|
Battle Of Iquique
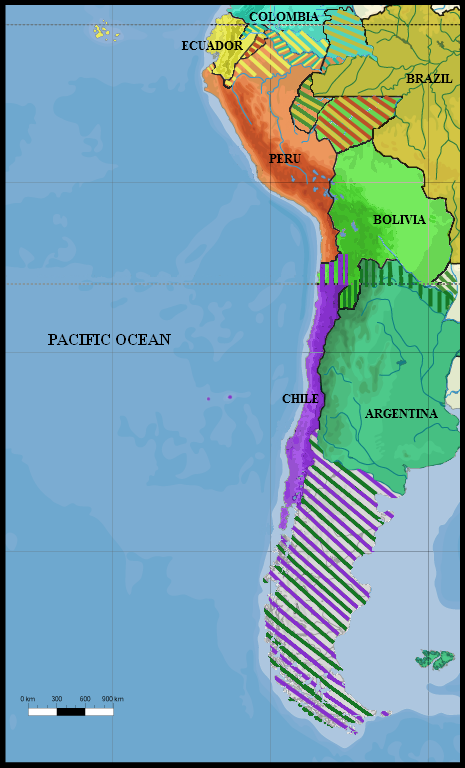
The Battle of Iquique was a Naval warfare, naval engagement on 21 May 1879, during the War of the Pacific, where a Chile, Chilean corvette commanded by Arturo Prat, Arturo Prat Chacón faced a Peru, Peruvian Ironclad warship, ironclad under Miguel Grau Seminario. The battle occurred off the port of Iquique, Peru, and ended with the sinking of the Chilean wooden corvette by the Peruvian ironclad after four hours of combat, marking a victory for Peru. Background In 1879, the Bolivia, Bolivian government threatened to confiscate and sell the Antofagasta Nitrate & Railway Company, a mining enterprise with Chilean and British Empire, British investors. In response, the Chilean government sent a small military force to seize control of the port of Antofagasta on February 14. This action prompted Bolivian President Hilarión Daza to Declaration of war, declare war on Chile and forced Peru to honor a secret 1873 treaty with Bolivia. Despite Peru's attempts to negotiate and prevent co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Pacific
The War of the Pacific (), also known by War of the Pacific#Etymology, multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Treaty of Defensive Alliance (Bolivia–Peru), Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Atacama Desert border dispute, Chilean claims on Litoral Department, coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. The direct cause of the war was a nitrate taxation dispute between Bolivia and Chile, with Peru being drawn in due to its secret alliance with Bolivia. Some historians have pointed to deeper origins of the war, such as the interest of Chile and Peru in the nitrate business, a long-standing rivalry between Chile and Peru for regional hegemony, as well as the political and economical disparities between the stability of Chile and the volatility of Peru and Bolivia. In February 1878, Bolivia increased taxes on the Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Topáter
The Battle of Topáter, or Battle of Calama, was fought on March 23, 1879, between Chile and Bolivia. It was the first battle of the War of the Pacific. The Chileans were taking possession of the Antofagasta (Litoral) Province, then a part of Bolivia. The few Bolivian troops decided to make a stand in the town of Calama. On their way to occupy Calama, 554 Chilean troops, including cavalry and with two Krupp Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer dur ... rifled guns, were opposed by 135 Bolivian soldiers and civilian residents led by Dr. Ladislao Cabrera, a civilian and a political authority in the region. The Bolivians fought next to the Topáter ford, which runs outside the city. Cabrera dug in at two destroyed bridges; calls to surrender were rejected before and during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Condell
Carlos Arnaldo Condell de la Haza (August 14, 1843, in Valparaíso – November 24, 1887, in Quilpué) was a Chilean naval officer and hero of the Battle of Punta Gruesa during the start of the War of the Pacific. Possessing a great sense of strategy and analysis in battle, he was always underestimated by the contemporary media due to his Peruvian origin (on his mother's side). His victories in unbalanced conditions were decisive to the triumph of Chile in the War of the Pacific. Early years Carlos Condell was born August 14, 1843, in Valparaíso, Chile. His father was the Scottish merchant marine Federico Condell, and his mother was the Peruvian aristocrat Lady Manuela De la Haza. His uncles were Diego and Antonio de la Haza, both rear admirals of the Peruvian Navy. Therefore, he had several cousins who were Peruvian naval officers. Condell did not have familial ties to Chile, and this fact resulted in ostracism and criticism during his life. He was the sixth of ten c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Guillermo More
Juan Guillermo Moore Ruiz (27 February 1833 – 7 June 1880) was a British Peruvian navy officer. He was killed during the Battle of Arica. Biography Moore (sometimes spelled ''More'' in some texts) was born in Lima, the son of John Moore, a Scottish sailor and of Dolores Ruiz, a Peruvian lady. He joined the British Navy as an ensign in 1854. Later he returned to Peru and was commissioned in the Peruvian Navy. He served in the frigates '' Apurímac'', ''Izcuchaca'' and ''Huaraz'', as well as the ''Guise'' and the pontoon ''Iquique''. In 1866, during the Chincha Islands War, he was appointed commander of the corvette '' Unión''. A few months later, Captain Moore took a Peruvian Navy crew to the United States to bring the ironclad Atahualpa to Peru. The monitor sailed from New Orleans, La. in early January 1869 arriving in Peru in June 1870. As a reward, he was appointed as commander of the frigate '' Independencia'' and in 1877, General Commander of the Southern Fleet. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a flag officer rank used by English-speaking navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank is called counter admiral. Rear admiral is usually immediately senior to commodore and immediately below vice admiral. It is usually equivalent to the rank of major general in armies. In the U.S. Navy and some other navies, there are two rear admiral ranks. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the British Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battleship
A battleship is a large, heavily naval armour, armored warship with a main battery consisting of large naval gun, guns, designed to serve as a capital ship. From their advent in the late 1880s, battleships were among the largest and most formidable weapon systems ever built, until they were surpassed by aircraft carriers beginning in the 1940s. The modern battleship traces its origin to the sailing ship of the line, which was developed into the steam ship of the line and soon thereafter the ironclad warship. After a period of extensive experimentation in the 1870s and 1880s, ironclad design was largely standardized by the British , which are usually referred to as the first "pre-dreadnought battleships". These ships carried an armament that usually included four large guns and several medium-caliber guns that were to be used against enemy battleships, and numerous small guns for self-defense. Naval powers around the world built dozens of pre-dreadnoughts in the 1890s and early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huáscar (ironclad)
''Huáscar'' is an ironclad turret ship owned by the Chilean Navy built in 1865 for the Peruvian government. It is named after the 16th-century Inca emperor, Huáscar. She was the flagship of the Peruvian Navy and participated in the Battle of Pacocha and the War of the Pacific of 1879–1883. At the Battle of Angamos, ''Huáscar'', captained by renowned Peruvian naval officer Miguel Grau Seminario, was captured by the Chilean fleet and commissioned into the Chilean Navy. Today ''Huáscar'' is one of the few surviving ships of her type. She has been restored and is a memorial ship anchored in Talcahuano, Chile. ''Huáscar'' is the second oldest armored warship afloat after , and the oldest monitor afloat. Technical details Captain Cowper Coles, wrote of ''Huáscar'': "...as a sea-going vessel of 1,100 tons, 300-horse power, and a speed of 12 1/4 knots. Her foremast is fitted with tripods; she carries two 300-pounders in one turret." And "...the "Huascar" class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship that is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . Subsequent vessels of this type were accordingly classed as "monitors". They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
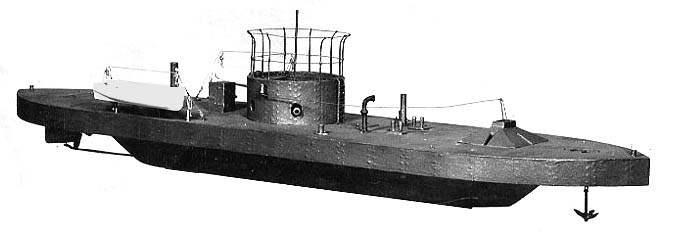
Spanish Schooner Virgen De Covadonga
''Virgen de Covadonga'' (English: ''Virgin of Covadonga''), sometimes referred to as ''Covadonga'', was a Spanish Navy screw schooner commissioned in 1859. During the Chincha Islands War, she was captured by the Chilean Navy in the Battle of Papudo in 1865. Incorporated into the Chilean Navy, she initially was assigned to exploration missions and later to the Chilean Navy squadron that participated in the War of the Pacific (1879–1883). In the Battle of Punta Gruesa she defeated the Peruvian Navy broadside ironclad . She was sunk in 1880. Characteristics ''Virgen de Covadonga'' was a screw schooner with a wooden hull. She displaced 415 tons. She was long, in beam, and in draft. Her steam engine, manufactured by Factory No. 4 at Ferrol, Spain, was rated at a nominal and produced , giving her a maximum speed of under steam, although her boilers performed poorly in operational use. Her armament consisted of two 68-pounder (31 kg) smoothbore guns amidships and a 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a Topgallant sail, topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a Course (sail), fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are Gaff rig, gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. Etymology The term "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The term may be related to a Scots language, Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. History The exact origins of schooner rigged vessels are obscure, but by early 17th century they appear in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The earliest known il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esmeralda (1855)
''Esmeralda'' was a wooden-hulled steam corvette of the Chilean Navy, launched in 1855, and sunk by the Peruvian turret ship on 21 May 1879 at the Battle of Iquique during the War of the Pacific. Ship history Construction Construction of the ship was authorized on 30 June 1852 by President Manuel Montt and the Minister of War and Navy José Francisco Gana. Chilean naval officer Roberto Simpson Winthrop and shipbuilder William Pitcher of Northfleet, England, signed a contract for her construction, at a total cost of £23,000, on 23 October 1854. The ship was laid down in December 1854, and launched on 26 June 1855 under the name ''Esmeralda'', after the frigate captured by Thomas Cochrane during the Chilean War of Independence. Her hull was of wood, and coppered. She was in length overall (excluding the bowsprit), with a beam of and a depth of . Four coal-fired boilers powered two horizontal condensing steam engines rated at , which gave the ship a speed of up to under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callao
Callao () is a Peruvian seaside city and Regions of Peru, region on the Pacific Ocean in the Lima metropolitan area. Callao is Peru's chief seaport and home to its main airport, Jorge Chávez International Airport. Callao municipality consists of the whole Callao region, which is also coterminous with the province of Callao. Founded in 1537 by the Spaniards, the city has a long naval history as one of the main ports in Latin America and the Pacific, as it was one of vital Spanish towns during the Spanish America, colonial era. Historic Centre of Callao, Central Callao is about west of the Historic Center of Lima. History El Callao was founded by Spanish colonists in 1537, just two years after Lima (1535). The origin of its name is unknown; both Amerindian (particularly Yunga language (Peru), Yunga, or Coastal Peruvian) and Spanish sources are credited, but it is certain that it was known by that name since 1550. Other sources point to the similarity with the Portuguese wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |