|
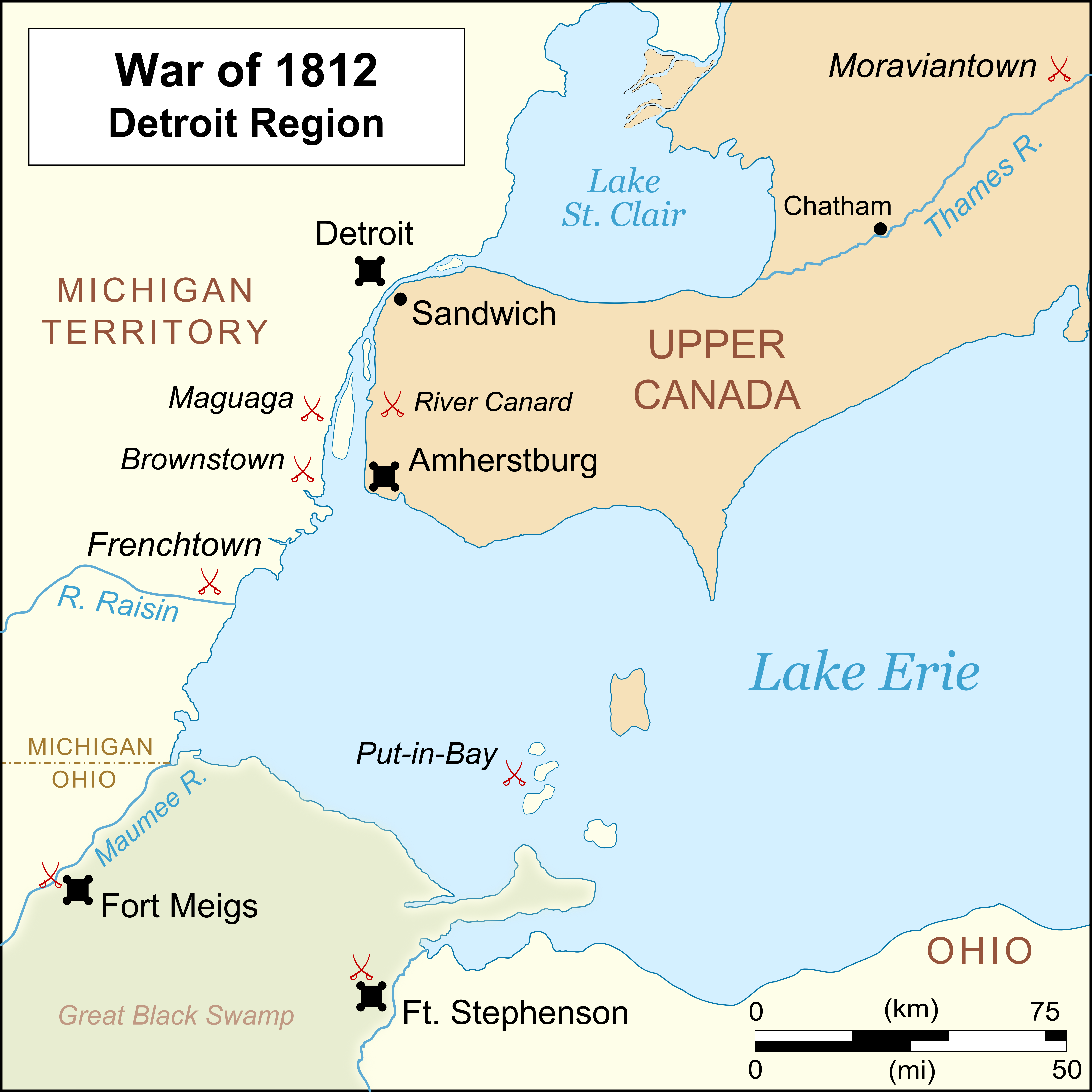
Battle Of Maguaga
The Battle of Maguaga (also known as the Battle of Monguagon or the Battle of the Oakwoods) was a small battle between British troops, Canadian militia and Tecumseh's natives against a larger force of American troops, Ohio Volunteers and Michigan Legion near the Wyandot village of Maguaga which become The Township of Monguagon Township, Michigan in what is now The City of Riverview, Michigan. Background In the early days of the War of 1812, an American army under Brigadier-General William Hull who was also the first Governor of Michigan Territory moved to Detroit, intending to use it as a base for an attack on Upper Canada. Hull's resolution quickly faded. After deciding not to attack the British at Fort Amherstburg, he learned that Mackinac Island had been captured by the British and feared that many Native Americans would flock south from there to join the British. On 3 August, he retreated to American territory. At the Miami Rapids, Captain Henry Brush's company of Ohio Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the United Kingdom, declared war on Britain on 18 June 1812. Although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, the war did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by the 13th United States Congress, United States Congress on 17 February 1815. AngloAmerican tensions stemmed from long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Tecumseh's confederacy, which resisted U.S. colonial settlement in the Old Northwest. In 1807, these tensions escalated after the Royal Navy began enforcing Orders in Council (1807), tighter restrictions on American trade with First French Empire, France and Impressment, impressed sailors who were originally British subjects, even those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Northwest (United States)
The Army of the Northwest was a United States Army formation formed at the outset of the War of 1812 and charged with taking control of the state of Ohio, the Indiana Territory, Michigan Territory and Illinois Territory. The army suffered initial defeats at Detroit and the Battle of Frenchtown, but was ultimately victorious in its objective of securing the Northwest and defeating Tecumseh. William Henry Harrison's successful campaigns while leading the Army of the Northwest are crediting with propelling him to national prominence. Campaigns Prior to the declaration of war in June 1812, Congress expanded the army from 7 regular infantry regiments to 25. The first commander of the Army of the Northwest was William Hull, who led his forces from Toledo to Detroit, building Hull's Trace along the way. Hull surrendered his forces to the British at Detroit in April 1812. By the autumn of 1812, much of the Indiana Territory was controlled by the British. James Winchester was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potawatomi
The Potawatomi (), also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquian family. They are additionally First Nations in Canada. The Potawatomi call themselves ''Neshnabé'', a cognate of the word ''Anishinaabe''. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibwe and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother". Their people are referred to in this context as ''Bodéwadmi'', a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples. In the 19th century, some bands of Potawatomi were pushed to the west by European/American encroachment. In the 1830s the federal government removed most from their lands east of the Mississippi River to Indian Territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AR Miller James
AR, Ar, or A&R may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Artists and repertoire * ''AR'' (EP), the debut EP by Addison Rae Periodicals * ''Absolute Return + Alpha'', a hedge fund publication *''The Adelaide Review'', an Australian arts magazine * ''American Renaissance'' (magazine), a white nationalist magazine and website * ''Architectural Review'', a British architectural journal * '' Armeerundschau'', a magazine of the East German army Other media * Ar, city on the fictional planet Gor * A.r. group, an avant-garde art group * Alternate reality (other), various fictional concepts Business * Accounts receivable, abbreviated as AR or A/R * Acoustic Research, an American audio electronics manufacturer * Aerojet Rocketdyne, an American aerospace and defense manufacturer * Aerolíneas Argentinas (IATA airline code AR) * AtkinsRéalis, Canadian engineering company * Some Alfa Romeo car models, e.g. AR51 * Toyota AR engine Language * ''Ar'', the Latin lette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Richardson (author)
John Richardson (4 October 1796 – 12 May 1852) was a Canadian officer in the British Army who became the first Canadian-born novelist to achieve international recognition. Life Richardson was born at Fort George or in Queenston on the Niagara River in 1796. His mother Madelaine was the daughter of the fur trader John Askin and an Odawa woman Monette. His father, Dr. Robert Richardson, was a surgeon with the Queen's Rangers. As a young boy, Richardson lived for a time with his grandparents in Detroit and later with his parents at Fort Malden, Amherstburg. His step-mother, Marie Archange Barthe, told him of stories about early Detroit and the Siege of Fort Detroit in 1763, which inspired his interest in writing. At age 16, Richardson enlisted in the British 41st Regiment of Foot. During his service with this regiment. he met Chief Tecumseh and Major General Isaac Brock, whom he later wrote about in his novel '' The Canadian Brothers''. While stationed at Fort Malden during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Dequindre
Antoine Dequindre (1781–1843) was a soldier, landowner and shopkeeper in Detroit, Michigan in the first half of the 19th century. He is best known for heroism at the Battle of Monguagon during the War of 1812, when he was serving as a captain in the Michigan Legion. Dequindre Road, which runs through Detroit as well as Oakland and Macomb counties, is named for him. Dequindre was born in Detroit. He served as an apprentice and clerk, and in 1810 opened his own store in the city. When war broke out with Great Britain in 1812, Dequindre raised a company of riflemen, which joined the Michigan Legion. During the Battle of Monguagon, Dequindre's company was the first to attack and enter the British breastworks, and his men later sank a British gunboat with a cannon mounted on shore. For his conduct, he was tendered a commission as major in the U.S. Army. He declined the position but was thereafter known as Major Dequindre. Dequindre also served as alderman in Detroit. His s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskrat French
The Muskrat French (; also known as Mushrat French or Detroit River French Canadien) are a cultural group and dialect found primarily in southeastern Michigan along the Detroit River and Lake St. Clair, the western and southern shores of Lake Erie from Monroe County, Michigan to Sandusky, Ohio, and in southwestern Ontario. This unique subculture is characterized by its historical roots in the French Canadian fur trade, its distinctive culinary traditions, and a regional French dialect. The name "Muskrat French" derives from the tradition of eating muskrat, particularly during Lent, a practice tied to a historical Catholic dispensation. History and Origins Early French Settlement and the Fur Trade The Muskrat French trace their origins to the early French settlers, habitants, voyageurs, and coureurs des bois who arrived in the Detroit River region in the late 17th and early 18th centuries as part of New France’s expansion. Detroit, founded in 1701 by Antoine de la Mothe Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Brownstown
The Battle of Brownstown was an early skirmish in the War of 1812. Although the United States military outnumbered the forces of Tecumseh's Confederacy 8 to 1, they lost the battle and suffered substantial losses while Tecumseh's forces were almost completely untouched. The battle occurred near Brownstown, a Wyandot village south of Fort Detroit on Brownstown creek. Brownstown was also known as "Sindathon's Village". Carlson High School in Gibraltar, Michigan, is near the site of the battle. Background Assisted by the British, the Mingo, Wyandotte, Miami, Delaware, Shawnee, Kickapoo, Sauk, Ottawa, Ojibwe, Potawatomi, Mohawk and Chickamauga joined an alliance in 1783 against the United States of America. The alliance was originally formed at the Sandusky villages of the Wyandot, but after those villages were destroyed, the council fire was moved to Brownstown. Walk-in-the-Water and seven other Wyandot chiefs petitioned the U.S. on February 5, 1812, and obtained a 50-ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead (Wyandot)
Roundhead (''c.'' 1760 – 1813), also known as Bark Carrier, Round Head, Stayeghtha, and Stiahta, was an American Indian chief of the Wyandot tribe. He was a strong member of Tecumseh's confederacy against the United States during the War of 1812. He died of unknown natural causes about a month or two before Tecumseh was killed at the Battle of the Thames. Early life Roundhead was born around 1760 near the Sandusky River in New France (the present-day state of Ohio). However, some sources indicate that he was born later in 1763. He rose to become chief of the Wyandot in the Sandusky area. He later moved to Brownstown and joined Tecumseh's anti-American cause. Little is known about Roundhead's life prior to 1794, when he led the Wyandots at the Battle of Fallen Timbers (as a war chief under Tarhe), but this was during a time when various Wyandot clans feuded over their relations with the United States. Chief Roundhead participated in the Treaty of Greenville in 1795, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Muir (army Officer)
Major Adam Charles Muir (1770 – 11 May 1829) was an officer in the British Army, who played a significant but little-known role in the Anglo-American War of 1812. Early life Muir was born in Scotland. The date is not definitely known; it may have been 1766 or 1770. Military career Early service, promotions He enlisted as a private soldier in the 41st Regiment of Foot in 1778. He was evidently well-educated and very quickly rose through the ranks, becoming a Sergeant in only five months and later Sergeant-Major, and being commissioned as an Adjutant in 1793. He became an Ensign shortly afterwards, and was promoted to lieutenant the next year. He served with the regiment in the West Indies. Arrival in Canada, marriage, further promotion In 1799, the regiment was posted to Canada. In 1801, Muir married Mary Elizabeth Alexowina Bender in Montreal. The couple would eventually have ten children. Muir was promoted to captain in 1804. In 1811, the regiment, noted by Major-Genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mackinac Island (1812)
The siege of Fort Mackinac was one of the first engagements of the War of 1812. A British and Native American force captured the island soon after the outbreak of war between Britain and the United States. Encouraged by the easy British victory, more Native Americans rallied to their support. Their cooperation was an important factor in several British victories during the remainder of the war. Background Mackinac Island was a U.S. fur trading post in the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Michigan and Lake Huron. Since the mid-seventeenth century, it had been important for its influence and control over the Native tribes in the area. British and Canadian traders had resented the island being ceded to the United States at the end of the American Revolutionary War.Elting, p.29 The United States Army maintained a small fort, named Fort Mackinac, on the island. The fur trade was the most important part of the economy of the large area known as the Northwest. Each spring, large nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Amherstburg
Fort Amherstburg was built by the Royal Canadian Volunteers at the mouth of the Detroit River to replace Fort Detroit, which Britain was required to cede to the United States of America in 1796 as a result of the Jay Treaty. Built in the years before the War of 1812, Fort Amherstburg included "King's Navy Yard" for shipbuilding on the upper Great Lakes (Lakes Erie, Huron, and Superior). The War of 1812 began and escalated quickly with US General William Hull invading Canada in July 1812. Soldiers from the fort repelled the Americans at River Canard. After General Hull retreated back to Fort Detroit, British General Isaac Brock and the Shawnee Chief Tecumseh met at Fort Amherstburg to plan the attack of Fort Detroit in the British Indian Department building located outside of the fort grounds. After losing the Battle of Lake Erie (including the flagship , which was built at the nearby Navy Yard Park), the British/Canadians destroyed the fort and retreated as most of the cann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |