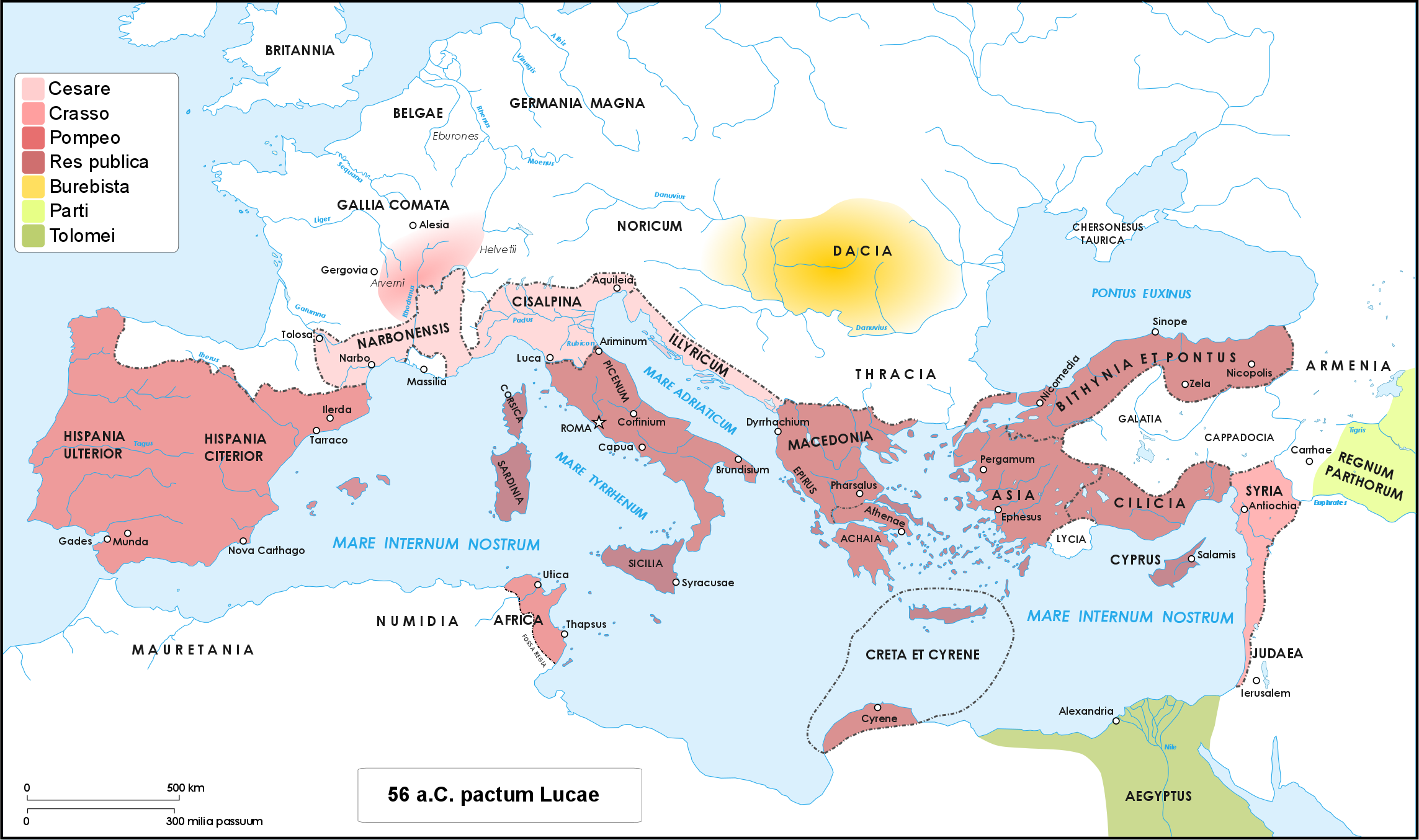
|
Battle Of Nicopolis (48 BC)
The Battle of Nicopolis was fought in December 48 BC between the army of Pharnaces II of Pontus, the son of Mithdridates VI Eupator, and a Roman army led by Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus. Prelude After defeating Pompey and the optimates at Pharsalus, Julius Caesar pursued his opponents to Anatolia and then to Egypt. In the Roman province of Asia, he left Calvinus in command with an army including the 36th Legion, mainly made up of veterans from Pompey's disbanded legions. With Caesar preoccupied in Egypt and the Roman Republic in the midst of a civil war, Pharnaces saw an opportunity to expand his Kingdom of the Bosphorus into his father's old Pontic empire. In 48 BC he invaded Cappadocia, Bithynia, and Armenia Parva. Calvinus concentrated his forces at Comana. These forces consisted of the veteran 36th legion, one recently levied legion of raw recruits (recruited from locals, not Romans), two legions of Galatians (armed, trained, and organized in the Roman style by King Deiotarus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Alexandrino
''De Bello Alexandrino'' (also ''Bellum Alexandrinum''; ''On the Alexandrine War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's commentaries, '' De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili''. It details Caesar's campaigns in Alexandria and Asia. Authorship De Bello Alexandrino is followed by '' De Bello Africo'' and '' De Bello Hispaniensi''. These three works end the Caesarean corpus relating Caesar's Civil War. Though normally collected and bound with Caesar's authentic writings, their authorship has been debated since antiquity. Suetonius suggests both Oppius and Hirtius as possible authors of De Bello Alexandrino. Alfred Klotz (1910) demonstrated in great detail that the style of De Bello Alexandrino is very similar to the style of the eighth and last book of '' De Bello Gallico'', which is very commonly attributed to Hirtius. Thus it seems likely on stylistic grounds that if it was Hirtius who completed the Gallic Wars, it was Hirtius also who wrote De Bello Alexandrino. Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zela
The Battle of Zela was fought in 47 BC between Julius Caesar and Pharnaces II of the Kingdom of Pontus. The battle took place near Zela (modern Zile), which is now a small hilltop town in the Tokat province of northern Turkey. The battle ended the ambitions of king Pharnaces who wanted to expand his rule over Asia Minor. Following his swift victory, Caesar famously declared, ' ("I came, I saw, I conquered"), emphasizing the speed and decisiveness of his triumph. Prelude After the defeat of the Ptolemaic forces at the Battle of the Nile, Caesar left Egypt and travelled through Syria, Cilicia, and Cappadocia to fight Pharnaces, son of Mithridates VI. Pharnaces had defeated Caesar's Legate Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus, and his small Roman and allied army at the Battle of Nicopolis. He then committed atrocities against the Roman prisoners and against any Roman civilians he found in the region. When Pharnaces received word of Caesar's approach, he sent envoys to seek peace, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asander (Bosporan King)
Asander, named Philocaesar Philoromaios (, – 17 BC) was a Roman client king of the Bosporan Kingdom. He was of Greek and possibly of Persian ancestry. Not much is known of his family and early life. He started his career as a general under Pharnaces II, the king of the Bosporus. According to some scholars, Asander took as his first wife a woman called Glykareia, known from one surviving Greek inscription, "Glykareia, wife of Asander". Revolt against Pharnaces II By 47 BC, Asander had married Dynamis, the daughter of Pharnaces II by a Sarmatian wife, as his second wife. She was a granddaughter of King Mithridates VI of Pontus by his first wife, his sister Laodice. In 47 BC, Pharnaces II put Asander in charge of the Bosporan Kingdom while he went with an army to invade the eastern parts of Anatolia. Following a successful campaign, Pharnaces advanced towards the western parts of Anatolia. However, he had to stop because Asander revolted against him. Asander hoped that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Infantry Tactics
Roman infantry tactics are the theoretical and historical deployment, formation, and manoeuvres of the Roman infantry from the start of the Roman Republic to the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The original Roman army was made up of ''hoplite, hoplites'', whose main strategy was forming into a ''phalanx''. By the early third century BCE, the Roman army would switch to the Maniple (military unit), maniple system, which would divide the Roman army into three units, ''hastati'', ''principes'', and ''triarii''. Later, in 107BCE, Gaius Marius, Marius would institute the so-called Marian reforms, creating the Roman legions. This system would evolve into the Late Roman army, Late Roman Army, which utilized the ''comitatenses'' and ''limitanei'' units to defend the Roman Empire, Empire. Roman legionaries had armour, a ''gladius'', a shield, two ''Pilum, pila'', and Rationing, food rations. They carried around tools such as a ''dolabra'', a wooden Stave (wood), stave, and a shallow wicke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye and Hatay. Name The name of Cilicia () was derived from (), which was the name used by the Neo-Assyrian Empire to designate the western part of what would become Cilicia. The English spelling is the same as the Latin, as it was transliterated directly from the Greek form Κιλικία. The palatalization of c occurring in Western Europe in later Vulgar Latin () accounts for its modern pronunciation in English. Geography Cilicia extends along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separate it from Syria. North and east of Cilicia stand the rugged Taurus Mountains, which separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, and which are pierced by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deiotarus
Deiotarus of Galatia (in Galatian and Greek Deiotaros, surnamed Philoromaios ("Friend of the Romans"); 42 BC, 41 BC or 40 BC) was a Chief Tetrarch of the Tolistobogii in western Galatia, Asia Minor, and a King of Galatia ("Gallo-Graecia"). He was considered one of the most adept of Celtic kings, ruling the three tribes of Celtic Galatia from his fortress in Blucium. The name Deiotarus is generally translated as Galatian Celtic "Divine-bull" (*''deiuo-tauros''; cf. Old Irish ''dia'', Welsh ''duw'', Old Welsh ''duiu'', "God" and Old Irish ''tarb'', Welsh ''tarw'' "bull", with Western Celtic metathesis of the cluster ''-uro''- to ''-ruo-''). Biography Deiotarus was a faithful ally of the Romans and became involved in the struggles between the Roman generals that led to the fall of the Republic from 44 BC. He changed sides and supported the triumvirs, keeping his kingdom until his death. He is first heard of at the beginning of the Third Mithridatic War, when he drove the troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatians (people)
The Galatians (; ; ) were a Celts, Celtic people dwelling in Galatia, a region of central Anatolia in modern-day Turkey surrounding Ankara during the Hellenistic period. They spoke the Galatian language, which was closely related to Gaulish language, Gaulish, a contemporary Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in Gaul. The Galatians were descended from Celts who had Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe#Invasions of Thrace and Greece, invaded Greece in the 3rd century BC. The original settlers of Galatia came through Thrace under the leadership of Leogarios and Leonnorius, Leonnorios c. 278 BC. They consisted mainly of three Gaulish tribes, the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii, but there were also other minor tribes. In 25 BC, Galatia (Roman province), Galatia became a province of the Roman Empire, with Ankara (''Ancyra'') as its capital. In the 1st century AD, many Galatians were Christianized by Paul the Apostle's missionary activities. The ''Epistle to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia (; ; ), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian-populated regions primarily to the west and northwest of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (also known as Kingdom of Greater Armenia), on the western side of the Euphrates River. It was also a kingdom, separate from Greater Armenia, from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century AD. The region was later reorganized into the Armeniac Theme under the Byzantine Empire. Geography Lesser Armenia (or Armenia Minor) was the portion of historic Armenia and the Armenian Highlands lying west and northwest of the river Euphrates. It received its name to distinguish it from the much larger eastern portion of historic Armenia—Greater Armenia (or Armenia Major). Early history Lesser Armenia corresponded to the location of the Late Bronze Age Hayasa-Azzi confederation, which is thought by some scholars to be the source of the Armenian endonym and the original state of the Proto-Armenians. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bithynia
Bithynia (; ) was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor. Hellenistic Bithynia was an independent kingdom from the 4th century BC. Its capital Nicomedia was rebuilt on the site of ancient Astacus in 264 BC by Nicomedes I of Bithynia. Bithynia was bequeathed to the Roman Republic in 74 BC, and became united with the Pontus region as the province of Bithynia and Pontus. In the 7th century it was incorporated into the Byzantine Opsikion theme. It became a border region to the Seljuk Empire in the 13th century, and was eventually conquered by the Ottoman Turks between 1325 and 1333. Description Several major cities sat on the fertile shores of the Propontis (which is now known as Sea of Marmara): Nicomedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir province. According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revolt (499 BC), the Cappadocians were reported as occupying a region from the Taurus Mountains to the vicinity of the Euxine (Black Sea). Cappadocia, in this sense, was bounded in the south by the chain of mountains that separate it from Cilicia, to the east by the upper Euphrates, to the north by the Pontus, and to the west by Lycaonia and eastern Galatia. Van Dam, R. ''Kingdom of Snow: Roman rule and Greek culture in Cappadocia.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002, p.13 The name, traditionally used in Christianity, Christian sources throughout history, continues in use as an international tourism concept to define a region of exceptional natural wond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |