|
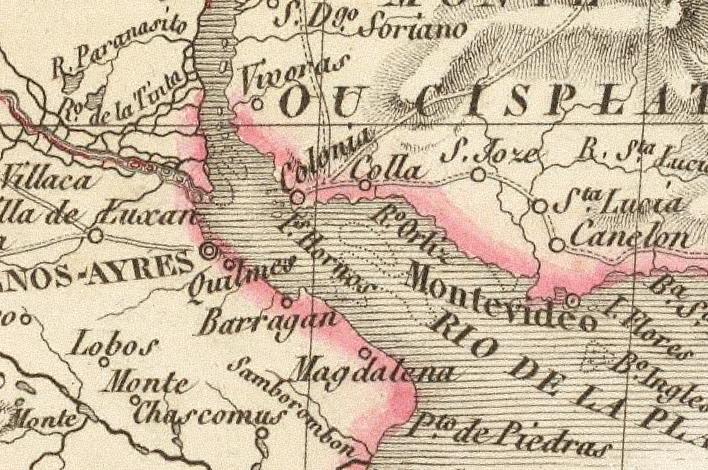
Battle Of Colonia Del Sacramento (1826)
The battle of Colonia del Sacramento (or Colônia do Sacramento) consisted of a series of failed attempts made by admiral William Brown of capturing the town of Colonia del Sacramento, which was under Brazilian control and being sieged on land by insurgent Uruguayan forces, in the context of the Cisplatine War between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. The confrontations began in the morning of 26 February 1826 and ended on 14 March 1826. Background The walled town of Colonia del Sacramento was a strategic point for the Brazilians due to its proximity to the city of Buenos Aires, capital of the United Provinces, which was suffering a naval blockade by the Imperial Brazilian Navy. The Brazilians used its port as a hub for resupplying ships in the Río de la Plata and thus continue on blockading the port of Buenos Aires. For this reason, the town was defended by a local garrison in the fort and batteries, and 4 small vessels: the brig ''Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisplatine War
The Cisplatine War (), also known as the Argentine-Brazilian War () or, in Argentine and Uruguayan historiography, as the Brazil War (''Guerra del Brasil''), the War against the Empire of Brazil (''Guerra contra el Imperio del Brasil'') or the Liberating Crusade (''Cruzada Libertadora'') in Uruguay, was an armed conflict in the 1820s between the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata and the Empire of Brazil over Brazil's Cisplatina province, in the aftermath of the United Provinces' and Brazil's independence from Spain and Portugal. It resulted in the independence of Cisplatina as the Oriental Republic of Uruguay. Background Led by José Gervasio Artigas, the region known as the Banda Oriental, in the Río de la Plata Basin, revolted against Spanish rule in 1811, against the backdrop of the 1810 May Revolution in Buenos Aires as well as the regional rebellions that followed in response to Buenos Aires' pretense of primacy over other regions in the Viceroyalty of the R� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannons, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grog
Grog is a term used for a variety of alcoholic beverages. The word originally referred to rum diluted with water (and later on long sea voyages, also added the juice of limes or lemons), which British Vice-Admiral Edward Vernon introduced into the naval squadron he commanded in the West Indies on 21 August 1740. Vernon wore a coat of grogram cloth and was nicknamed ''Old Grogram'' or ''Old Grog''. The ''Merriam–Webster Collegiate Dictionary'', which agrees with this story of the word's origin, states that the word ''grog'' was first used in this sense in 1770, though other sources cite 1749. In modern times, the term ''grog'' has had a variety of meanings in a number of different cultures, but is most commonly used in Australia and New Zealand where it is a slang word for alcohol. Origin and history Background During the early modern period (1500–1800), sailors required significant quantities of fresh water on extended voyages. Since desalinating sea water w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Gabriel Island
San Gabriel Island is a small island belonging to Uruguay, located on the Río de la Plata near the city of Colonia del Sacramento. It was named by explorer Sebastian Cabot in 1527. San Gabriel and nearby Farallón have been declared National Monument. References External links River islands of Uruguay Islands of the Río de la Plata Geography of Colonia Department {{island-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joaquim José Inácio, Viscount Of Inhaúma
Joaquim José Inácio, Viscount of Inhaúma (; 1 August 1808 – 8 March 1869), was a naval officer, politician and monarchist of the Empire of Brazil. He was born in the Kingdom of Portugal, and his family moved to Brazil two years later. After Brazilian independence in 1822, Inhaúma enlisted in the Brazilian navy. Early in his career during the latter half of the 1820s, he participated in the subduing of secessionist rebellions: first the Confederation of the Equator, and then the Cisplatine War, which precipitated a long international armed conflict with the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. Throughout the chaos that characterized the years when Emperor Dom Pedro II was a minor, Inhaúma remained loyal to the government. He helped quell a military mutiny in 1831 and was involved in suppressing some of the other rebellions that erupted during that troubled period. He saw action in the Sabinada between 1837 and 1838, followed by the Ragamuffin War fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence. The war started when the French and Spanish armies invaded and occupied Portugal in 1807 by transiting through Spain, and it escalated in 1808 after Napoleonic France occupied Spain, which had been its ally. Napoleon Bonaparte forced the abdications of Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV and then installed his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne and promulgated the Bayonne Constitution. Most Spaniards rejected French rule and fought a bloody war to oust them. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation. It is also significant for the emergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutter (boat)
A cutter is a type of watercraft. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or Sail plan, sailplan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placement of the mast and the rigging details of the bowsprit taken into account so a boat with two headsails may be classed as a sloop. Government agencies use the term "cutter" for vessels employed in patrolling their territorial waters and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
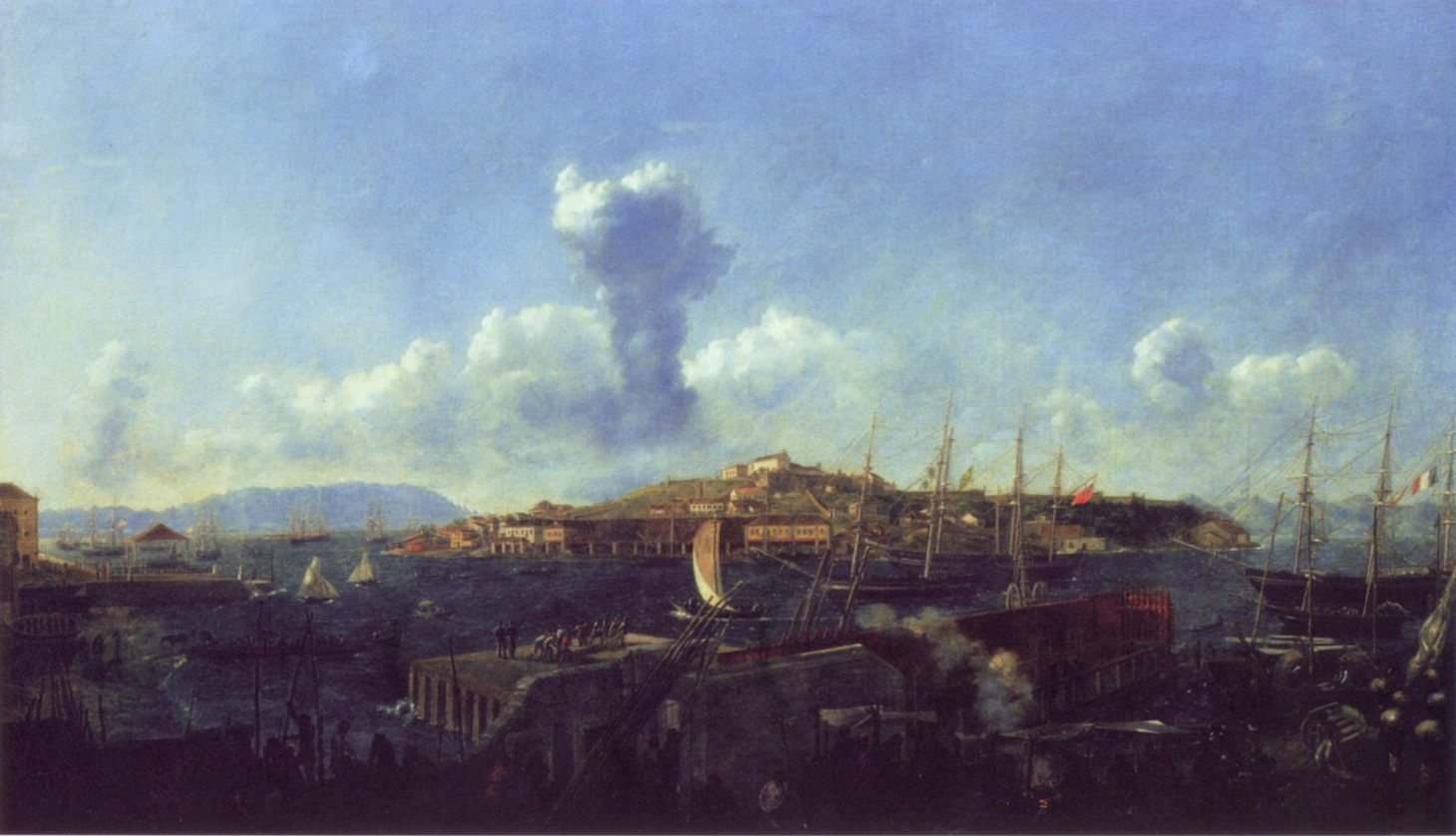
Montevideo
Montevideo () is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern coast of the country, on the northeastern bank of the Río de la Plata. The city was established in 1724 by a Spanish soldier, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst the Spanish- Portuguese dispute over the platine region. It was also under brief British rule in 1807, but eventually the city was retaken by Spanish criollos who defeated the British invasions of the River Plate. Montevideo is the seat of the administrative headquarters of Mercosur and ALADI, Latin America's leading trade blocs, a position that entailed comparisons to the role of Brussels in Europe. The 2019 Mercer's report on quality of life, rated Montevideo first in Latin America, a rank the city has consistently held since 2005. , Montevideo was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Murature
José Félix Murature was a commodore of the Argentine Navy and a painter of Italian origin who served in several conflits including the Argentine Civil Wars, the Cisplatine War and the Paraguayan War. Arrival at the Río de la Plata Murtature was born in Genoa during the War of the Third Coalition. At the age of 11, he started as a midshipman on a French war frigate. During his youth he traveled in the Atlantic Ocean several times, reaching Brazil twice. In 1825 he arrived in Buenos Aires, a few weeks before the declaration of war by the Empire of Brazil. For a time, he worked with an uncle who owned merchant ships in Montevideo which was occupied by the Brazilians, and then returned to Buenos Aires. In January 1826 he enlisted in the fleet organized by Captain Guillermo Brown, and soon became an expert in river navigation on the Río de la Plata, Paraná and Uruguay. He was put in command of a small scout ship, which was very useful to Brown for information about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Punta Colares
The naval Battle of Punta Colares, also known as the Battle of Corales, was the first major naval engagement of the Cisplatine War. It took place between a fleet of the Empire of Brazil, commanded by admiral Rodrigo José Ferreira Lobo, and a squadron of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata under the command of admiral William Brown. The confrontations began at around 10 o'clock on 9 February 1826 and lasted for seven hours. Background After war broke out between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata on 10 December 1825, the Brazilian government responded by imposing a naval blockade on the port of Buenos Aires on 31 December 1825, aiming to cripple Argentine finances. Since then there had been no major naval engagements between both belligerent states. In the early morning of 9 February 1826 the Argetine squadron left the port of Buenos Aires and made its first attempt to break the blockade. Order of battle Empire of Brazil Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)