|
Berlin-Britz Transmitter
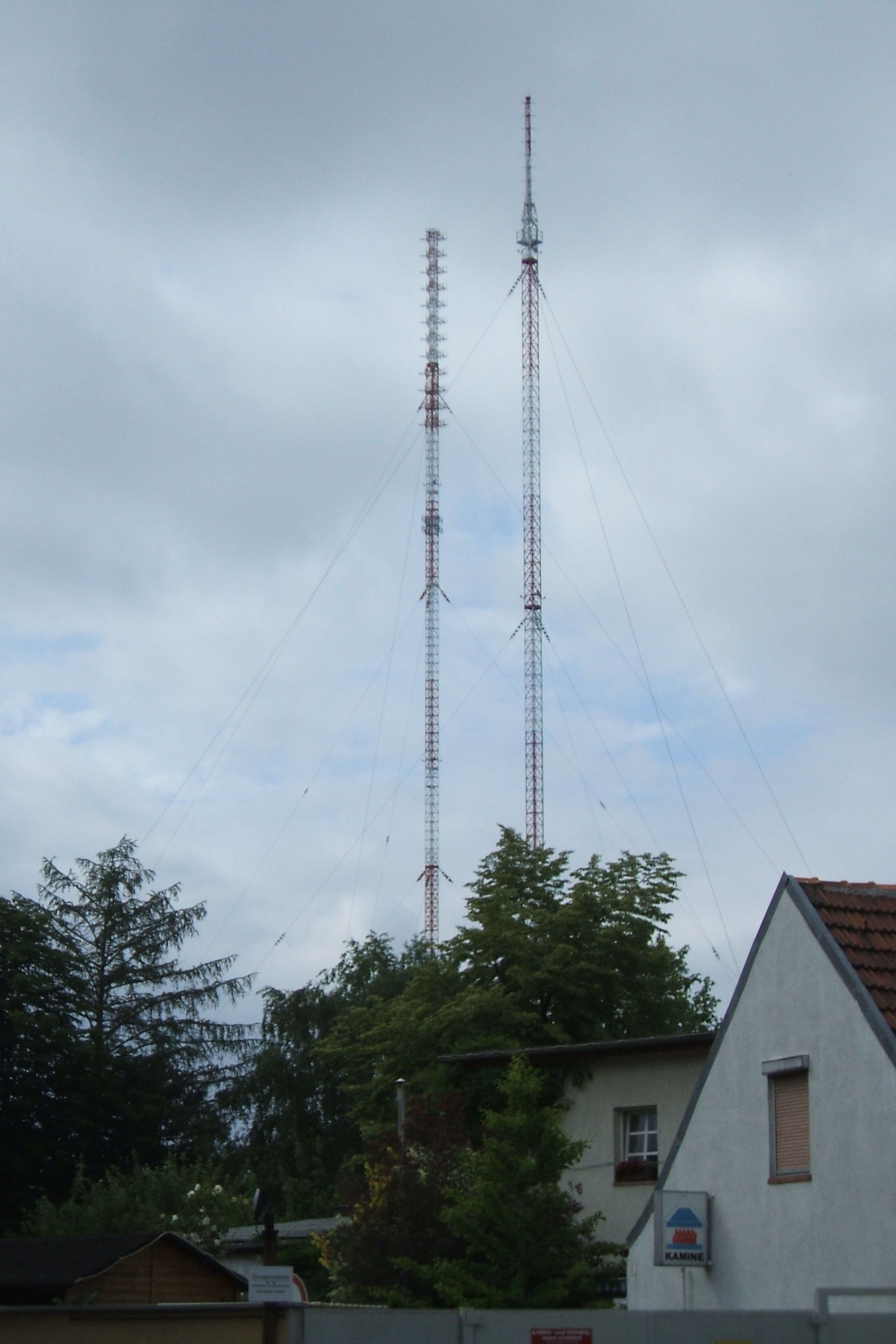
Transmitter Berlin-Britz was a broadcasting facility for medium wave, shortwave and frequency modulation, FM on the site of a former tree nursery in Berlin-Britz. It was established in 1946 and until 1993 it was the most important transmitter of Rundfunk im amerikanischen Sektor, RIAS. It was used by Deutschlandradio until 4 September 2013, and was finally demolished on 18 July 2015. The Berlin-Britz transmitter initially used a wire supported between two tall wooden poles. This aerial was replaced in 1947 by a guyed insulated steel framework mast. This mast was replaced in turn in 1948 by two guyed insulated steel framework masts, each with a height of and which still exist today. These masts were extended in subsequent years so that today they are and tall and carry FM radio broadcasting antennas. Since 1949 the Berlin-Britz transmitter has also been a shortwave transmission facility. A Dipole antenna, dipole aerial aligned in east–west direction was installed. A second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin-Britz Sendeanlage
Britz () is a German boroughs and localities of Berlin, locality (''Ortsteil'') within the Berlin borough (''Bezirk'') of Neukölln. History The village of ''Britzig'' was first mentioned in 1273. It was incorporated by the 1920 Greater Berlin Act. It is known for being the site of the ''Hufeisensiedlung'' ("Horseshoe Estate"), part of the UNESCO Berlin Modernism Housing Estates World Heritage Site since 2008. Public transport Britz is served by the U7 (Berlin U-Bahn) traveling North / South from and to the terminus at Rudow (Berlin U-Bahn).Sights *Village church with foundation walls from the 13th century *Schloss Britz (Britz Manor), rebuilt in 1883, former residence of Prussian statesman Ewald Friedrich von Hertzberg *Britz windmill built in 1866 *Britzer G ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, most implementations of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Wave
Medium wave (MW) is a part of the medium frequency (MF) radio band used mainly for AM radio broadcasting. The spectrum provides about 120 channels with more limited sound quality than FM stations on the FM broadcast band. During the daytime, reception is usually limited to more local stations, though this is dependent on the signal conditions and quality of radio receiver used. Improved signal propagation at night allows the reception of much longer distance signals (within a range of about 2,000 km or 1,200 miles). This can cause increased interference because on most channels multiple transmitters operate simultaneously worldwide. In addition, amplitude modulation (AM) is often more prone to interference by various electronic devices, especially power supplies and computers. Strong transmitters cover larger areas than on the FM broadcast band but require more energy and longer antennas. Digital modes are possible but had not yet reached momentum. MW was the main radio b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (approximately 100 to 10 metres in wavelength). It lies between the medium frequency band (MF) and the bottom of the VHF band. Radio waves in the shortwave band can be reflected or refracted from a layer of electrically charged atoms in the atmosphere called the ionosphere. Therefore, short waves directed at an angle into the sky can be reflected back to Earth at great distances, beyond the horizon. This is called skywave or "skip" propagation. Thus shortwave radio can be used for communication over very long distances, in contrast to radio waves of higher frequency, which travel in straight lines (line-of-sight propagation) and are generally limited by the visual horizon, about 64 km (40 miles). Shortwave broadcasts of radio pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proportion to a property, primarily the instantaneous amplitude, of a message signal, such as an audio signal. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and Run-length limited#FM: .280.2C1.29 RLL, computing. In Analog signal, analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting of voice and music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude. Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin-Britz
Britz () is a German locality (''Ortsteil'') within the Berlin borough (''Bezirk'') of Neukölln. History The village of ''Britzig'' was first mentioned in 1273. It was incorporated by the 1920 Greater Berlin Act. It is known for being the site of the ''Hufeisensiedlung'' ("Horseshoe Estate"), part of the UNESCO Berlin Modernism Housing Estates World Heritage Site since 2008. Public transport Britz is served by the traveling North / South from and to the terminus at Rudow (Berlin U-Bahn).Sights *Village ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rundfunk Im Amerikanischen Sektor
RIAS (; ''Radio in the American Sector'') was a radio and television station in the American Sector of Berlin during the Cold War. It was founded by the US occupational authorities after World War II in 1946 to provide the German population in and around Berlin with news and political reporting. History By the end of 1945 the US Military Administration in Berlin decided to establish its own broadcasting system, after the Soviets had refused to provide air time on the '' Berliner Rundfunk'' radio station. Supervised by the US Information Control Division, broadcasting commenced on 7 February 1946. For the first months the programme could be distributed via telephone line only (as DIAS – '' Drahtfunk im amerikanischen Sektor''), until a first medium wave transmitter was installed in September. By its creative and innovative programming, the station quickly gained much popularity. Its importance was magnified during the Berlin Blockade in 1948-49, when it carried the message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutschlandradio
Deutschlandradio (DLR; ) is a national German public radio broadcaster. History ''Deutschlandfunk'' was originally a West German news radio targeting listeners within West Germany as well as in neighbouring countries, ''Deutschlandfunk Kultur'' is the result of a merger of West Berlin's RIAS station and East Berlin's DS Kultur after German reunification. Both networks that used to broadcast mainly on the AM bands have since spread throughout Germany, having been allocated many additional FM transmitters. However, because of lack of analogue frequencies, during 2003 Deutschlandradio changed its distribution strategy to digital terrestrial transmission. Stations It operates four national networks: *Deutschlandfunk: mainly news and information * Deutschlandfunk Kultur: culture in a broader sense * Deutschlandfunk Nova: aimed at young adults, mainly spoken-word *: opt-out channel, often for special events ''Dokumente und Debatten'' is a digital-only special-event channel. It br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipole Antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is one of the two simplest and most widely used antenna types, types of antenna; the other is the monopole antenna, monopole. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each far end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the radio receiver, receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a Socialist state, socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The Economy of East Germany, economy of the country was Central planning, centrally planned and government-owned corporation, state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc. Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the Berlin Declaration (1945), Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II. The Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet occupation zone in Germany, Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Masts
The tallest structure in the world is the Burj Khalifa skyscraper at . Listed are guyed masts (such as telecommunication masts), self-supporting towers (such as the CN Tower), skyscrapers (such as the Willis Tower), oil platforms, electricity transmission towers, and bridge support towers. This list is organized by absolute height. See History of the world's tallest structures, Tallest structures by category, and List of tallest buildings for additional information about these types of structures. Terminology Terminological and listing criteria follow Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat definitions. Guyed masts are differentiated from towers – the latter not featuring any guy wires or other support structures; and buildings are differentiated from towers – the former having at least 50% of occupiable floor space although both are self-supporting structures. Lists by height This list includes structures of all types over 350 meters (1148 feet). Plus it includes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Radio Masts And Towers
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |