|
Beware Of The Dog
Beware of the dog (also rendered as beware of dog) is a warning sign posted at the entrance to a building or other private area indicating that a dangerous dog is within. Such signs may be placed to deter burglary even if there is no dog, or if the dog is not actually a competent guard dog. History Warning signs of this sort have been found in ancient Roman buildings such as the House of the Tragic Poet in Pompeii, which contains a mosaic with the caption (). The Roman work ''Satyricon'', written by Petronius, includes a passage mentioning the phrase painted on a wall with large letters, in the chapter ''Dinner with Trimalchio''. Philippians 3:2 is translated as "beware of the dogs" or "beware of dogs" in the King James Bible and many other editions. For example: This is often interpreted as a euphemism, bad people having been described as dogs in a number of previous biblical passages. Nonetheless, the yard signs are sometimes alluded to in reference to the passage. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burglary
Burglary, also called breaking and entering (B&E) or housebreaking, is a property crime involving the illegal entry into a building or other area without permission, typically with the intention of committing a further criminal offence. Usually that offence is theft, larceny, robbery, or murder, but most jurisdictions include others within the ambit of burglary. To commit burglary is to ''burgle'', a term back-formed from the word ''burglar'', or to ''burglarize''. Etymology Sir Edward Coke (1552–1634) explains at the start of Chapter 14 in the third part of '' Institutes of the Lawes of England'' (pub. 1644), that the word ''Burglar'' ("or the person that committeth burglary"), is derived from the words ''burgh'' and ''laron'', meaning ''house-thieves''. A note indicates he relies on the ''Brooke's case'' for this definition. According to one textbook, the etymology originates from Anglo-Saxon or Old English, one of the Germanic languages. (Perhaps paraphrasing Sir Edward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
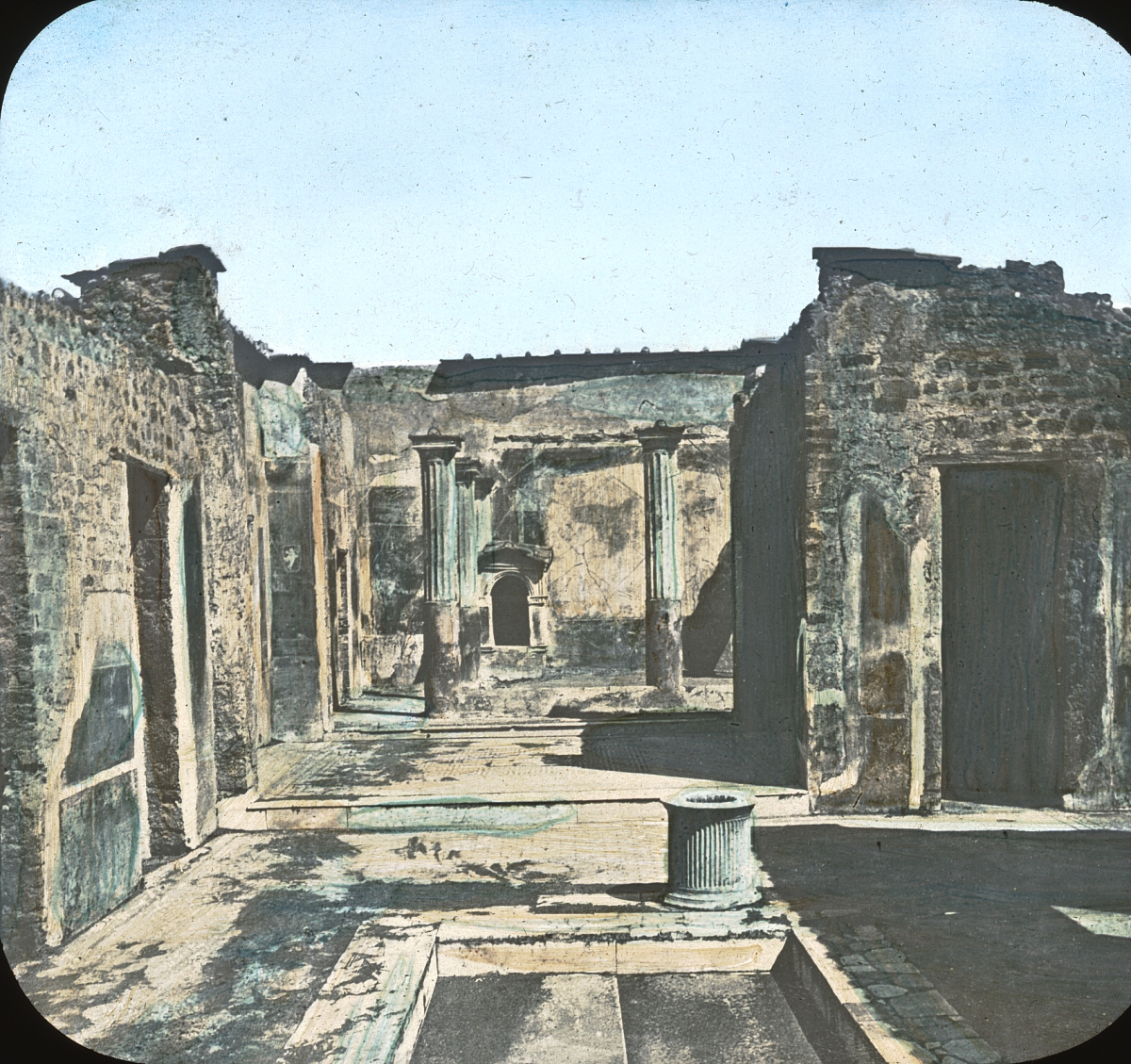
House Of The Tragic Poet
The House of the Tragic Poet (also called ''The Homeric House'' or ''The Iliadic House'') is a Roman house in Pompeii, Italy dating to the 2nd century BCE. The house is famous for its elaborate mosaic floors and frescoes depicting scenes from Greek mythology. Discovered in November 1824 by the archaeologist Antonio Bonucci, the House of the Tragic Poet has interested scholars and writers for generations. Although the size of the house itself is in no way remarkable, its interior decorations are not only numerous but of the highest quality among other frescoes and mosaics from ancient Pompeii. Because of the mismatch between the size of the house and the quality of its decoration, much has been wondered about the lives of the homeowners. Little is known about the family members, who were likely killed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Traditionally, Pompeii is geographically broken up into nine regional areas, which are then further broken up into insular areas. The Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean civilisation, Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman dynasty, Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satyricon
The ''Satyricon'', ''Satyricon'' ''liber'' (''The Book of Satyrlike Adventures''), or ''Satyrica'', is a Latin work of fiction believed to have been written by Gaius Petronius in the late 1st century AD, though the manuscript tradition identifies the author as Titus Petronius. The ''Satyricon'' is an example of Menippean satire, which is different from the formal verse satire of Juvenal or Horace. The work contains a mixture of prose and verse (commonly known as ); serious and comic elements; and erotic and decadent passages. As with ''The Golden Ass'' by Apuleius (also called the ''Metamorphoses''), classical scholars often describe it as a Roman novel, without necessarily implying continuity with the modern literary form. The surviving sections of the original (much longer) text detail the bizarre exploits of the narrator, Encolpius, and his (possible) slave and catamite Giton, a handsome sixteen-year-old boy. It is the second most fully preserved Roman novel, after the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petronius
Gaius Petronius Arbiter"Gaius Petronius Arbiter" Britannica.com. (; ; ; sometimes Titus Petronius Niger) was a Roman Empire, Roman courtier during the reign of Nero (). He is generally believed to be the author of the ''Satyricon'', a satire, satirical novel believed to have been written during the Neronian era. He is one of the most important characters in Henryk Sienkiewicz' historical novel ''Quo Vadis (novel), Quo Vadis'' (1895). Leo Genn portrays him in Quo Vadis (1951 film), the 1951 film of the same name. Life A reference to Petronius by Sidonius Apollinaris places him, or his ''Satyricon'', in Massalia (ancient Marseille). He might have been born and educated there. Tacitus, Plutarch and Pliny the Elder describe Petronius as the ''elegantiae arbiter'' (also phrased '' ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimalchio
Trimalchio is a character in the 1st-century AD Roman work of fiction ''Satyricon'' by Petronius. He features as the ostentatious, nouveau-riche host in the section titled the "Cēna Trīmalchiōnis" (The Banquet of Trimalchio, often translated as "Dinner with Trimalchio"). Trimalchio is an arrogant former slave who has become quite wealthy as a wine merchant. The name "Trimalchio" is formed from the Greek prefix τρις and the Semitic מלך ( melech) in its occidental form Malchio or Malchus. The fundamental meaning of the root is "King", and the name "Trimalchio" would thus mean "Thrice King" or "greatest King". Character description His full name is "Gaius Pompeius Trimalchio Maecenatianus"; the references to Pompey and Maecenas in his name serve to enhance his ostentatious character. His wife's name is Fortunata, a former slave and chorus girl. Trimalchio is known for throwing lavish dinner parties, where his numerous slaves bring course after course of exotic delicacies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistle To The Philippians
The Epistle to the Philippians is a Pauline epistle of the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The epistle is attributed to Paul the Apostle and Saint Timothy, Timothy is named with him as co-author or co-sender. The letter is addressed to the Christian church in Philippi. Paul, Timothy, Silas (and perhaps Luke the Evangelist, Luke) first visited Philippi in Early centers of Christianity#Greece, Greece (Macedonia (Roman province), Macedonia) during Paul's second Missionary journeys of Paul, missionary journey from Antioch, which occurred between approximately 50 and 52 AD. In the account of his visit in the Acts of the Apostles, Paul and Silas are accused of "disturbing the city". There is a general consensus that Philippians consists of authentically Pauline material, and that the epistle is a composite of multiple letter fragments from Paul to the church in Philippi. These letters could have been written from Ephesus in 52–55 AD or Caesarea Maritima in 57–59, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of King James VI and I. The 80 books of the King James Version include 39 books of the Old Testament, 14 books of Apocrypha, and the 27 books of the New Testament. Noted for its "majesty of style", the King James Version has been described as one of the most important books in English culture and a driving force in the shaping of the English-speaking world. The King James Version remains the preferred translation of many Protestant Christians, and is considered the only valid one by some Evangelicals. It is considered one of the important literary accomplishments of early modern England. The KJV was the third translation into English approved by the English Church authorities: the first had been the Great Bible (1535), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |