|
Betulaceae
Betulaceae, the birch family, includes six genera of deciduous nut-bearing trees and shrubs, including the birches, alders, hazels, hornbeams, hazel-hornbeam, and hop-hornbeams, numbering a total of 167 species. They are mostly natives of the temperate Northern Hemisphere, with a few species reaching the Southern Hemisphere in the Andes in South America. Their typical flowers are catkins and often appear before leaves. In the past, the family was often divided into two families, Betulaceae (''Alnus'', ''Betula'') and Corylaceae (the rest). Recent treatments, including the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, have described these two groups as subfamilies within an expanded Betulaceae: Betuloideae and Coryloideae. Betulaceae flowers are monoecious, meaning that they have both male and female flowers on the same tree. Their flowers present as catkins and are small and inconspicuous, often with reduced perianth parts. These flowers have large feathery stamen and produce a high vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coryloideae
Coryloideae is a subfamily in the woody angiosperm family Betulaceae, commonly known as the birch family, and consists of four extant genera - '' Corylus'' L., '' Ostryopsis'' Decne., ''Carpinus'' L., and ''Ostrya'' Scop. These deciduous trees and shrubs are primarily distributed in the boreal and cool temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere, with the majority occurring in Asia, many occurring in North America and a few species occurring as far south as South America.Stults, D. Z. & Axsmith, B. J. 2009. Betulaceae From The Pliocene And Pleistocene Of Southwest Alabama, Southeastern United States. ''Review Of Palaeobotany And Palynology'', 155, 25-31. Synapomorphies such reduced staminate flowers, advanced wood anatomy features, and the presence of spermidines in pollen define the Coryloideae.Chen, Z. D., Manchester, S. R. & Sun, H. Y. 1999. Phylogeny And Evolution Of The Betulaceae As Inferred From Dna Sequences, Morphology, And Paleobotany. ''American Journal of Botany'', 86, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 to 60 known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are typically short-lived pioneer species and are widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates. Birch wood is used for a wide range of purposes. Description Birch species are generally small to medium-sized trees or shrubs, mostly of northern temperate and boreal climates. The simple leaves are alternate, singly or doubly serrate, feather-veined, petiolate and stipulate. They often appear in pairs, but these pairs are really borne on spur-like, two-leaved, lateral branchlets. The fruit is a small samara, although the wings may be obscure in some species. They differ from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the family Betulaceae. Its species occur across much of the temperateness, temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names The common English name ''hornbeam'' derives from the hardness of the woods (likened to Horn (anatomy), horn) and the Old English ''beam'', "tree" (cognate with Dutch ''Boom'' and German ''Baum''). The American hornbeam is also occasionally known as blue-beech, ironwood, or musclewood, the first from the resemblance of the bark to that of the American beech ''Fagus grandifolia'', the other two from the hardness of the wood and the muscled appearance of the trunk and limbs. The botanical name for the genus, ''Carpinus'', is the original Latin name for the European species, although some etymologists derive it from the Celtic for a yoke. Description Hornbeams are small, slow-growing, understory trees with a natural, rounded form growing tall and wide; the exemplar species—the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder
Alders are trees of the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus includes about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . though some botanists split the hazels (with the hornbeams and allied genera) into a separate family Corylaceae. The fruit of the hazel is the hazelnut. Hazels have simple, rounded leaves with double-serrate margins. The flowers are produced very early in spring before the leaves, and are monoecious, with single-sex catkins. The male catkins are pale yellow and long, and the female ones are very small and largely concealed in the buds, with only the bright-red, 1-to-3 mm-long styles visible. The fruits are nuts long and 1–2 cm diameter, surrounded by an involucre (husk) which partly to fully encloses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alnus Glutinosa
''Alnus glutinosa'', the common alder, black alder, European alder, European black alder, or just alder, is a species of tree in the family (biology), family Betulaceae, native plant, native to most of Europe, southwest Asia and northern Africa. It thrives in wet locations where its association with the bacterium ''Frankia alni'' enables it to grow in poor quality soils. It is a medium-sized, short-lived tree growing to a height of up to 30 metres (98 feet). It has short-stalked rounded leaves and separate male and female flowers in the form of catkins. The small, rounded fruits are cone-like and the seeds are dispersed by wind and water. The common alder provides food and shelter for wildlife, with a number of insects, lichens and fungi being completely dependent on the tree. It is a pioneer species, colonising vacant land and forming mixed forests as other trees appear in its wake. Eventually common alder dies out of woodlands because the seedlings need more light than is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostryopsis
''Ostryopsis'' is a small genus of deciduous shrubs belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. The species have no common English name, though hazel-hornbeam has been suggested, reflecting their similarities to the closely related hazels and hop-hornbeams. The genus is native to China. They are shrubs reaching 3–5 m tall, with alternate, double-toothed hazel-like leaves 2–7 cm long. The flowers are produced in spring, with separate male and female catkins. The fruit form in clusters 3–5 cm long with 6-10 seeds; each seed is a small nut 4–6 mm long, fully enclosed in a sheath-like involucre. The local people in Northeast China has found hazelnut The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to ...s of '' Ostryopsis davidiana'' and '' Corylus mandshurica'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
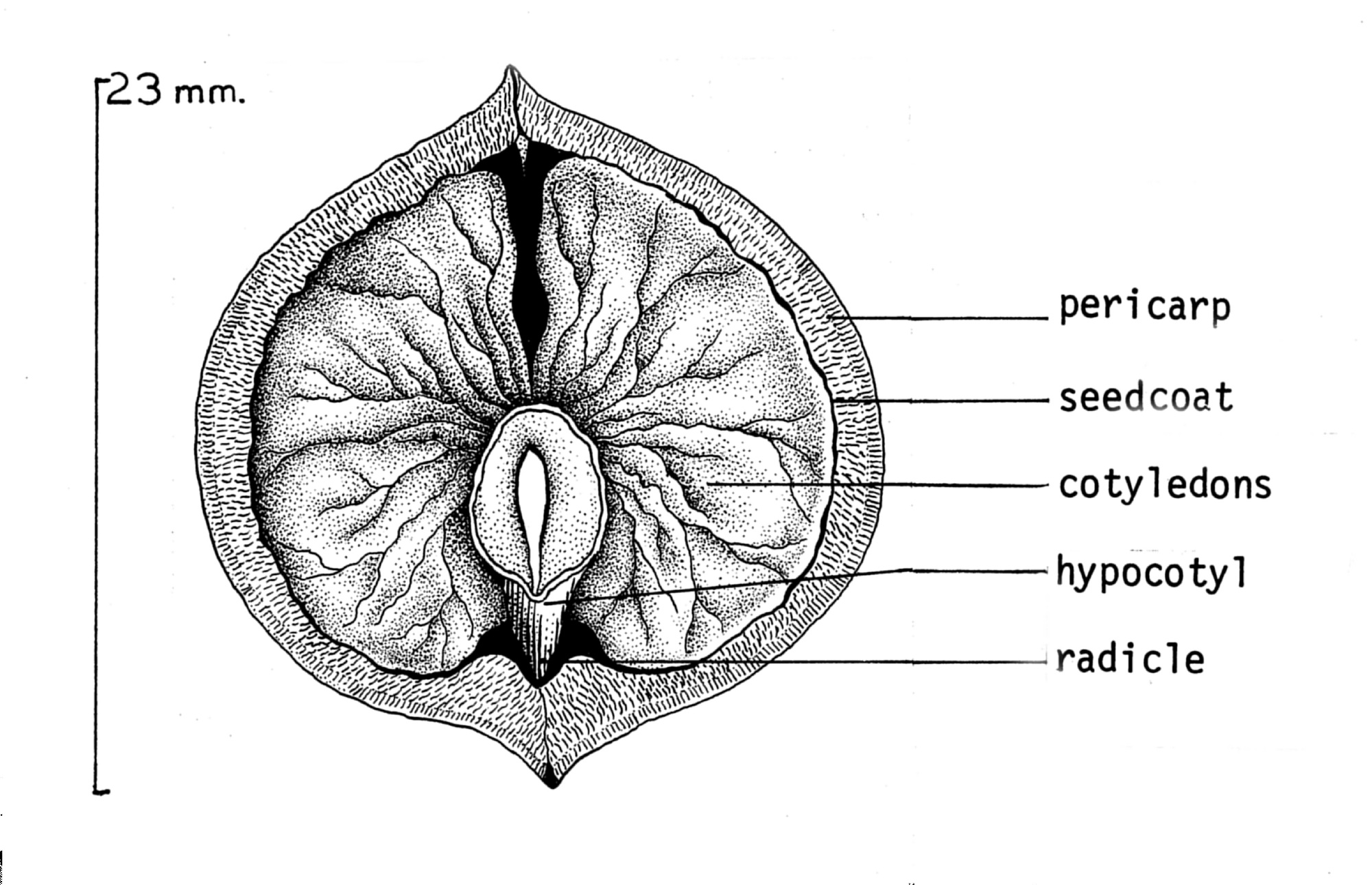
Nut (fruit)
A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, many dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context, "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed (Dehiscence (botany), indehiscent). Most seeds come from fruits that naturally free themselves from the shell, but this is not the case in nuts such as hazelnuts, chestnuts, and acorns, which have hard shell walls and originate from a compound ovary. Definition A seed is the mature fertilised ovule of a plant; it consists of three parts, the embryo which will develop into a new plant, stored food for the embryo, and a protective seed coat. Botany, Botanically, a nut is a fruit with a woody pericarp developing from a syncarpous gynoecium. Nuts may be contained in an Bract#Involucral bracts, involucre, a cup-shaped structure formed from the flower bracts. The involucre may be scaly, spiny, leafy or tubular, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catkins Corylus Avellana-Mont Bart-5124~2015 12 26
A catkin or ament is a slim, cylindrical flower cluster (a spike), with inconspicuous or no petals, usually wind-pollinated (anemophilous) but sometimes insect-pollinated (as in ''Salix''). It contains many, usually unisexual flowers, arranged closely along a central stem that is often drooping. Catkins are found in many plant families, including Betulaceae, Fagaceae, Moraceae, and Salicaceae. Occurrence Catkin-bearing plants include many trees or shrubs such as birch, willow, aspen, hickory, sweet chestnut, and sweetfern (''Comptonia''). In many of these plants, only the male flowers form catkins, and the female flowers are single (hazel, oak), a cone (alder), or other types (mulberry). '' Corylus jacquemontii'' has male catkins and also female spikes. In other plants (such as poplar), both male and female flowers are borne in catkins. ''Populus alba'' has male catkins which are grey and the female catkins are greyish-green. While the blooming months for catkins may vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrya
''Ostrya'' is a genus of eight to 10 small deciduous trees belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. Common names include hop-hornbeam and hophornbeam. It may also be called ironwood, a name shared with a number of other plants. The genus is native in southern Europe, southwest and eastern Asia, and North America, North and Central America. They have a conical or irregular crown and a scaly, rough bark. They have alternate and double-toothed birch-like leaf, leaves 3–10 cm long. The flowers are produced in spring, with male catkins 5–10 cm long and female aments 2–5 cm long. The fruit form in pendulous clusters 3–8 cm long with 6–20 seeds; each seed is a small nut (fruit), nut 2–4 mm long, fully enclosed in a bladder-like Involucral bract, involucre. The wood is very hard and heavy. The genus name ''Ostrya'' is derived from the Greek word (), which may be related to () "shell (of an animal)". Regarded as a weed tree by some foresters, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catkins
A catkin or ament is a slim, cylindrical flower cluster (a spike), with inconspicuous or no petals, usually wind-pollinated (anemophilous) but sometimes insect-pollinated (as in ''Salix''). It contains many, usually unisexual flowers, arranged closely along a central stem that is often drooping. Catkins are found in many plant families, including Betulaceae, Fagaceae, Moraceae, and Salicaceae. Occurrence Catkin-bearing plants include many trees or shrubs such as birch, willow, aspen, hickory, sweet chestnut, and sweetfern (''Comptonia''). In many of these plants, only the male flowers form catkins, and the female flowers are single (hazel, oak), a cone (alder), or other types (mulberry). '' Corylus jacquemontii'' has male catkins and also female spikes. In other plants (such as poplar), both male and female flowers are borne in catkins. ''Populus alba'' has male catkins which are grey and the female catkins are greyish-green. While the blooming months for catkins may vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |