|
Battle Of Wippedesfleot
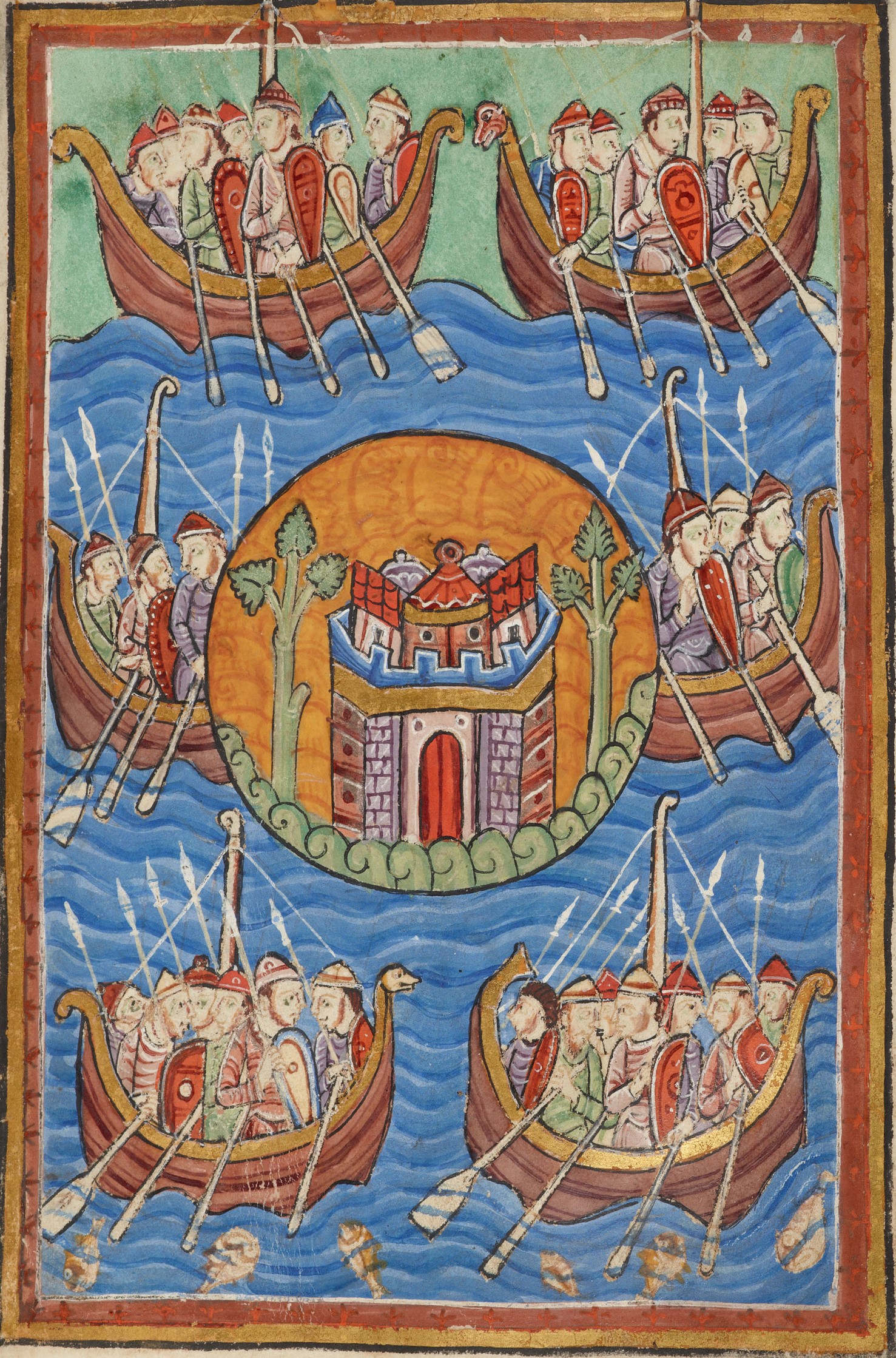
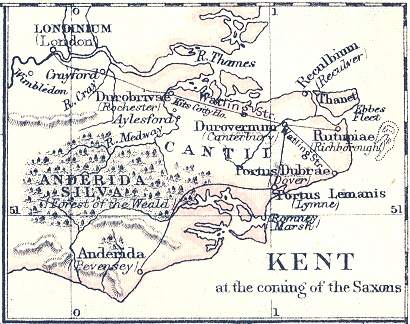
The Battle of Wippedesfleot took place in or around 465 CE between the Anglo-Saxons (or Jutes), said to have been led by Hengest, and the Britons. The battle is described in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' thus: :465: :465: This year Hengist and Æsc fought against the Welsh near Wippidsfleet, bbsfleet?and there slew twelve Welsh ealdormen, and one of their own thanes was slain there, whose name was Wipped. This battle is said to have resulted in much bloodshed and slaughter on both sides, to the extent that hostilities abated for a while thereafter. Some historians believe in a Saxon victory, but that is not what is mentioned in the text. The limited number of casualties is an indication that the battle was a small one. The number of ''warriors'' involved must not have reached 200 men. Wippedesfleot is thought to be Ebbsfleet in Kent, near Ramsgate. Its location made the author of the ''Historia Brittonum'' think that all Saxons had now been driven out of Britain. ''Wip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Settlement Of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, spoken on the other side of the North Sea. The first Germanic speakers to settle Britain permanently are likely to have been soldiers recruited by the Roman administration in the 4th century AD, or even earlier. In the early 5th century, during the end of Roman rule in Britain and the breakdown of the Roman economy, larger numbers arrived, and their impact upon local culture and politics increased. There is Historiography of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, ongoing debate about the scale, timing and nature of the Anglo-Saxon settlements and also about what happened to the existing populations of the regions where the migrants settled. The available evidence includes a small number of medieval texts which emphasize Saxons, Saxon settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions have a preface written in that name. Some experts have dismissed the Nennian preface as a late forgery and argued that the work was actually an anonymous compilation. Overview The ''Historia Brittonum'' describes the supposed settlement of Britain by Trojan settlers and says that Britain was named for Brutus, a descendant of Aeneas. The "single most important source used by Geoffrey of Monmouth in his pseudohistorical ''Historia Regum Britanniae''" and through the enormous popularity of the latter work, this version of the early history of Britain, including the Trojan origin tradition, was incorporated into subsequent chronicles of the long-running history of the land, such as the Middle English '' Brut of England'', also known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Anglo-Saxons
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Britons
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
460s Conflicts
46 may refer to: * 46 (number) * One of the years 46 BC, AD 46, 1946, 2046 * ''46'', a 1983 album by Kino * "Forty Six", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Appalachian Incantation'', 2010 * 46 Hestia 46 Hestia is a large, dark main-belt asteroid. It is also the primary body of the Hestia clump, a group of asteroids with similar orbits. Hestia was discovered by N. R. Pogson on August 16, 1857, at the Radcliffe Observatory, Oxford. Pogson ..., a main-belt asteroid * DAF 46, a small family car {{Number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Badon
The Battle of Badon, also known as the Battle of Mons Badonicus, was purportedly fought between Britons and Anglo-Saxons in Post-Roman Britain during the late 5th or early 6th century. It was credited as a major victory for the Britons, stopping the westward encroachment of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms for a period. The earliest known references to the battle, by the British cleric Gildas, date to the 6th century. It is chiefly known today for the supposed involvement of the man who would later be remembered as the legendary King Arthur; although it is not agreed that Arthur was a historical person, his name first appears in the 9th-century '' Historia Brittonum'', where he is mentioned as having participated in the battle alongside the Brittonic kings as a war commander, though is not described as a king himself. Because of the limited number of sources, there is no certainty about the date, location, or details of the fighting. Almost all scholars agree that this battle did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gildas
Gildas (English pronunciation: , Breton language, Breton: ''Gweltaz''; ) — also known as Gildas Badonicus, Gildas fab Caw (in Middle Welsh texts and antiquarian works) and ''Gildas Sapiens'' (Gildas the Wise) — was a 6th-century Britons (historic), British monk best known for his religious polemic , which recounts the history of the Britons before and during Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, the coming of the Saxons. He is one of the best-documented figures of the Christian church in the British Isles during the Sub-Roman Britain, sub-Roman period, and was renowned for his Biblical knowledge and literary style. In his later life, he emigrated to Brittany, where he founded a monastery known as Saint-Gildas-de-Rhuys. Hagiography Birthplace Differing versions of the ''Life of Saint Gildas'' exist, but both agree that he was born at a place called ''Arecluta'' which is described by the author as taking its name from a "certain river called the Clut, by which that district is, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Excidio Et Conquestu Britanniae
(English: ''On the Ruin and Conquest of Britain'') is a work written in Anglo-Latin literature, Latin in the late fifth or sixth century by the Britons (historical), British religious polemicist Gildas. It is a sermon in three parts condemning the acts of Gildas' contemporaries, both secular and religious, whom he blames for the dire state of affairs in sub-Roman Britain. It is one of the most important sources for the history of Britain in the fifth and sixth centuries, as it is the only significant historical source for the period written by a near contemporary of the people and events described. Part I contains a narrative of British history from the Roman conquest of Britain, Roman conquest to Gildas' time; it includes references to Ambrosius Aurelianus and the Britons' victory against the Saxons at the Battle of Mons Badonicus. Part II is a condemnation of five kings for their various sins, including both obscure figures and relatively well-documented ones such as Maelgwn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
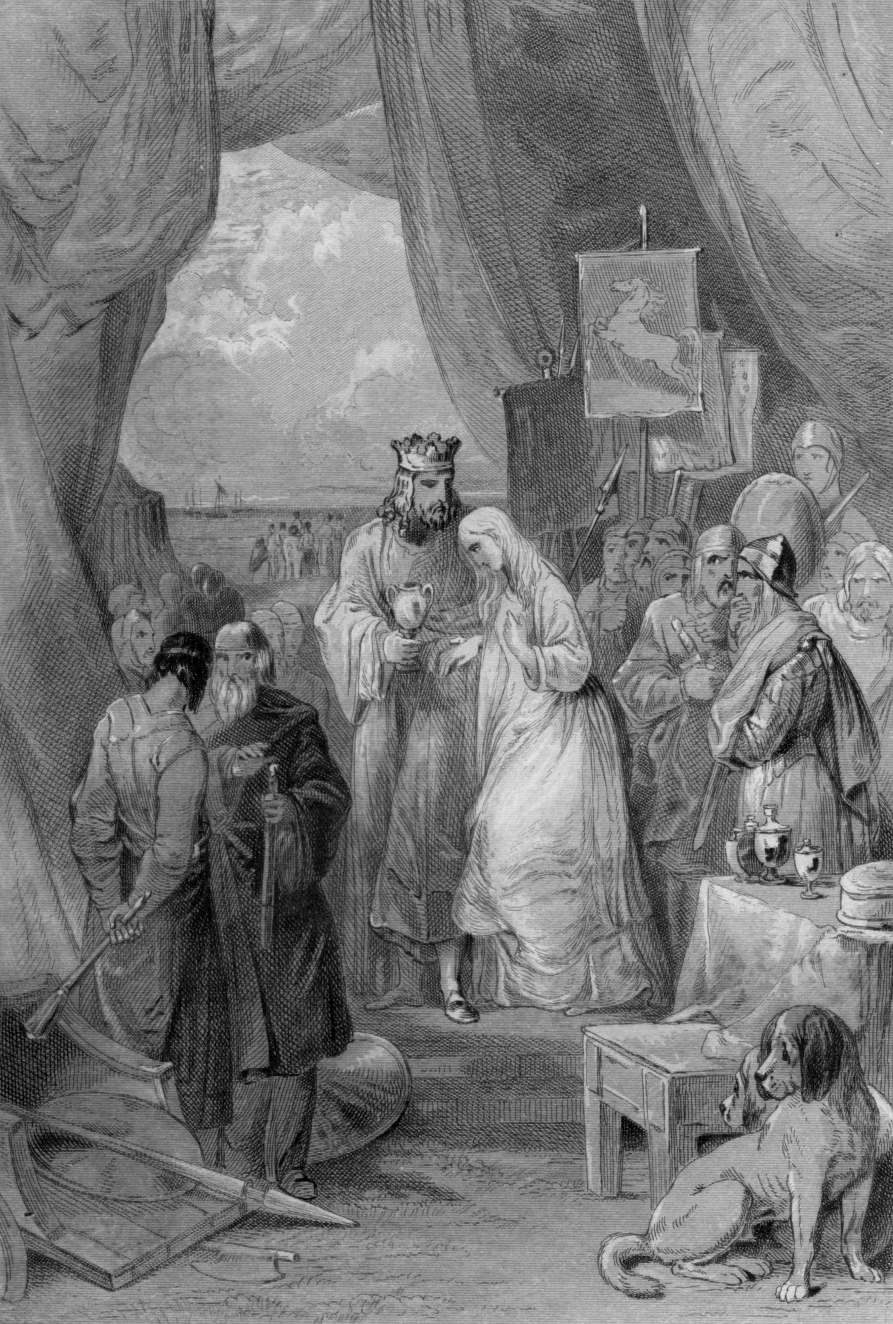
Vortigern
Vortigern (; , ; ; ; Old Breton: ''Gurdiern'', ''Gurthiern''; ; , , , etc.), also spelled Vortiger, Vortigan, Voertigern and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Sub-Roman Britain, Britain, known perhaps as a king of the Britons or at least connoted as such in the writings of Bede and Gildas. His existence is contested by scholars and information about him is obscure. He may have been the "superbus tyrannus" said to have invited Hengist and Horsa to aid him in fighting the Picts and the Scottish people, Scots, whereupon they revolted, killing his son in the process and forming the Kingdom of Kent. It is said that he took refuge in North Wales, and that his grave was in Dyfed or the Llŷn Peninsula. Gildas later denigrated Vortigern for his misjudgement and also blamed him for the loss of Britain. He is cited at the beginning of the genealogy of the early Kingdom of Powys, Kings of Powys. Medieval accounts Gildas The 6th-century cleric and historian Gildas wrote ''De Excidio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Thanet
The Isle of Thanet () is a peninsula forming the easternmost part of Kent, England. While in the past it was separated from the mainland by the Wantsum Channel, it is no longer an island. Archaeological remains testify to its settlement in ancient times. Today, it is a tourist destination, and has an active agricultural base. Etymology The island of Thanet is mentioned as ''Tonetic'' (c. AD 150; the TON- of this form was misread as TOΛI-, hence it appears as ''Toliatis'' in the surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy); ''Tanat's'', ''Athanatos'' and ''Thanatos'' (in various copies of 3rd C AD, Solinus); ''Tanatos'' (AD 731); ''Tenid'' in 679 and ''Tenet'' (e.g. charters of AD 679, 689 and thereafter); and the Old Welsh forms ''Tanet'' and ''Danet'', found in the ''Historia Brittonum'' (c. AD 829/30) and Armes Prydein (c. AD 930). Standard reference works for English place-names (such as Eilert Ekwall's ''Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-Names'') state the name ''Tane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered a secondary (10th-century) tradition. Nennius was a student of Elvodugus, commonly identified with the bishop Elfodd of Bangor who convinced British ecclesiastics to accept the Continental dating for Easter, and who died in 809 according to the '' Annales Cambriae''. Nennius is believed to have lived in the area made up by Brecknockshire and Radnorshire in present-day Powys, Wales. Thus, he lived outside the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, isolated by mountains in a rural society. Because of the lack of evidence concerning the life of Nennius, he has become the subject of legend himself. Welsh traditions include Nennius with Elbodug and others said to have escaped the massacre of Welsh monks by Ethelfrid in 613, fleeing to the north. Authorsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsgate
Ramsgate is a seaside resort, seaside town and civil parish in the district of Thanet District, Thanet in eastern Kent, England. It was one of the great English seaside towns of the 19th century. In 2021 it had a population of 42,027. Ramsgate's main attraction is its coastline, and its main industries are tourism and fishing. The town has one of the largest marinas on the English south coast, and the Port of Ramsgate provided cross-English Channel, channel ferries for many years. History Ramsgate began as a fishing and farming hamlet. The Christian missionary Augustine of Canterbury, St Augustine, sent by Pope Gregory I, Pope Gregory the Great, landed near Ramsgate in AD 597. The town is home to the Pugin's Church and Shrine of St Augustine, Shrine of St Augustine. The earliest reference to the town is in the Kent Hundred Rolls of 1274–5, both as ''Remmesgate'' (in the local personal name of 'Christina de Remmesgate') and as ''Remisgat'' (with reference to the town). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |