|
Battle Of Ilipa
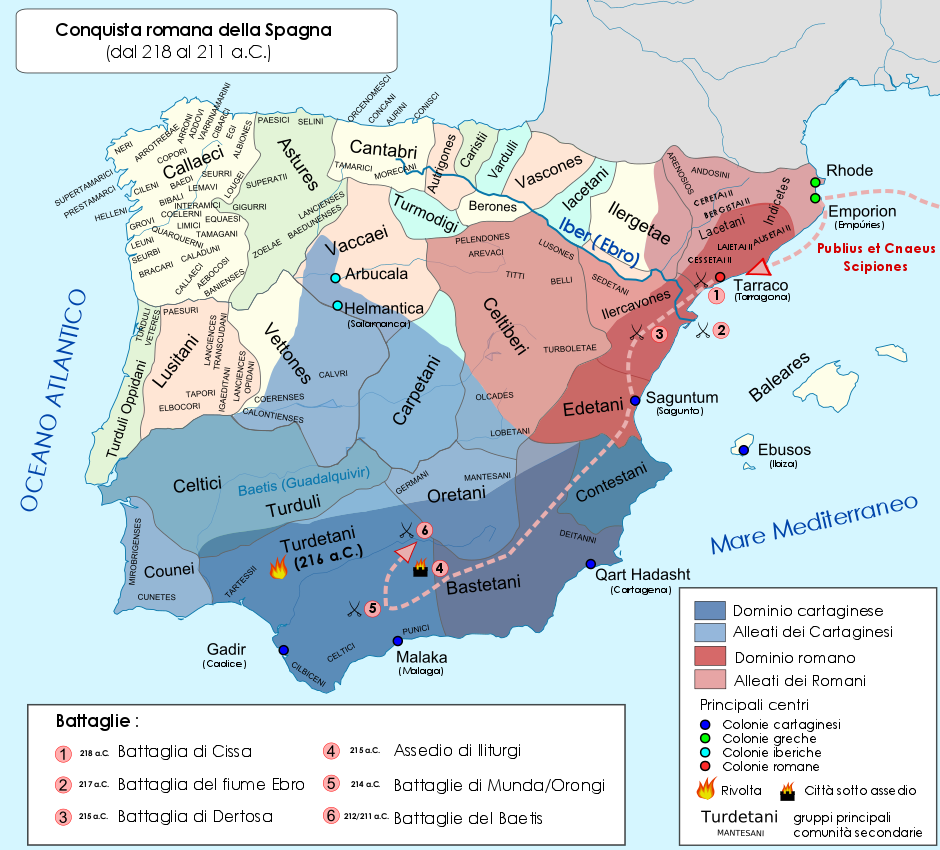
The Battle of Ilipa () was an engagement considered by many as Scipio Africanus’s most brilliant victory in his military career during the Second Punic War in 206 BC. It may have taken place on a plain east of Alcalá del Río, Seville, Spain, near the village of Esquivel, the site of the Carthaginian camp. Though it may not seem to be as original as Hannibal’s tactic at Battle of Cannae, Cannae, Scipio's pre-battle maneuver and his ''reverse Cannae'' formation stands as the acme of his military tactics, tactical ability, in which he permanently broke the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian hold in Iberian Peninsula, Iberia, thus denying any further land invasion into Italy and cutting off a rich base for the Hannibal, Barca dynasty both in silver and manpower. Prelude After the Carthaginian defeat at the Battle of Baecula and Hasdrubal Barca's (Hannibal’s brother) departure for Italy, new reinforcements were sent to Iberia from Carthage at the beginning of 207 BC under the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Roman Italy, Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, Kingdom of Syracuse, Syracuse and several Numidians, Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Celtiberians, Iberian and Gauls, Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main Theater (military), military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal (Barcid), Hasdru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprising most of the region, as well as the tiny adjuncts of Andorra, Gibraltar, and, pursuant to the traditional definition of the Pyrenees as the peninsula's northeastern boundary, a small part of France. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second-largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Etymology The Iberian Peninsula has always been associated with the River Ebro (Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin). The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny the Elder, Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of the peninsula" Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius''; : ''legionarii'') was a citizen soldier of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the Republic and Principate eras, alongside auxiliary and cavalry detachments. At its height, Roman Legionnaires were viewed as the foremost fighting force in the Roman world, with commentators such as Vegetius praising their fighting effectiveness centuries after the classical Roman legionary disappeared. Roman legionnaires were recruited from Roman citizens under age 45. They were first predominantly made up of recruits from Roman Italy, but more were recruited from the provinces as time went on. As legionnaires moved into newly conquered provinces, they helped Romanize the native population and helped integrate the disparate regions of the Roman Empire into one polity. They enlisted in a legion for 25 years of service, a change from the early practice of enlisting only for a campaign. Legionna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legionaries
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizens serving as legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. After the Marian reforms in 107 BC, the legions were formed of 5,200 men and were restructured around 10 cohorts, the first cohort being double strength. This structure persisted throughout the Principate and middle Empire, before further changes in the fourth century resulted in new formations of around 1,000 men. Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 ''equites'' (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republic, to 5,500 in the Imperial period, when most legions were led by a Roman Imperial Legate. A legion had 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) from the late republic to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velites
''Velites'' (; : ) were a class of infantry in the Roman army of the mid-Republic from 211 to 107 BC. ''Velites'' were light infantry and skirmishers armed with javelins (), each with a 75cm (30 inch) wooden shaft the diameter of a finger, with a 25cm (10 inch) narrow metal point, to fling at the enemy. They also carried short thrusting swords, or gladius, ''gladii'', for use in melee. They rarely wore armour as they were the youngest and poorest soldiers in the legion and could not afford much equipment. They did carry small wooden shields called ''Parma (shield), parma'' for protection, and wore headdresses made from wolf skins so their brave deeds could be recognized. The ''velites'' were placed at the front partly for tactical reasons, and also so that they had the opportunity to secure glory for themselves in single combat. ''Velites'' did not form their own units; a number of them were attached to each Maniple (military unit), maniple of ''hastati'', ''principes'' and ''tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberians
The Iberians (, from , ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Miletus, Avienius, Herodotus and Strabo). Roman sources also use the term ''Hispani'' to refer to the Iberians. The term ''Iberian'', as used by the ancient authors, had two distinct meanings. One, more general, referred to all the populations of the Iberian peninsula without regard to ethnic differences ( Pre-Indo-European, Celts and non-Celtic Indo-Europeans). The other, more restricted ethnic sense and the one dealt with in this article, refers to the people living in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, which by the 6th century BC had absorbed cultural influences from the Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Greeks. This pre-Indo-European cultural group spoke the Iberian language from the 7th to at least the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Cavalry
Roman cavalry (Latin: ''equites Romani'') refers to the horse-mounted forces of the Roman army throughout the regal, republican, and imperial eras. In the regal era, the Roman cavalry was a group of 300 soldiers called ''celeres'', tasked with guarding the Kings of Rome. Later their numbers were doubled to 600, then possibly 1,800. All of the cavalrymen were patricians. In the republican era, the general name for the cavalry was equites and these united consisted of the equestrian class and the first class, with a group of 300 cavalrymen in every legion. They were divided into 10 groups of 30 men. Each group elected three leaders known as '' decuriones''. Later the Roman cavalry stopped using Roman citizens as cavalrymen and relied on Auxilia and foreign recruits. Roman cavalrymen wore a Corinthian helmet, bronze chestplate, and bronze greaves. Later mail was adopted into the army. Their arms included a lance ('' lancea''), a long sword ('' spatha''), and a short throwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilipa2
Ilipa (Ancient Greek: ''Ἴλιπα'') or Ilipa Magna was an ancient Iberian city located on the right bank of the River Betis (now known as the Guadalquivir) within one of its meanders. It later became part of the province of Hispania Ulterior and the legal district of Hispalis. Today, its remains can be found in the municipality of Alcalá del Río, in the province of Seville, Spain. Located in the territory of the Turdetani, the city, due to its strategic position and fortified by large walls, controlled the land and river routes that connected with the silver mines of Sierra Morena. Due to its fertile agriculture, it held a significant position in the region. The city was supplied with potable water by an aqueduct that spanned approximately 17 km from the Sierra Norte of Seville. No remains of this aqueduct exist today. Its significance and magnitude earned it the name "Magna," which means "the Great." Second Punic War During the Second Punic War between the Romans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasdrubal Barca
Hasdrubal Barca (245– 22June 207BC), a latinization of names, latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal () son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca. Youth and Iberian leadership Little is known of Hasdrubal's early life. He was present, along with his older brother Hannibal, when his father, Hamilcar Barca, died in battle against the Iberians. Hamilcar may have drowned in the Júcar, although the sources do not agree. Little is also known about Hasdrubal's activities during the time Hasdrubal the Fair led the Punic forces in Spain, or during the campaigns of Hannibal Barca in Spain and his Siege of Saguntum. Hannibal left a force of 13,000 infantry, 2,550 cavalry and 21 war elephants in Hispania when he marched for Italy in 218 BC. Hasdrubal commanded this force and he was to set out for Italy in 217 BC to reinforce Hannibal. Hannibal left another army under Hanno in Catalonia, consisting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Junius Silanus (consul 15)
Marcus Junius C. f. M. n. Silanus (c. 26 BC – AD 37) Barrett (1989), p. 76 was an Ancient Roman senator who became suffect consul in AD 15. Barrett (1989), p. 32 His daughter Junia Claudilla was the first wife of Emperor Caligula. Biography Early life Marcus' father was Gaius Junius Silanus who was the son of Marcus Junius Silanus, the consul of 25 BC. Syme (1986), p.194–195 Marcus had two brothers Decimus Junius Silanus and Gaius Junius Silanus, and a sister named Junia Torquata. Decimus was banished for having an affair with Vipsania Julia during the reign of Augustus. Their mother may have been an Atia, daughter of Marcus Atius Balbus and Claudia. Balbus was the uncle of emperor Augustus. Syme (1986), p. 194 Political career Ancient historians considered Marcus Silanus a highly respected man. When Tiberius came to power, if a judicial decision made by Silanus was appealed to the emperor, Tiberius invariably rejected the appeal, trusting Silanus' decision, and Tiberi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated from neighbouring San Fernando, Cádiz, San Fernando by a narrow isthmus. Cádiz, one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, was founded by the Phoenicians as a trading post.Strabo, ''Geographica'' 3.5.5 In the 18th century, the Port in the Bay of Cádiz consolidated as the main harbour of mainland Spain, enjoying the virtual monopoly of trade with the Americas until 1778. It is also the site of the University of Cádiz. Situated on a narrow slice of land surrounded by the sea‚ Cádiz is, in most respects, a typical Andalusian city with well-preserved historical landmarks. The older part of Cádiz, within the remnants of the defensive wall, city walls, is commonly refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |