|
Beam Search
In computer science, beam search is a heuristic search algorithm that explores a graph by expanding the most promising node in a limited set. Beam search is a modification of best-first search that reduces its memory requirements. Best-first search is a graph search which orders all partial solutions (states) according to some heuristic. But in beam search, only a predetermined number of best partial solutions are kept as candidates. It is thus a greedy algorithm. Details Beam search uses breadth-first search to build its search tree. At each level of the tree, it generates all successors of the states at the current level, sorting them in increasing order of heuristic cost. However, it only stores a predetermined number, \beta, of best states at each level (called the beam width). Only those states are expanded next. The greater the beam width, the fewer states are pruned. With an infinite beam width, no states are pruned and beam search is identical to best-first search. Conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Translation
Machine translation is use of computational techniques to translate text or speech from one language to another, including the contextual, idiomatic and pragmatic nuances of both languages. Early approaches were mostly rule-based or statistical. These methods have since been superseded by neural machine translation and large language models. History Origins The origins of machine translation can be traced back to the work of Al-Kindi, a ninth-century Arabic cryptographer who developed techniques for systemic language translation, including cryptanalysis, frequency analysis, and probability and statistics, which are used in modern machine translation. The idea of machine translation later appeared in the 17th century. In 1629, René Descartes proposed a universal language, with equivalent ideas in different tongues sharing one symbol. The idea of using digital computers for translation of natural languages was proposed as early as 1947 by England's A. D. Booth and Warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anytime Algorithm
In computer science, an anytime algorithm is an algorithm that can return a valid solution to a problem even if it is interrupted before it ends. The algorithm is expected to find better and better solutions the longer it keeps running. Most algorithms run to completion: they provide a single answer after performing some fixed amount of computation. In some cases, however, the user may wish to terminate the algorithm prior to completion. The amount of computation required may be substantial, for example, and computational resources might need to be reallocated. Most algorithms either run to completion or they provide no useful solution information. Anytime algorithms, however, are able to return a partial answer, whose quality depends on the amount of computation they were able to perform. The answer generated by anytime algorithms is an approximation of the correct answer. Names An anytime algorithm may be also called an "interruptible algorithm". They are different from contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Stack Search
Beam stack search is a search algorithm that combines chronological backtracking (that is, depth-first search) with beam search and is similar to depth-first beam search.Furcy, David. Koenig, Sven. "Limited Discrepancy Beam Search". 2005. Both search algorithms are anytime algorithms that find good but likely sub-optimal solutions quickly, like beam search, then backtrack and continue to find improved solutions until convergence to an optimal solution. Implementation Beam stack search uses the beam stack as a data structure to integrate chronological backtracking with beam search and can be combined with the divide and conquer algorithm technique, resulting in divide-and-conquer beam-stack search. Alternatives Beam search using limited discrepancy backtracking (BULB) is a search algorithm that combines limited discrepancy search with beam search and thus performs non-chronological backtracking, which often outperforms the chronological backtracking done by beam stack search a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth-first Search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. Extra memory, usually a stack, is needed to keep track of the nodes discovered so far along a specified branch which helps in backtracking of the graph. A version of depth-first search was investigated in the 19th century by French mathematician Charles Pierre Trémaux as a strategy for solving mazes. Properties The time and space analysis of DFS differs according to its application area. In theoretical computer science, DFS is typically used to traverse an entire graph, and takes time where , V, is the number of vertices and , E, the number of edges. This is linear in the size of the graph. In these applications it also uses space O(, V, ) in the worst case to store the stack of vertices on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Completeness (logic)
In mathematical logic and metalogic, a formal system is called complete with respect to a particular property if every formula having the property can be derived using that system, i.e. is one of its theorems; otherwise the system is said to be incomplete. The term "complete" is also used without qualification, with differing meanings depending on the context, mostly referring to the property of semantical validity. Intuitively, a system is called complete in this particular sense, if it can derive every formula that is true. Other properties related to completeness The property converse to completeness is called soundness: a system is sound with respect to a property (mostly semantical validity) if each of its theorems has that property. Forms of completeness Expressive completeness A formal language is ''expressively complete'' if it can express the subject matter for which it is intended. Functional completeness A set of logical connectives associated with a formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
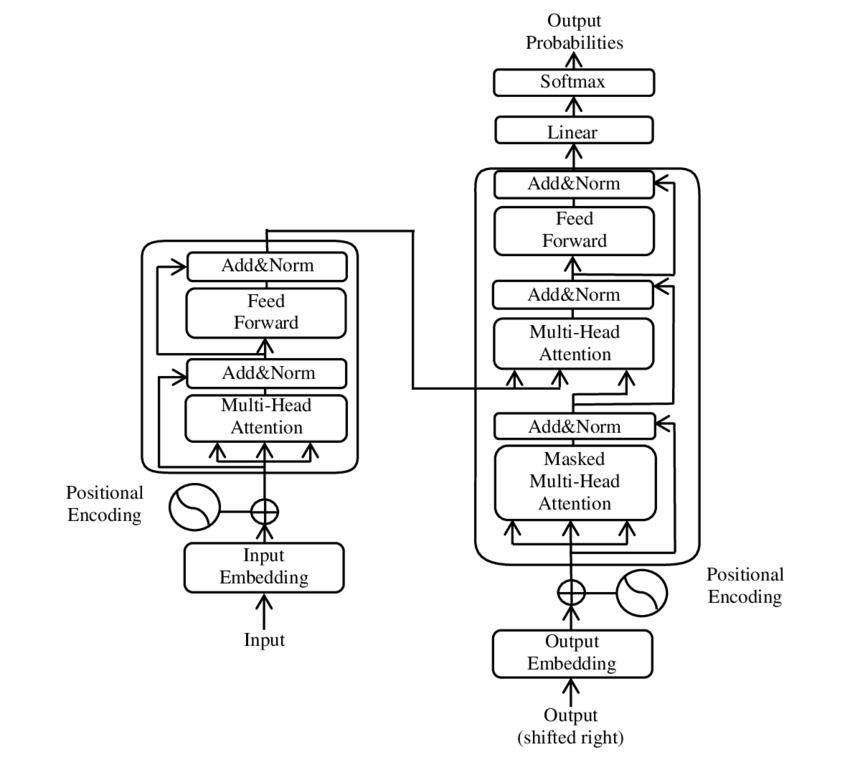
Large Language Models
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with Self-supervised learning, self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially Natural language generation, language generation. The largest and most capable LLMs are Generative pre-trained transformer, generative pretrained transformers (GPTs), which are largely used in Generative artificial intelligence, generative Chatbot, chatbots such as ChatGPT or Gemini (chatbot), Gemini. LLMs can be Fine-tuning (deep learning), fine-tuned for specific tasks or guided by prompt engineering. These models acquire Predictive learning, predictive power regarding syntax, semantics, and Ontology (information science), ontologies inherent in human Text corpus, language corpora, but they also inherit inaccuracies and Algorithmic bias, biases present in the Training, validation, and test data sets, data they are trained in. History Before the emergence of transformer-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Machine Translation
Neural machine translation (NMT) is an approach to machine translation that uses an artificial neural network to predict the likelihood of a sequence of words, typically modeling entire sentences in a single integrated model. It is the dominant approach today and can produce translations that rival human translations when translating between high-resource languages under specific conditions. However, there still remain challenges, especially with languages where less high-quality data is available, and with domain shift between the data a system was trained on and the texts it is supposed to translate. NMT systems also tend to produce fairly literal translations. Overview In the translation task, a sentence \mathbf = x_ (consisting of I tokens x_i) in the source language is to be translated into a sentence \mathbf = x_ (consisting of J tokens x_j) in the target language. The source and target tokens (which in the simple event are used for each other in order for a particular gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Climbing
numerical analysis, hill climbing is a mathematical optimization technique which belongs to the family of local search. It is an iterative algorithm that starts with an arbitrary solution to a problem, then attempts to find a better solution by making an incremental change to the solution. If the change produces a better solution, another incremental change is made to the new solution, and so on until no further improvements can be found. For example, hill climbing can be applied to the travelling salesman problem. It is easy to find an initial solution that visits all the cities but will likely be very poor compared to the optimal solution. The algorithm starts with such a solution and makes small improvements to it, such as switching the order in which two cities are visited. Eventually, a much shorter route is likely to be obtained. Hill climbing finds optimal solutions for convex problems – for other problems it will find only local optima (solutions that cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Traversal
In computer science, tree traversal (also known as tree search and walking the tree) is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting (e.g. retrieving, updating, or deleting) each node in a Tree (data structure), tree data structure, exactly once. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the nodes are visited. The following algorithms are described for a binary tree, but they may be generalized to other trees as well. Types Unlike linked lists, one-dimensional arrays and other List of data structures#Linear data structures, linear data structures, which are canonically traversed in linear order, trees may be traversed in multiple ways. They may be traversed in Depth-first search, depth-first or Breadth-first search, breadth-first order. There are three common ways to traverse them in depth-first order: in-order, pre-order and post-order. Beyond these basic traversals, various more complex or hybrid schemes are possible, such as depth-limited searche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breadth-first Search
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for searching a tree data structure for a node that satisfies a given property. It starts at the tree root and explores all nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. Extra memory, usually a queue, is needed to keep track of the child nodes that were encountered but not yet explored. For example, in a chess endgame, a chess engine may build the game tree from the current position by applying all possible moves and use breadth-first search to find a win position for White. Implicit trees (such as game trees or other problem-solving trees) may be of infinite size; breadth-first search is guaranteed to find a solution node if one exists. In contrast, (plain) depth-first search (DFS), which explores the node branch as far as possible before backtracking and expanding other nodes, may get lost in an infinite branch and never make it to the solution node. Iterative deepening depth-first search ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |