|
Beowulf In Middle-earth
J. R. R. Tolkien, a fantasy author and professional philologist, drew on the Old English poem ''Beowulf'' for multiple aspects of his Middle-earth legendarium, alongside other influences. He used elements such as names, monsters, and the structure of society in a heroic age. He emulated its style, creating an impression of depth and adopting an elegiac tone. Tolkien admired the way that ''Beowulf'', written by a Christian looking back at a pagan past, just as he was, embodied a "large symbolism" without ever becoming allegorical. He worked to echo the symbolism of life's road and individual heroism in ''The Lord of the Rings''. The names of races, including ents, orcs, and elves, and place names such as Orthanc and Meduseld, derive from ''Beowulf''. The werebear Beorn in ''The Hobbit'' has been likened to the hero Beowulf himself; both names mean "bear" and both characters have enormous strength. Scholars have compared some of Tolkien's monsters to those in ''Beowulf''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philologist
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative and historical linguistics. Classical philology studies classical languages. Classical philology principally originated from the Library of Pergamum and the Library of Alexandria around the fourth century BC, continued by Greeks and Romans throughout the Roman and Byzantine Empire. It was eventually resumed by European scholars of the Renaissance, where it was soon joined by philologies of other European ( Romance, Germanic, Celtic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gollum
Gollum is a Tolkien's monsters, monster with a distinctive style of speech in J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy world of Middle-earth. He was introduced in the 1937 Fantasy (genre), fantasy novel ''The Hobbit'', and became important in its sequel, ''The Lord of the Rings''. Gollum was a Stoor Hobbit of the River-folk who lived near the Gladden Fields. In ''The Lord of the Rings'', it is stated that he was originally known as Sméagol, corrupted by the One Ring, and later named Gollum after his habit of making "a horrible swallowing noise in his throat". Sméagol obtained the Ring by murdering his relative Déagol, who found it in the River Anduin. Gollum called the Ring "my precious", and it extended his life far beyond natural limits. Centuries of the Ring's influence twisted Gollum's body and mind, and, by the time of the novels, he "loved and hated [the Ring], as he loved and hated himself." Throughout the story, Gollum was torn between his lust for the Ring and his desire to be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrothgar
Hrothgar ( ; ) was a semi-legendary Danish king living around the early sixth century AD. Hrothgar appears in the Anglo-Saxon epics ''Beowulf'' and '' Widsith'', in Norse sagas and poems, and in medieval Danish chronicles. In both Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian tradition, Hrothgar is a Scylding, the son of Halfdan, the brother of Halga, and the uncle of Hrólfr Kraki. Moreover, in both traditions, the mentioned characters were the contemporaries of the Swedish king Eadgils; and both traditions also mention a feud with men named Fróði and Ingeld. The consensus view is that Anglo-Saxon and Scandinavian traditions describe the same person. Names Hrothgar, also rendered ''Hrōðgār'', is an Old English form attested in ''Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'', the earliest sources to mention the character. In non-English sources, the name appears in more or less corresponding Old Icelandic, Old Danish, and Latinized versions. He appears as ''Hróarr'', ''Hroar'', etc., in sagas and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heorot
Heorot (Old English 'hart, stag') is a mead-hall and major point of focus in the Anglo-Saxon poem ''Beowulf''. The hall serves as a seat of rule for King Hrothgar, a legendary Danish king. After the monster Grendel slaughters the inhabitants of the hall, the Geatish hero Beowulf defends the royal hall before subsequently defeating him. Later Grendel's mother attacks the inhabitants of the hall, and she too is subsequently defeated by Beowulf. Name The name ''Heorot'' is the Old English word for a stag. Its use may stem from an association between royalty and stags in Germanic paganism. Archaeologists have unearthed a variety of Anglo-Saxon finds associating stags with royalty. For example, a sceptre or whetstone discovered in mound I of the Anglo-Saxon burial site Sutton Hoo prominently features a standing stag at its top.For general discussion, see Fulk, Bjork, & Niles (2008:119–120). For images and details regarding the sceptre or whetstone, see the British Museum'coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
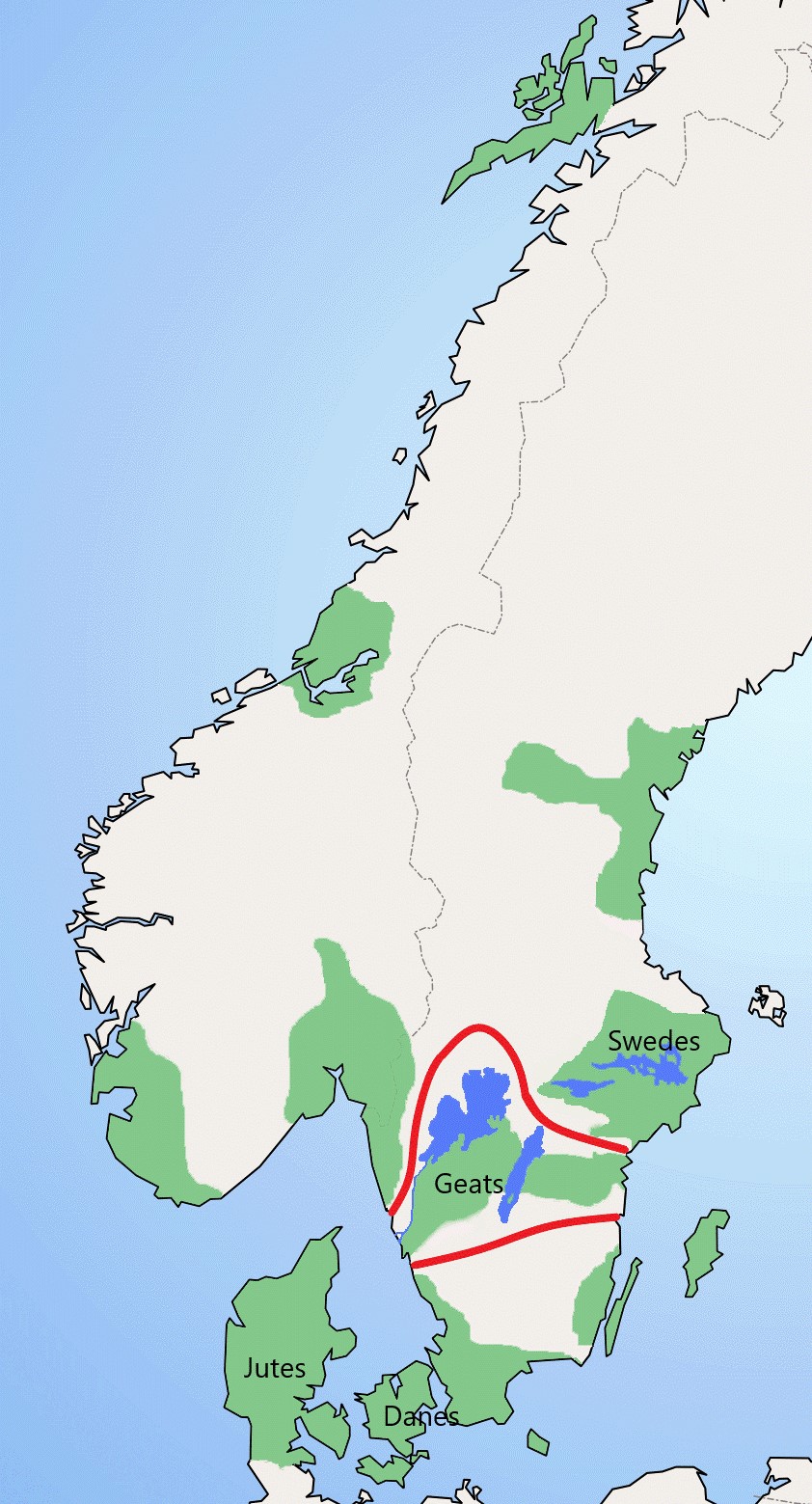
Geats
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Geats#Goths, Goths'', were a large North Germanic peoples, North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with the tribes of Swedes (tribe), Swedes and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Provinces of Sweden, Swedish provinces of and , the western and eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, ''Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from Indo-European ablaut, ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poetry
In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to oral tradition, epic poems consist of formal speech and are usually learnt word for word, and are contrasted with narratives that consist of everyday speech where the performer has the license to recontextualize the story to a particular audience, often to a younger generation. Influential epics that have shaped Western literature and culture include Homer's ''Iliad'' and '' Odyssey''; Virgil's '' Aeneid''; and the anonymous '' Beowulf'' and '' Epic of Gilgamesh''. The genre has inspired the adjective '' epic'' as well as derivative works in other mediums (such as epic films) that evoke or emulate the characteristics of epics. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin , which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Straight Road
The Old Straight Road, the Straight Road, the Lost Road, or the Lost Straight Road, is J. R. R. Tolkien's conception, in his fantasy world of Arda, that his Elves are able to sail to the earthly paradise of Valinor, realm of the godlike Valar. The tale is mentioned in ''The Silmarillion'' and in ''The Lord of the Rings'', and documented in ''The Lost Road and Other Writings''. The Elves are immortal, but may grow weary of the world, and then sail across the Great Sea to reach Valinor. The men of Númenor are persuaded by Sauron, servant of the first Dark Lord Melkor, to attack Valinor to get the immortality they feel should be theirs. The Valar ask for help from the creator, Eru Ilúvatar. He destroys Númenor and its army, in the process reshaping Arda into a sphere, and separating it and its continent of Middle-earth from Valinor so that men can no longer reach it. Elves can still set sail from the shores of Middle-earth in ships, bound for Valinor: they sail into the Uttermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valinor
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar''), the Blessed Realm, or the Undying Lands is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar and Maiar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to mean Valinor. It includes Eldamar, the land of the Elves, who as immortals are permitted to live in Valinor. The name "the Undying Lands" does not mean that the land itself causes mortals to live forever. Generally, only immortal beings are allowed to reside there. Exceptions are made for the surviving bearers of the One Ring: Bilbo and Frodo Baggins and Sam Gamgee, who dwell there for a time, and the dwarf Gimli., "The Grey Havens", and Appendix B, entry for S.R. 1482 and 1541. Tolkien's myth of the attempt of Númenor to capture Aman has been likened to the biblical Tower of Babel and the ancient Greek Atlantis, and the resulting destruction in both cases. They note, too, that a mortal's stay in Valino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthly Paradise
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden (; ; ) or Garden of God ( and ), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the biblical paradise described in Genesis 2–3 and Ezekiel 28 and 31.. The location of Eden is described in the Book of Genesis as the source of four tributaries. Various suggestions have been made for its location: at the head of the Persian Gulf, in southern Mesopotamia where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers run into the sea; and in Armenia. Others theorize that Eden was the entire Fertile Crescent or a region substantial in size in Mesopotamia, where its native inhabitants still exist in cities such as Telassar. Like the Genesis flood narrative, the Genesis creation narrative and the account of the Tower of Babel, the story of Eden echoes the Mesopotamian myth of a king, as a primordial man, who is placed in a divine garden to guard the tree of life. Scholars note that the Eden narrative shows parallels with aspects of Solomon's Temple and Jerusalem, attest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valar
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth writings. They are "angelic powers" or "gods" subordinate to the one God ( Eru Ilúvatar). The '' Ainulindalë'' describes how some of the Ainur choose to enter the world ( Arda) to complete its material development after its form is determined by the Music of the Ainur. The mightiest of these are called the Valar, or "the Powers of the World", and the others are known as the Maiar. The Valar are mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'' but Tolkien had developed them earlier, in material published posthumously in ''The Silmarillion'', especially the "Valaquenta" (Quenya: "Account of the Valar"), ''The History of Middle-earth'', and '' Unfinished Tales''. Scholars have noted that the Valar resemble angels in Christianity but that Tolkien presented them rather more like pagan gods. Their role in providing what the characters in Middle-earth experience as luck or providence is also discussed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riders Of Rohan
Riders can refer to Arts, entertainment, media * ''Riders'' (novel), a book by Jilly Cooper ** ''Riders'' (1993 film), a British film based on the book * ''Steal'' (film), a 2002 American action film also called ''Riders'' *"Riders", a 2002 song by Blue from the album ''One Love'' (Blue album) Videogames * Sonic Riders, a 2006 racing video game from the Sonic the Hedgehog series * Sonic Riders: Zero Gravity, a 2008 racing video game from the Sonic the Hedgehog series * Sonic Free Riders, a 2010 racing video game from the Sonic the Hedgehog series * The Riders, collective refers to three of the ''Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse'' in NetHack, serving as the game's final bosses. Sports *Saskatchewan Roughriders (the 'Riders), a Canadian football team from Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada *Ottawa Rough Riders (the 'Riders), a defunct Canadian football team from Ottawa, Ontario, Canada *Leicester Riders, a British basketball team from Leicester, Leicestershire, England, UK *Frisco Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |