|
Battle Of Seonghwan
The Battle of Seonghwan () was the first major land battle of the First Sino-Japanese War. It took place on 29 July 1894 at the hamlet of Seonghwan, outside of Cheonan, Chungcheongnam-do Korea between the forces of Meiji Japan and Qing China. It is also referred to as the Battle of Asan (Japanese: 牙山作戦 ). Background Following the capture of the Royal Palace at Seoul and disarmament of the Korean troops, the Japanese began preparations for an attack against Chinese forces camped at Asan. On 25 July, charged with implementing the Imperial Japanese Army's commission from new Korean government to expel the Chinese Beiyang Army from Korean territory by force, a detachment of the Japanese First Army consisting of 4,000 men and four artillery pieces under command of Major General Ōshima Yoshimasa marched south from Seoul towards the major port city of Asan. The Chinese forces stationed near Seonghwan numbered about 3,880 men under General Ye Zhichao, and had anticipated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
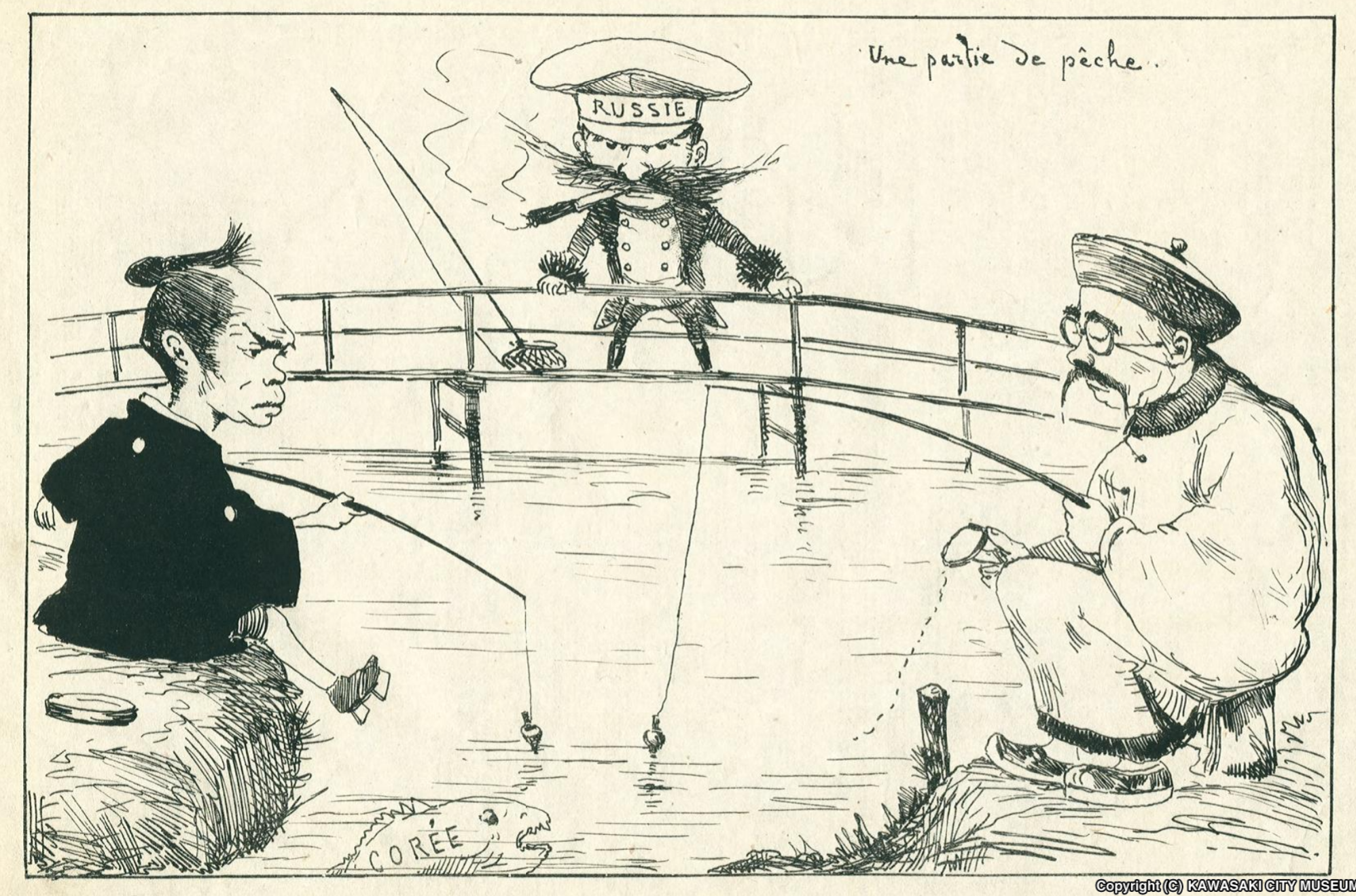
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as the Jiawu War. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ports of Lüshunkou (Port Arthur) and Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895 and signed the Unequal treaties, unequal Treaty of Shimonoseki two months later, ending the war. In the late 19th century, Korea remained one of China's tributary states, while Japan viewed it as a target of imperial expansion. In June 1894, the Qing government, at the request of the Korean emperor Gojong of Korea, Gojong, sent 2,800 troops to aid in suppressing the Donghak Peasant Revolution. The Japanese considered this a violation of the 1885 Convention of Tientsin, and sent an expeditionary force of 8,000 troops, which la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abatis
An abatis, abattis, or abbattis is a field fortification consisting of an obstacle formed (in the modern era) of the branches of trees laid in a row, with the sharpened tops directed outwards, towards the enemy. The trees are usually interlaced or tied with wire. Abatis are used alone or in combination with wire entanglements and other obstacles. History Gregory of Tours mentions the use of abatises several times in his writing about the history of the early Franks. He wrote that the Franks ambushed and destroyed a Roman army near Neuss during the reign of Magnus Maximus with the use of an abatis. He also wrote that Mummolus, a general working for Burgundy, successfully used an abatis to defeat a Lombard army near Embrun. Gregory of Tours. A History of the Franks. Pantianos Classics, 1916 A classic use of an abatis was at the Battle of Carillon (1758) during the Seven Years' War. The 3,600 French troops defeated a massive army of 16,000 British and Colonial troops by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1894 In Japan
Events January * January 4 – A military alliance is established between the French Third Republic and the Russian Empire. * January 7 – William Kennedy Dickson receives a patent for motion picture film in the United States. * January 9 – New England Telephone and Telegraph installs the first battery-operated telephone switchboard, in Lexington, Massachusetts. February * February 12 – French anarchist Émile Henry sets off a bomb in a Paris café, killing one person and wounding twenty. * February 15 ** In Korea, peasant unrest erupts in the Donghak Peasant Revolution, a massive revolt of followers of the Donghak movement. Both China and Japan send military forces, claiming to come to the ruling Joseon dynasty government's aid. ** French anarchist Martial Bourdin dies of an accidental detonation of his own bomb, next to the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. March * March 1 – The Local Government Act (coming into effect Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of South Chungcheong Province
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The First Sino-Japanese War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1894
Conflict may refer to: Social sciences * Conflict (process), the general pattern of groups dealing with disparate ideas * Conflict continuum from cooperation (low intensity), to contest, to higher intensity (violence and war) * Conflict of interest, involvement in multiple interests which could possibly corrupt the motivation or decision-making * Cultural conflict, a type of conflict that occurs when different cultural values and beliefs clash * Ethnic conflict, a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups * Group conflict, conflict between groups * Intragroup conflict, conflict within groups * Organizational conflict, discord caused by opposition of needs, values, and interests between people working together * Role conflict, incompatible demands placed upon a person such that compliance with both would be difficult * Social conflict, the struggle for agency or power in something * Work–family conflict, incompatible demands between the work and family roles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declaration Of War
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the public signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national government, in order to create a state of war between two or more states. The legality of who is competent to declare war varies between nations and forms of government. In many nations, that power is given to the head of state or sovereign. In other cases, something short of a full declaration of war, such as a letter of marque or a covert operation, may authorise war-like acts by privateers or mercenaries. The official international protocol for declaring war was defined in the Hague Convention (III) of 1907 on the Opening of Hostilities. Since 1945, developments in international law such as the United Nations Charter, which prohibits both the threat and the use of force in international conflicts, have made declarations of war large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons were developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armour. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannon, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to Shell (projectile), shell-firing Field gun, guns, howitzers, and Mortar (weapon), mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, Screening (tactical), screening, and skirmisher, skirmishing, or as heavy cavalry for decisive economy of force and shock attacks. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as a cavalryman, Equestrianism, horseman, trooper (rank), trooper, cataphract, knight, Drabant Corps of Charles XII, drabant, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, samurai or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any Military animal, military forces that used other animals or platforms for mounts, such as chariots, Camel cavalry, camels or War elephant, elephants. Infantry who m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics behind military tactics. Modern military engineering differs from civil engineering. In the 20th and 21st centuries, military engineering also includes CBRN defense and other engineering disciplines such as mechanical and electrical engineering techniques. According to NATO, "military engineering is that engineer activity undertaken, regardless of component or service, to shape the physical operating environment. Military engineering incorporates support to maneuver and to the force as a whole, including military engineering functions such as engineer support to force protection, counter improvised explosive devices, environmental protection, engineer intelligence and military search. Military engineering does not encompass the activities u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |