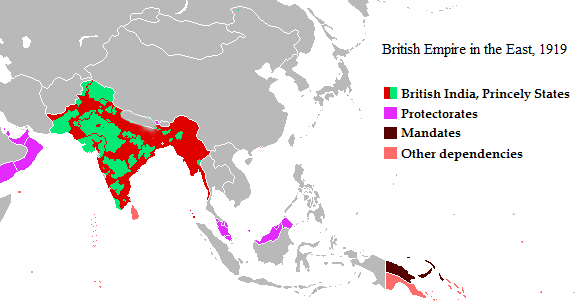
|
Bhopal Agency
The Bhopal Agency was a section of British India's colonial Central India Agency, a British political unit which managed the relations of the British with a number of autonomous princely states existing outside British India.Great Britain India Office. ''The Imperial Gazetteer of India''. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1908. History The Agency was formed in 1818 at the conclusion of the Third Anglo-Maratha War, and covered the princely states of Bhopal (largest and eponymous), Khilchipur, Kurwai, Narsingarh, Muhammadgarh, Pathari and Rajgarh surrounding Bhopal, as well as the districts of Bhilsa and Isagarh, which belonged to the Gwalior State and also the district of Sironj, which belonged to Tonk State in Rajputana. The head of the Agency was appointed by the British Governor-General of India. In 1854 the Bhopal Agency became part of the newly created Central India Agency. In 1895 the Gwalior districts of Bhilsa and Isagarh were transferred from Bhopal Agency to Gw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757, the East India Company set up "factories" (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century three ''Presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India, 1757–1858, the Company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "Presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government oversight, in effect sharing sovereig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sironj
Sironj is a town and a municipality in Vidisha district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Its also a Tehsil Headquarter. History Sironj was previously known as Sengar Raj.It was founded by Sengar Rajput warrior Shankar Singh in 1103 A.D. Due to ruling dynasty it was called Sengar Raj later name corrupted to become Sironj. Shankar Singh Sengar with his 2 brothers established Sengar Raj in Malwa. Shankar Singh founded Basilgarh fort in Sironj. Other two brothers Girdhar Singh founded Girdharpur Village constructed Kokangarh fort and Rana Singh founded Ranapur Village constructed kokangarh fort. Remnants of these forts can be still found nearby Sironj and Lateri. Sironj was under the control of Rajputs till 18th century.After ascending the throne Aurangzeb attacked Sironj, Ruling Sengar Rajputs fought valiantly and around 4,000 Sengars were killed fighting the battle.Only few of them left alive after battle. Later Hoklars accorded sironj to Pashtun Amir khan for his service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Commissioner's Province
Chief Commissioner's Province refers to a middle-level and minor type of province in British India and in the post-colonial successor states, not headed by a ( lieutenant-)governor but by a Chief commissioner, notably : * in present India : ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Ajmer-Merwara (the British Political Agent in Rajputana served as ''ex officio'' Chief Commissioner) ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Delhi ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Andaman and Nicobar Islands ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Assam ** Central Provinces and Berar ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Coorg (the British Resident in Mysore served as ''ex officio'' Chief Commissioner) ** Chief Commissioner's Province of Himachal Pradesh * in present Pakistan Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhopal State (1949–56)
Bhopal State (pronounced ) was founded by the Maharaja of Parmar Rajputs. In the beginning of the 18th-century, Bhopal State was converted into an Islamic principality, in the invasion of the Afghan Mughal noble Dost Muhammad Khan. It was a tributary state within the Maratha Empire during the 18th century (1737–1818), a princely salute state with rights to a 19-gun salute in a subsidiary alliance with British India from 1818 to 1947, and an independent state from 1947 to 1949. Islamnagar was founded and served as the State's first capital, which was later shifted to the city of Bhopal. The state was founded in 1707 by Dost Mohammad Khan, a Pashtun soldier in the Mughal army, who became a mercenary after the Emperor Aurangzeb's death and annexed several territories to his fiefdom. It came under the suzerainty of the Nizam of Hyderabad in 1723 shortly after its foundation. In 1737, the Marathas defeated the Mughals and the Nawab of Bhopal in the Battle of Bhopal, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh. The union had an area of .Gwalior was made the capital and the first legislative assembly took place inside the Moti Mahal of Gwalior. It was bordered by the states of Bombay (presently Gujarat and Maharashtra) to the southwest, Rajasthan to the northwest, Uttar Pradesh to the north, and Vindhya Pradesh to the east, and Bhopal State and Madhya Pradesh to the southeast. The population was mostly Hindu and Hindi-speaking. On 1 November 1956, Madhya Bharat, together with the states of Vindhya Pradesh and Bhopal State, was merged into Madhya Pradesh. Districts Madhya Bharat comprised sixteen districts and these districts were initially divided into three Commissioners' Divisions, which were later reduced to two. The districts were: # Bhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India, * * was an independent dominion in the British Commonwealth of Nations existing between 15 August 1947 and 26 January 1950. Until its Indian independence movement, independence, India had been ruled as an informal empire by the United Kingdom. The empire, also called the British Raj and sometimes the British Indian Empire, consisted of regions, collectively called British India, that were directly administered by the British government, and regions, called the princely states, that were ruled by Indian rulers under a system of paramountcy, in favor of the British. The Dominion of India was formalised by the passage of the Indian Independence Act 1947, which also formalised an independent Dominion of Pakistan—comprising the regions of British India that are today Pakistan and Bangladesh. The Dominion of India remained "India" in common parlance but was geographically reduced by the lands that went to Pakistan, as a separate d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Of Accession
The Instrument of Accession was a legal document first introduced by the Government of India Act 1935 and used in 1947 to enable each of the rulers of the princely states under British paramountcy to join one of the new dominions of Dominion of India, India or Dominion of Pakistan, Pakistan created by the Partition of India, Partition of British India. The instruments of accession executed by the rulers, provided for the accession of states to the Dominion of India (or Pakistan) on three subjects, namely, defence, external affairs and communications. Background 565 princely states existed in British Raj, India during the British Raj. These were not parts of British India, having never become possessions of the Crown, the British Crown, but were tied to the Crown by various treaties and were under the suzerainty of the Crown. British India and the princely states were together referred to as the "Indian Empire", commonly called "India". The Government of India Act 1935 intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Provinces And Berar
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the British from the Hyderabad State. Through an agreement signed on 5 November 1902, 6th Nizam Mahbub Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VI leased Berar permanently to the British for an annual payment of 25 lakhs rupees. Lord Curzon decided to merge Berar with the Central Provinces, and this was proclaimed on 17 September 1903. The Central Provinces was formed in 1861 by the merger of the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories and Nagpur Province. Administration of the Berar region of the Hyderabad princely state was assigned to the Chief Commissioner of the Central Provinces in 1903, and for administrative purposes, Berar was merged with the Central Provinces to form the Central Provinces and Berar on 24 October 1936. After Indian Independence in 1947, a num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makrai
Makrai is a village in the Harda district of Madhya Pradesh, India. The village was the headquarters of the Makrai princely state during the British Raj. History According to legend the Makrai princely state was established in 1663 by Raj Gond Raja Karkat Rai in the 16th century. It later came under the administrative authority of the Central India Agency until 1933, when it was transferred to the Bhopal Agency subdivision of the Central India Agency in 1933 from the Central Provinces and Berar. In 1892, it covered an area of and had a population of 16,784. The state's rulers were of Rajput lineage and bore the title ''Maharaja''. After Indian independence in 1947, the rulers of Makrai acceded to the Union of India, and the principality was incorporated into the state of Madhya Pradesh, which in turn was created from the former Central Provinces and Berar. As of 2012, the titular Maharaja of Makrai is Raja Ajay Shah, born on 21 January 1956, married on 20 May 1986 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewas Junior
Dewas Junior was established by Jivaji Rao I Puar in 1728 during the Maratha conquest of Central India. It was a 15-gun salute Maratha princely state. On 12 December 1818, it became a British protectorate. History The original state was founded in 1728 by Jivaji Rao, from the Puar clan of Marathas who together with his older brother (Tukoji) had advanced into Malwa with Peshwa Baji Rao, as part of the Maratha conquest. The brothers divided the territory among themselves; their descendants ruled as the junior and senior branches of the family. After 1841, each branch ruled his own portion as a separate state, though the lands belonging to each were intimately entangled; in Dewas, the capital town, the two sides of the main street were under different administrations and had different arrangements for water supply and lighting. The Junior branch had an area of and had a population of 54,904 in 1901. Both Dewas states were in the Malwa Agency of the Central India Agency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewas Senior
Dewas Senior was established by Tukoji Rao I Pawar during the Maratha conquest of Central India. It was a 15 Gun Salute Maratha princely state. On 12 December 1818 it became a British protectorate. History The original state was founded in 1728 by Tukoji Rao, from the Pawar clan of the Marathas who together with his younger brother Jivaji Rao, had advanced into Malwa with Peshwa Baji Rao I as part of the Maratha Conquest of Malwa. The brothers divided the territory among themselves; their descendants ruled as the senior and junior branches of the family. After 1841, each branch ruled his own portion as a separate state, though the lands belonging to each were intimately entangled; in Dewas, the capital town, the two sides of the main street were under different administrations and had different arrangements for water supply and lighting. The two Rajas heading Dewas states both lived in separate residences in the town of Dewas, and ruled over separate areas. The Senior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwalior Residency
Gwalior Residency was a political office in the British Indian Empire, which existed from 1782 until the British withdrawal from India in 1947. The Gwalior Residency was placed under the Central India Agency in 1854, and separated from it in 1921. States under the residency The Gwalior residency dealt with a number of Princely States of Central India. Salute states, in order of precedence : * principally Gwalior State, title Maharaja Scindia, Hereditary salute of 21-guns * Rampur, title Nawab; Hereditary salute of 15-guns * Benares, title Maharaja, Hereditary salute of 13-guns (15-guns local) Non-salute states : * Bhadaura, * Garha * Khaniadhana * Paron * Raghugarh * Umri * Agra Barkhera. * Kathaun * Khiaoda * Sangul Wardha * Sirsi Also the Chhabra pargana (district) of Tonk State History After the Treaty of Salbai was concluded in 1782 between the British and Maharaja Mahadji Sindhia of Gwalior, David Anderson, who contributed to drafting the treaty, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |