|
Battle Of Dun Nechtain
The Battle of Dun Nechtain or Battle of Nechtansmere (; ) was fought between the Picts, led by King Bridei Mac Bili, and the Northumbrians, led by King Ecgfrith, on 20 May 685. The Northumbrian hegemony over northern Britain, won by Ecgfrith's predecessors, had begun to disintegrate. Several of Northumbria's subject nations had rebelled in recent years, leading to a number of large-scale battles against the Picts, Mercians and Irish, with varied success. After sieges of neighbouring territories carried out by the Picts, Ecgfrith led his forces against them, despite advice to the contrary, in an effort to reassert his suzerainty over the Pictish nations. A feigned retreat by the Picts drew the Northumbrians into an ambush at Dun Nechtain near the lake of Linn Garan. The battle site has long been thought to have been near the present-day village of Dunnichen in Angus. Recent research, however, has suggested a more northerly location near Dunachton, on the shores of Loch Insh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in sub-Roman and early medieval Britain, approximately during the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Castle, and apparently included much of the area below the Firth of Forth. It was the most important district of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin, and a significant power in the Hen Ogledd, or Old North, the Brittonic-speaking area of what is now southern Scotland and northern England. The site of Din Eidyn has been nearly continuously occupied since the Bronze Age, serving as a stronghold of the Votadini during the Roman era and later the principal centre of their successors, the Gododdin kingdom. Eidyn's importance to the Hen Ogledd is reflected in the medieval poem ''Y Gododdin'', which concerns a war band that gathered there for a raid around AD 600. After years of decline, Eidyn was conquered by the Angles in 638. Eidyn is the source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beornhæth
Beornhæth was an Anglo-Saxon nobleman in Northumbria in the reign of King Ecgfrith (ruled 671–685). He was the first of his family to come to notice. Eddius's ''Life of Saint Wilfrid'', recounting Ecgfrith's campaign against the Picts in 671 or 672, states that he was accompanied by the "sub-king" Beornhæth. It is presumed that Beornhæth ruled a part of northern Bernicia, perhaps in modern Lothian where there was a major Northumbrian fortress at Dunbar. Beornhæth's son Berhtred (died c. 698), also called Berht, commanded King Ecgfrith's punitive expedition to kingdom of Brega, in Ireland, in 684. Beorhtred's paternity is known from the notice of his death in the Irish annals, where he is called the son of Beornhæth. Historians presume that Berhtfrith, "a nobleman second in rank only to Osred, was a son of Berhtred. Berhtfrith was largely responsible for the defeat of the would-be King Eadwulf, and the installation of Aldfrith">Eadwulf I of Northumbria">Eadwulf, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfrid
Wilfrid ( – 709 or 710) was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Francia, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon. In 664 Wilfrid acted as spokesman for the Roman position at the Synod of Whitby, and became famous for his speech advocating that the Roman method for calculating the date of Easter should be adopted. His success prompted the king's son, Alhfrith, to appoint him Bishop of Northumbria. Wilfrid chose to be consecrated in Gaul because of the lack of what he considered to be validly consecrated bishops in England at that time. During Wilfrid's absence Alhfrith seems to have led an unsuccessful revolt against his father, Oswiu, leaving a question mark over Wilfrid's appointment as bishop. Before Wilfrid's return Oswiu had appointed Ceadda in his place, resulting in Wilfrid's retirement to R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagiographer
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an wiktionary:adulatory, adulatory and idealized biography of a preacher, priest, founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian hagiographies might consist of a biography or ' (from Latin ''vita'', life, which begins the title of most medieval biographies), a description of the saint's deeds or miracles, an account of the saint's martyrdom (called a ), or be a combination of these. Christian hagiographies focus on the lives, and notably the miracles, ascribed to men and women canonization, canonized by the Roman Catholic church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches, and the Church of the East. Other religious traditions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, Daoism, Taoism, Islam, Sikhism and Jainism also create and maintain hagiographical texts (such as the Sikh Janamsakhis) concerning saints, gurus and other in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Of Ripon
Stephen of Ripon was the author of the eighth-century Hagiography, hagiographic text ''Vita Sancti Wilfrithi'' ("Life of Wilfrid, Saint Wilfrid"). Other names once traditionally attributed to him are Eddius Stephanus or Æddi Stephanus, but these names are no longer preferred or accepted by historians today; modern usage tends to favour "Stephen". Life Very little is known about the life of Stephen of Ripon. The author of "The life of Saint Wilfrid" identifies himself as "Stephen, a priest". Bede mentions that Wilfrid brought a singing master from Kent, ''Ædde Stephanus'', to Ripon in 669 to teach chant, and traditionally he is thought to be the same person as the "Stephen" mentioned in the text. The written evidence suggest there are two candidates for the same person. If the two were the same, Stephen would have been at least twenty years old when he came north, placing him in his sixties or older at Wilfrid's death in 709. He was then recorded as being present at the annivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Two Rivers
The Battle of Two Rivers was fought between the Picts and Northumbrians in the year 671. The exact battle site is unknown. It marked the end of the Pictish rebellion early in the reign of Ecgfrith, with a decisive victory for the Northumbrians. Attestation of the battle is limited to the account in Stephen of Ripon's ''Vita Sancti Wilfrithi''. Background During the 7th century, the Northumbrians gradually extended their territory to the north. The ''Annals of Tigernach'' record a siege of "Etain" in 638, which has been interpreted as Northumbria's conquest of Eidyn (Edinburgh) during the reign of Oswald, marking the annexation of Gododdin territories to the south of the River Forth. To the north of the Forth, the Pictish nations consisted at this time of the Kingdom of Fortriu to the north of the Mounth, and a "Southern Pictish Zone" to the south, stretching as far as the Forth. Evidence from the 8th-century Anglo-Saxon historian Bede points to the Picts also being subjugate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswiu Of Northumbria
Oswiu, also known as Oswy or Oswig (; c. 612 – 15 February 670), was King of Bernicia from 642 and of Northumbria from 654 until his death. He is notable for his role at the Synod of Whitby in 664, which ultimately brought the church in Northumbria into conformity with the wider Catholic Church. One of the sons of Æthelfrith of Bernicia and Acha of Deira, Oswiu became king following the death of his brother Oswald in 642. Unlike Oswald, Oswiu struggled to exert authority over Deira, the other constituent kingdom of medieval Northumbria, for much of his reign. Oswiu and his brothers were raised in exile in the Irish kingdom of Dál Riata in present-day Scotland after their father's death at the hands of Edwin of Northumbria (not by Edwin but possibly by Rædwald and his son Rægenhere at the Battle of the River Idle) only returning after Edwin's death in 633. Oswiu rose to the kingship when his brother Oswald was killed in battle against Penda of Mercia. The early part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most famous work, '' Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', gained him the title "The Father of English History". He served at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom of Northumbria of the Angles. Born on lands belonging to the twin monastery of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow in present-day Tyne and Wear, England, Bede was sent to Monkwearmouth at the age of seven and later joined Abbot Ceolfrith at Jarrow. Both of them survived a plague that struck in 686 and killed the majority of the population there. While Bede spent most of his life in the monastery, he travelled to several abbeys and monasteries across the British Isles, even visiting the archbishop of York and King Ceolwulf of Northumbria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounth
The Mounth ( ) is the broad upland in northeast Scotland between the Highland Boundary and the River Dee, at the eastern end of the Grampians. Name and etymology The name ''Mounth'' is ultimately of Pictish origin. The name is derived from ''*monɪð'', meaning "mountain" (cf. Welsh ''mynydd''). It is invariably referred to as "the Mounth" and pronounced "munth". Details The ranges to the north-west are known as the Monadh Liath and the Monadh Ruadh (called the Cairngorms in English), meaning the ''Grey Mounth'' and the ''Red Mounth''. Some sources regard the Mounth as extending as far west as Drumochter Pass ( A9), but it is now generally agreed to start at the Cairnwell Pass ( A93 – highest main road pass in Britain, Glen Shee ski centre). Here, a high undulating plateau invaded by deep glacial troughs (Glen Isla, Glen Callater, Glen Muick, Glen Clova) culminates in Glas Maol () on the main watershed, with the outlying granite Lochnagar () and its surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
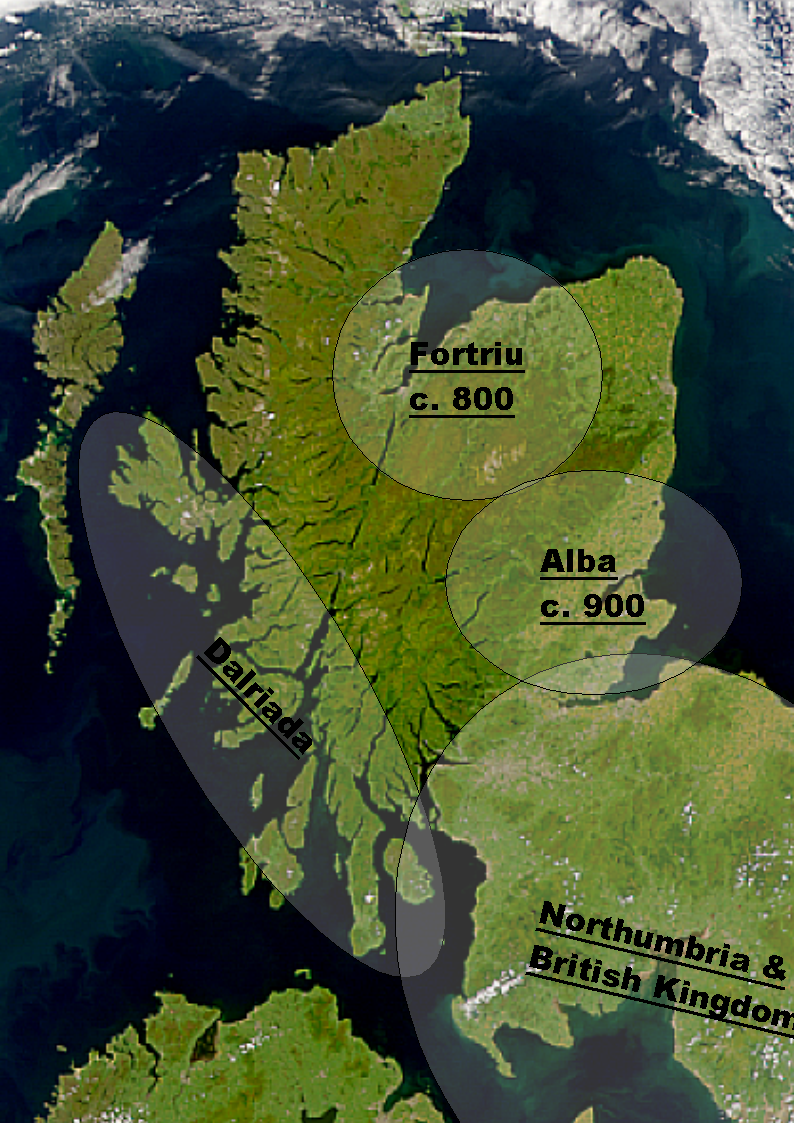
Fortriu
Fortriu (; ; ; ) was a Pictish kingdom recorded between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is more likely to have been based in the north, in the Moray and Easter Ross area. ''Fortriu'' is a term used by historians as it is not known what name its people used to refer to their polity. Historians also sometimes use the name synonymously with Pictland in general. Name The people of Fortriu left no surviving indigenous writings and the name they used to describe themselves is unrecorded. They were first documented in the late 4th century by the Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus, who referred to them in Latin as the ''Verturiones (or Vecturiones)''. The Latin root ''verturio'' has been connected etymologically by John Rhys with the later Welsh word ''gwerthyr'', meaning "fortress", suggesting that both came from a Common Brittonic root ''vertera'', and implying that the group's name meant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Forth
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic name for the upper reach of the river, above Stirling, is ''Abhainn Dubh'', meaning "black river". The name for the river below the tidal reach (just past where it is crossed by the M9 motorway) is ''Uisge For''. Name ''Forth'' derives from Proto-Celtic ''*Vo-rit-ia'' (slow running), yielding '':gd:Linne Foirthe, Foirthe'' in Old Gaelic. Course The Forth rises in the Trossachs, a mountainous area west of Stirling. Ben Lomond's eastern slopes drain into the Duchray Water, which meets with Avondhu River coming from Loch Ard. The confluence of these two streams is the nominal start of the River Forth. From there it flows roughly eastward through Aberfoyle, Stirling, Aberfoyle, joining with the Kelty Water about 5 km further downstream. It then flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |