|
Battle Of Kafr El Dawwar
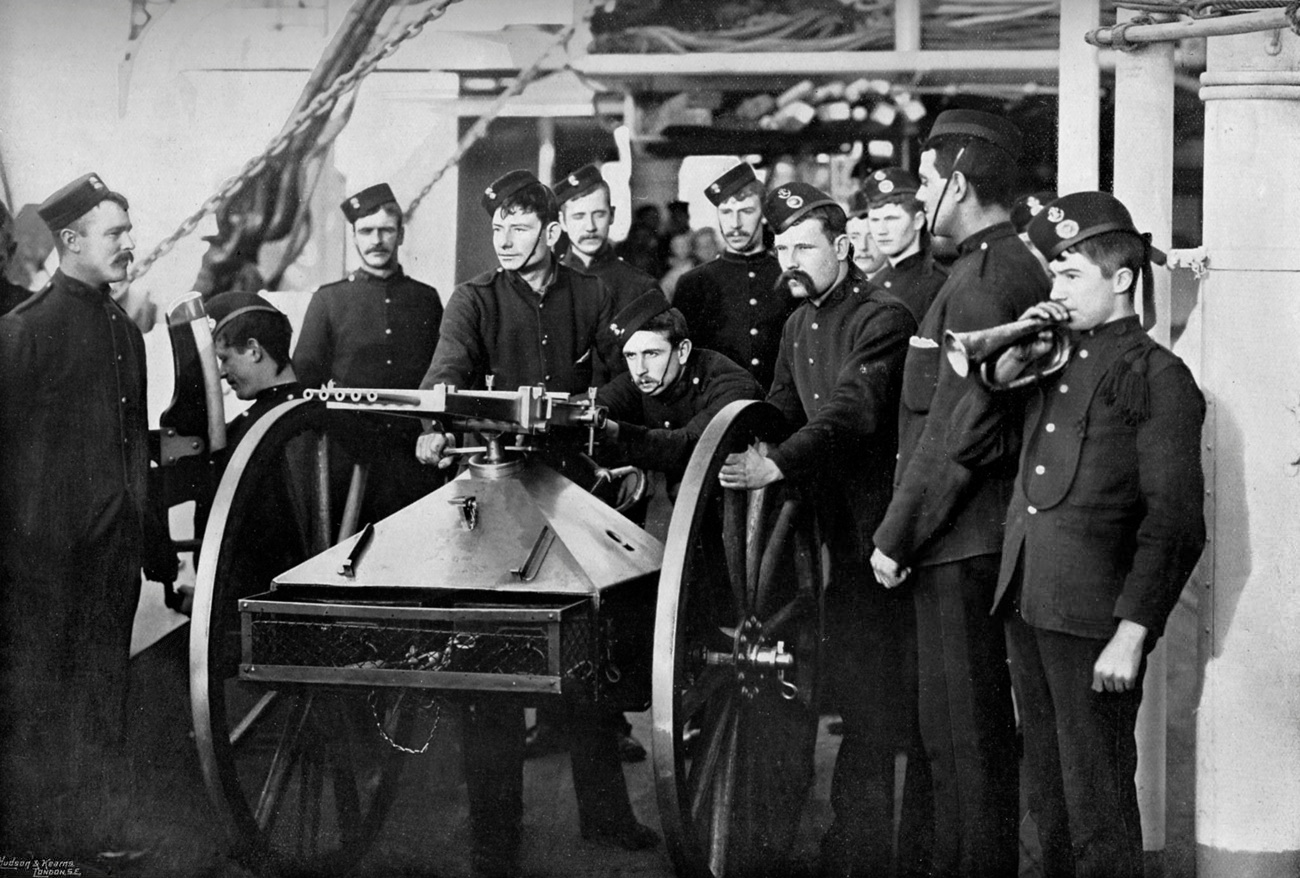
The Battle of Kafr El Dawwar was a conflict during the Anglo-Egyptian War near Kafr El Dawwar, Egypt. The battle took place between an Egyptian army, headed by Ahmed ‘Urabi, and British forces headed by Sir Archibald Alison. As a result, the British abandoned any hope they may have had of reaching Cairo from the north, and shifted their base of operations to Ismailia instead. Prelude After the bombardment of Alexandria on 11 July, the city was occupied by a mixed force of sailors and marines. The Egyptians withdrew to Kafr El Dawwar, where they began the construction of an entrenched camp which would block the route to Cairo. ‘Urabi demanded that one-sixth of the male population of every province should be sent to Kafr El Dawwar. All old soldiers of every description were called upon to serve again, and horses and provisions were everywhere requisitioned for the army. On 17 July, Sir Archibald Alison landed in Alexandria with the leading elements of the British expeditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1882 Anglo-Egyptian War
The British conquest of Egypt, also known as the Anglo-Egyptian War (), occurred in 1882 between Egyptian and Sudanese forces under Ahmed ‘Urabi and the United Kingdom. It ended a nationalist uprising against the Khedive Tewfik Pasha. It established firm British influence over Egypt at the expense of the Egyptians, the French, and the Ottoman Empire, whose already weak authority became nominal. Background In 1881, an Egyptian army officer, Ahmed ‘Urabi (then known in English as Arabi Pasha), mutinied and initiated a coup against Tewfik Pasha, the Khedive of Egypt and Sudan, in order to end Imperial British and French influence over the country. In January 1882 the British and French governments sent a "Joint Note" to the Egyptian government, declaring their recognition of the Khedive's authority. On 20 May, British and French warships arrived off the coast of Alexandria. On 11 June, an anti-Christian riot occurred in Alexandria that killed 50 Europeans. Colonel ‘U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
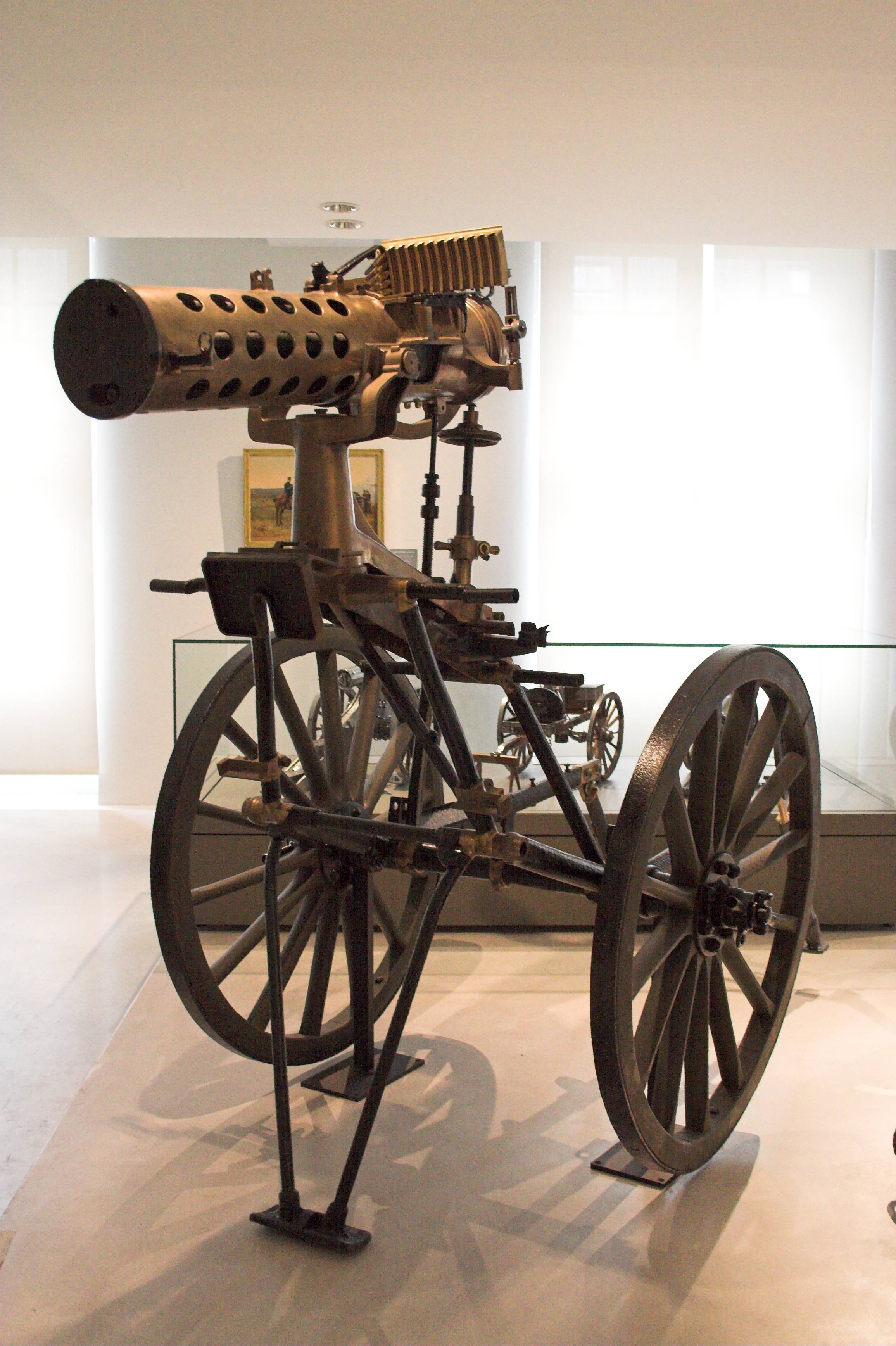
Gatling Gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling of North Carolina. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon. The Gatling gun's operation centered on a cyclic multi-barrel design which facilitated cooling and synchronized the firing-reloading sequence. As the handwheel is cranked, the barrels rotate, and each barrel sequentially loads a single cartridge (firearms), cartridge from a top-mounted magazine (firearms), magazine, fires off the shot when it reaches a set position (usually at clock position, 4 o'clock), then ejects the spent casing out of the left side at the bottom, after which the barrel is empty and allowed to cool until rotated back to the top position and gravity-fed another new round. This configuration eliminated the need for a single reciprocating motion, reciprocating bolt (firearms), bolt design and allowed higher rates of fire to be achieved without the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (British Army And Royal Marines)
Captain (Capt) is a junior officer rank of the British Army and Royal Marines and in both services it ranks above Lieutenant (British Army and Royal Marines), lieutenant and below Major (United Kingdom), major with a NATO ranking code of OF-2. The rank is equivalent to a Lieutenant (British Army and Royal Marines), lieutenant in the Royal Navy and to a flight lieutenant in the Royal Air Force. The rank of Captain (Royal Navy), captain in the Royal Navy is considerably more senior (equivalent to the Army/RM rank of colonel) and the two ranks should not be confused. In the 21st-century British Army, captains are often appointed to be second-in-command (2IC) of a Company (military unit), company or equivalent sized unit of up to 120 soldiers. History A rank of second captain existed in the Ordnance at the time of the Battle of Waterloo. From 1 April 1918 to 31 July 1919, the Royal Air Force maintained the junior officer rank of captain. RAF captains had a rank insignia based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several Company (military unit), companies, each typically commanded by a Major (rank), major or a Captain (armed forces), captain. The typical battalion is built from three operational companies, one weapons company and one headquarters company. In some countries, battalions are exclusively infantry, while in others battalions are unit-level organizations. The word ''battalion'' has its origins in the Late Latin word ''battalion'', which is derived from ''battalia'', meaning "battle" or "combat." The term was used to describe a large group of soldiers ready for battle. Over time, its meaning evolved in military terminology. The word "battalion" came into the English language in the 16th century from the French language, French , meaning "battle squadron" (similar to the Italian language, Italian meaning the same thing) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordenfelt Gun
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different calibres up to . Larger calibres were also used, but for these calibres the design simply permitted rapid manual loading rather than true automatic fire. This article covers the anti-personnel rifle-calibre (typically ) gun. Development The weapon was designed by a Swedish engineer, Helge Palmcrantz. He created a mechanism to load and fire a multiple barreled gun by simply moving a single lever backwards and forwards. It was patented in 1873. Production of the weapon was funded by a Swedish steel producer and banker (later weapons maker) named Thorsten Nordenfelt, who was working in London. The name of the weapon was changed to the Nordenfelt gun. A plant producing the weapon was set up in England with sales offices in London and lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher
Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet John Arbuthnot Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, (25 January 1841 – 10 July 1920), commonly known as Jacky or Jackie Fisher, was a British Admiral of the Fleet. His efforts to reform the Royal Navy helped to usher in an era of modernisation which saw the supersession of wooden sailing ships armed with muzzleloader, muzzle-loading cannon by steel-hulled battlecruisers, submarines and the first aircraft carriers. Fisher has a reputation as an innovator, strategist and developer of the navy rather than as a seagoing admiral involved in major battles, although in his career he experienced all these things. When appointed First Sea Lord in 1904 he removed from active service 150 ships which were no longer useful and set about constructing modern replacements, developing a modern fleet prepared to meet German Empire, Germany during the First World War. Fisher saw the need to improve the range, accuracy and rate-of-fire of naval gunne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
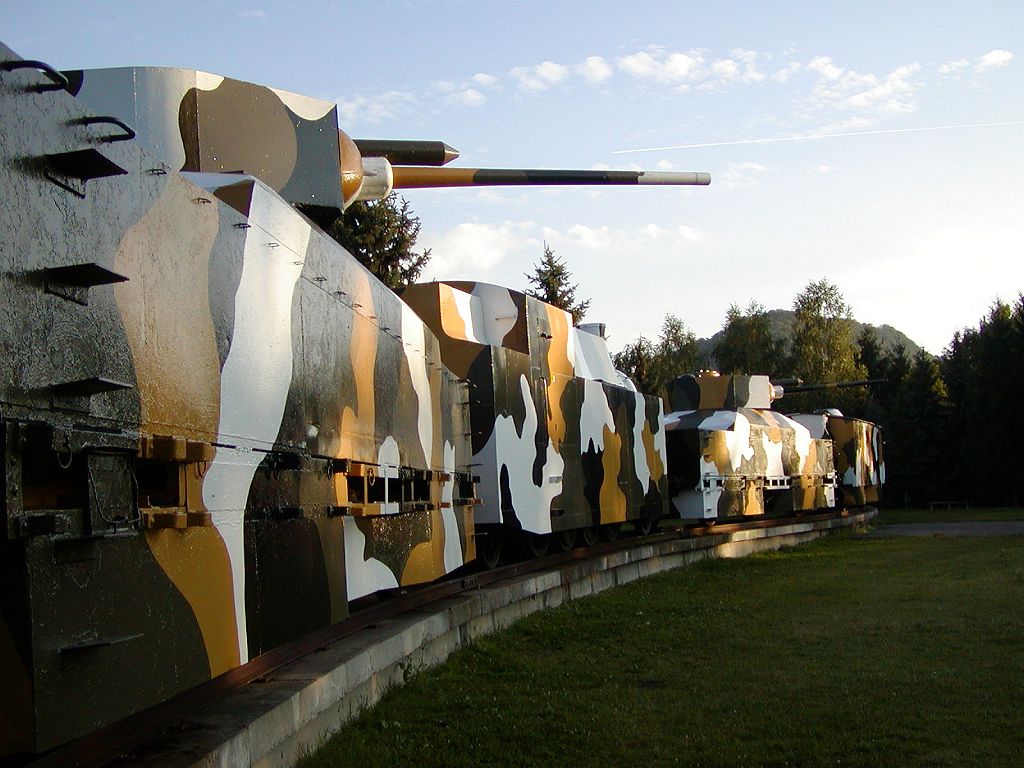
Armoured Train
An armoured train (Commonwealth English) or armored train (American English) is a railway train protected with heavy metal plating and which often includes railway wagons armed with artillery, machine guns, and autocannons. Some have also had ports used to fire small arms from the inside of the train, especially in earlier armoured trains. For the most part, they were used during the late 19th and the early 20th centuries, when they offered an innovative way to quickly move large amounts of firepower into a new location. Most countries have discontinued their use since road vehicles became much more powerful and offered more flexibility, train tracks proved too vulnerable to sabotage and attacks from the air, and air transportation was an even more flexible way to relocate firepower to a new location. However, there have been occasional uses in the late 20th century and early 21st century. Russia has used improvised armoured trains during the Second Chechen War (1999–2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounted Infantry
Mounted infantry were infantry who rode horses instead of marching. Unlike cavalry, mounted infantry dismounted to fight on foot. The original dragoons were essentially mounted infantry. According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition'' (1910–1911), "Mounted rifles are half cavalry, mounted infantry merely specially mobile infantry." Today, with motor vehicles having replaced horses for military transport, the motorized infantry are in some respects successors to mounted infantry. History Pre-gunpowder The origins of mounted infantry go back to at least the beginnings of organised warfare. With the weight of ancient bronze Body armor, armor, the opposing Champion warfare, champions would travel to battle on chariots before dismounting to fight. With the evolution of hoplite warfare, some hoplites would travel to battle on horseback, before dismounting to take their place in the phalanx. The early pre-Gaius Marius, Marian Military of ancient Rome, Roman military had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company (military Unit)
A company is a Military organization#Commands, formations, and units, military unit, typically consisting of 100–250 soldiers and usually commanded by a Major (rank), major or a Captain (armed forces), captain. Most companies are made up of three to seven platoons, although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure. Usually several companies are grouped as a battalion or regiment, the latter of which is sometimes formed by several battalions. Occasionally, ''independent'' or ''separate'' companies are organized for special purposes, such as the Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company, 1st Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company or the 3rd Force Reconnaissance Company. These companies are not organic to a battalion or regiment, but rather report directly to a higher level organization such as a Marine Expeditionary Force headquarters (i.e., a corps-level command). Historical background The modern military company became popularized during the reorganization of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Troop Train In Egypt 1882 Cropped
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
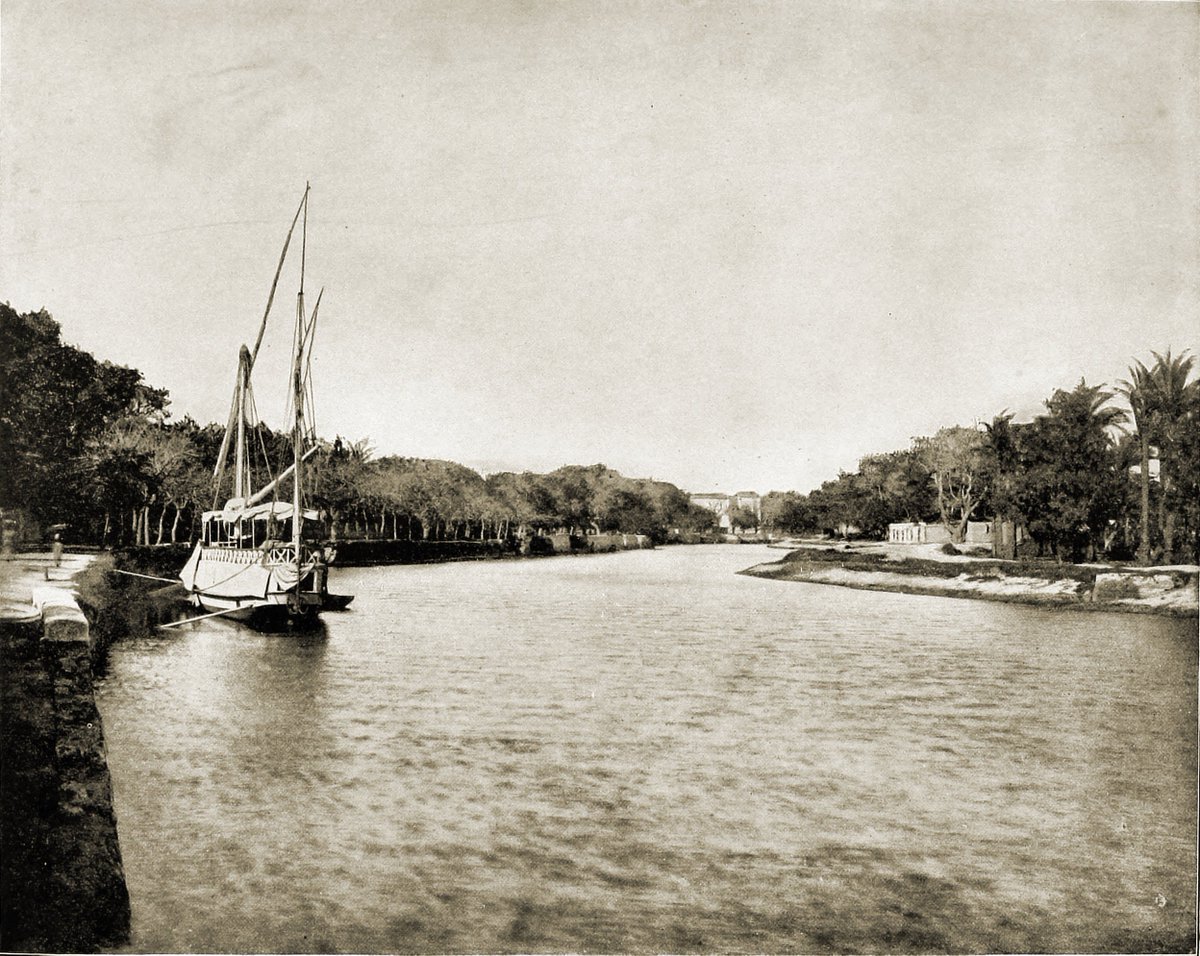
Mahmoudiyah Canal
Maḥmūdiyya Canal ( ''Agathos Daimon'' or ''Megas potamos'') is a sub-canal from the Nile River which starts at the Nile-port of Mahmoudia and goes through Alexandria to the Mediterranean Sea. It was built to supply Alexandria with food and fresh water from the Nile. History Prior to 1817 The first freshwater canal from the Nile to Alexandria was built under the rule of Ptolemy I. Ibn Batuta (1304–1369), the Moroccan traveller, in his " Rihla: My Travels", discusses passing through Alexandria in 1326 and references a canal from Alexandria to The Nile that was finished a few years before his arrival. This might contradict with Wali Muhammad Ali building it almost four centuries later. However, regarding the geographic location and the fact that this part of the land, which has been reclaimed not a long time ago, was plain desert then, the canal might have been covered in sand sometime before it was re-established, not necessarily following the same route, by Muhammed Ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Country Around Alexandria
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |