|
Berman V. Parker
''Berman v. Parker'', 348 U.S. 26 (1954), is a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that interpreted the Takings Clause ("nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation") of the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The Court voted 8–0 to hold that private property could be taken for a public purpose with just compensation. The case laid the foundation for the Court's later important public use cases, ''Hawaii Housing Authority v. Midkiff'', 467 U.S. 229 (1984) and ''Kelo v. City of New London'', 545 U.S. 469 (2005). Critics of recent occurrences of eminent domain uses trace what they view as property rights violations to this case. Background The United States Congress passed the District of Columbia Redevelopment Act of 1945 to address the vast blighted area found in the District of Columbia. The Act created a commission of five members called the District of Columbia Redevelopment Land Agency and granted it the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Fifth Amendment (Amendment V) to the United States Constitution addresses criminal procedure and other aspects of the Constitution. It was ratified, along with nine other articles, in 1791 as part of the Bill of Rights. The Fifth Amendment applies to every level of the government, including the federal, state, and local levels, in regard to a US citizen or resident of the US. The Supreme Court furthered the protections of this amendment through the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. One provision of the Fifth Amendment requires that felonies be tried only upon indictment by a grand jury. Another provision, the Double Jeopardy Clause, provides the right of defendants to be tried only once in federal court for the same offense. The self-incrimination clause provides various protections against self-incrimination, including the right of an individual not to serve as a witness in a criminal case in which they are the defendant. "Pleading the Fifth" is a col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Restraint
Judicial restraint is a judicial interpretation that recommends favoring the status quo in judicial activities; it is the opposite of judicial activism. Aspects of judicial restraint include the principle of stare decisis (that new decisions should be consistent with previous decisions); a conservative approach to standing and a reluctance to grant certiorari; and a tendency to deliver narrowly tailored verdicts, avoiding "unnecessary resolution of broad questions." Judicial restraint may lead a court to avoid hearing a case in the first place. The court may justify its decision by questioning whether the plaintiff has standing; or by refusing to grant certiorari; or by determining that the central issue of the case is a political question better decided by the executive or legislative branches of government; or by determining that the court has no jurisdiction in the matter. Judicial restraint may lead a court to decide in favor of the status quo. In a case of judicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Supreme Court Cases
This page serves as an index of lists of United States Supreme Court cases. The United States Supreme Court is the highest federal court of the United States. By Chief Justice Court historians and other legal scholars consider each Chief Justice of the United States who presides over the Supreme Court of the United States to be the head of an era of the Court. These lists are sorted chronologically by Chief Justice and include most major cases decided by the Court. * Jay, Rutledge, and Ellsworth Courts (October 19, 1789 – December 15, 1800) * Marshall Court (February 4, 1801 – July 6, 1835) * Taney Court (March 28, 1836 – October 12, 1864) * Chase Court (December 15, 1864 – May 7, 1873) * Waite Court (March 4, 1874 – March 23, 1888) * Fuller Court (October 8, 1888 – July 4, 1910) * White Court (December 19, 1910 – May 19, 1921) * Taft Court (July 11, 1921 – February 3, 1930) * Hughes Court (February 24, 1930 – Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1954 In United States Case Law
Events January * January 1 – The Soviet Union ceases to demand war reparations from West Germany. * January 3 – The Italian broadcaster RAI officially begins transmitting. * January 7 – Georgetown-IBM experiment: The first public demonstration of a machine translation system is held in New York, at the head office of IBM. * January 10 – BOAC Flight 781, a de Havilland Comet jet plane, disintegrates in mid-air due to metal fatigue, and crashes in the Mediterranean near Elba; all 35 people on board are killed. * January 12 – 1954 Blons avalanches, Avalanches in Austria kill more than 200. * January 15 – Mau Mau rebellion, Mau Mau leader Waruhiu Itote is captured in Kenya. * January 17 – In Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia, Milovan Đilas, one of the leading members of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, is relieved of his duties. * January 20 – The US-based National Negro Network is established, with 46 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Land Use Case Law
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe Television * ''United'' (TV series), a 1990 BBC Two documentary series * ''United!'', a soap opera that aired on BBC One from 1965 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendell Pritchett
Wendell Eric Pritchett is an American lawyer, legal scholar, professor, and university administrator. He is currently the James S. Riepe Presidential Professor of Law and Education at the University of Pennsylvania Law School. Since February 2022, Pritchett has served as interim president of the University of Pennsylvania; he is the first Black individual to serve as the university's president. Pritchett previously served as Chancellor of Rutgers University–Camden (2009–2014), Interim Dean of the University of Pennsylvania Law School (2014-2015), and Provost of the University of Pennsylvania (2017–2022). Biography Pritchett's father, also named Wendell Pritchett, was a classical pianist and public school teacher, and his mother Carolyn was a high school English teacher. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Supreme Court Cases, Volume 348
This is a list of all the United States Supreme Court cases from volume 348 of the ''United States Reports The ''United States Reports'' () are the official record ( law reports) of the Supreme Court of the United States. They include rulings, orders, case tables (list of every case decided), in alphabetical order both by the name of the petitioner ...'': External links {{SCOTUSCases, 348 Volume 348 1954 in United States case law 1955 in United States case law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
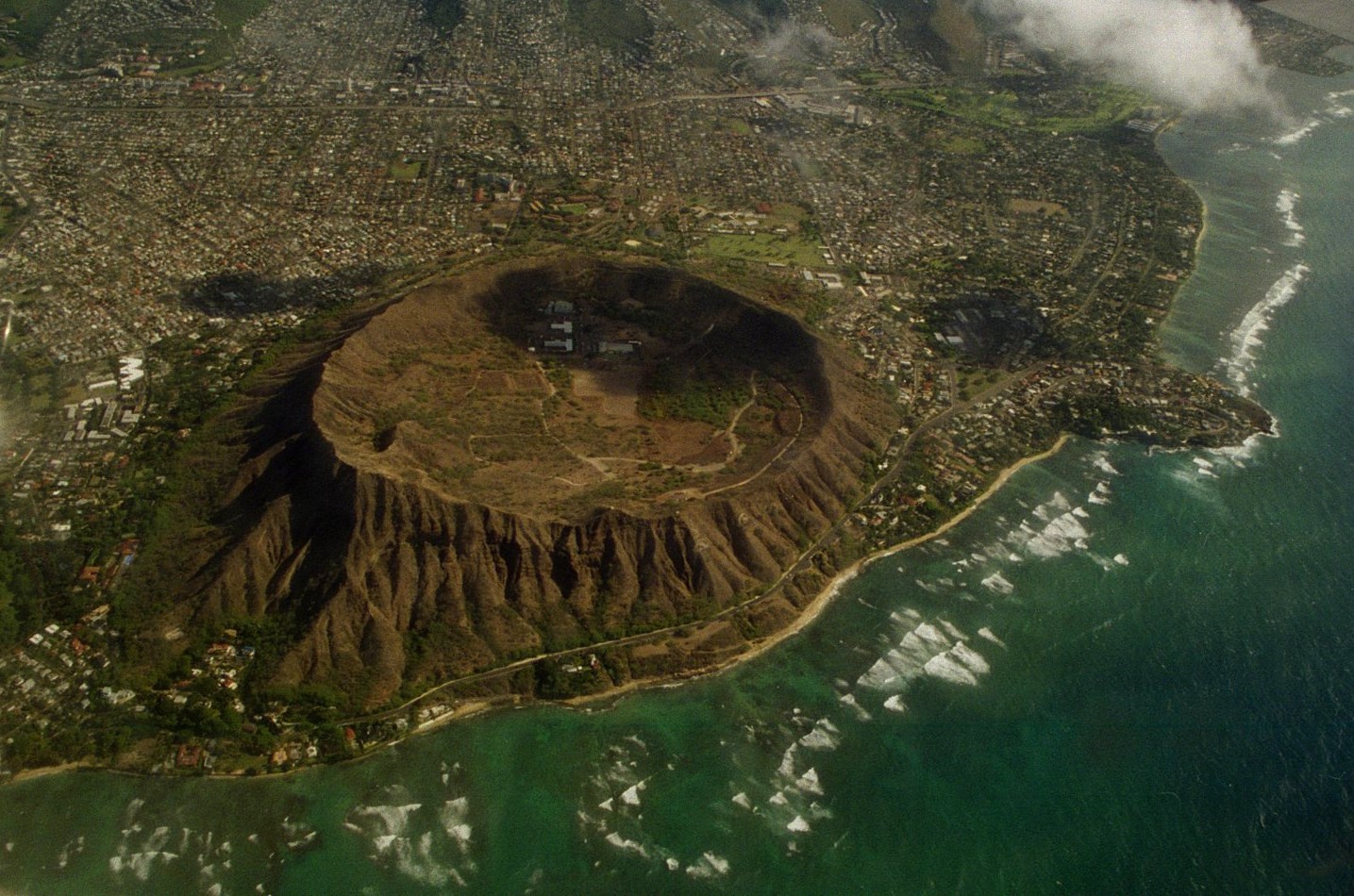
Kāhala, Hawaii
Kāhala, is a neighborhood in Honolulu, Hawaii. Kahala contains a large concentration of expensive real estate and beachfront properties, which include some of the most expensive in the entire state. Kahala consists of approximately 1,200 homes. The neighborhood is considered a “cinderella story” because it went from farmland to one of the nicest neighborhoods on Oahu. Kahala is also home to the Kahala Hotel & Resort, formerly known as the Kahala Mandarin Oriental, and prior to the Kahala Hilton. Also located along the borders are Kahala Mall, and Diamond Head crater. There are a variety of residents of many ages, the newer arrivals to the island generally own the more modern and spacious homes, though many of the older homes are beautiful and finely aged. Many celebrities and Business persons have also bought vacation homes in the area. Kahala is a favored spot for investors to purchase and renovate homes to sell. In 2006, typical prices for a house in Kahala ranged fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian Island, however, in ancient times, O{{okinaahu was not populous and was outranked by the status of other islands. The translation of ''"ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fee Simple
In English law, a fee simple or fee simple absolute is an estate in land, a form of freehold ownership. A "fee" is a vested, inheritable, present possessory interest in land. A "fee simple" is real property held without limit of time (i.e., permanently) under common law, whereas the highest possible form of ownership is a "fee simple absolute," which is without limitations on the land's use (such as qualifiers or conditions that disallow certain uses of the land or subject the vested interest to termination). The rights of the fee-simple owner are limited by government powers of taxation, compulsory purchase, police power, and escheat, and may also be limited further by certain encumbrances or conditions in the deed, such as, for example, a condition that required the land to be used as a public park, with a reversion interest in the grantor if the condition fails; this is a fee simple conditional. History The word "fee" is related to the term fief, meaning a feudal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligopoly
An oligopoly (from Greek ὀλίγος, ''oligos'' "few" and πωλεῖν, ''polein'' "to sell") is a market structure in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of large sellers or producers. Oligopolies often result from the desire to maximize profits, which can lead to collusion between companies. This reduces competition, increases prices for consumers, and lowers wages for employees. Many industries have been cited as oligopolistic, including civil aviation, electricity providers, the telecommunications sector, Rail freight markets, food processing, funeral services, sugar refining, beer making, pulp and paper making, and automobile manufacturing. Most countries have laws outlawing anti-competitive behavior. EU competition law prohibits anti-competitive practices such as price-fixing and manipulating market supply and trade among competitors. In the US, the United States Department of Justice Antitrust Division and the Federal Trade Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Blight
Urban decay (also known as urban rot, urban death or urban blight) is the sociological process by which a previously functioning city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude. There is no single process that leads to urban decay which is why it can be hard to encapsulate its magnitude. Urban decay can include the following aspects: * Deindustrialization * Depopulation * Counterurbanization * Economic Restructuring * Abandoned buildings or infrastructure * High local unemployment * Increased poverty * Fragmented families * Low overall living standards or quality of life * Political disenfranchisement * Crime * Elevated levels of pollution * Desolate cityscape known as greyfield land or urban prairie Since the 1970s and 1980s, urban decay has been a phenomenon associated with some Western cities, especially in North America and parts of Europe. Cities have experienced population flights to the suburbs and exurb commuter towns; often in the form of whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(c).jpg)