|
Battle Of Catana (397 BC)
The Battle of Catana took place in the summer of 397 BC. The Greek fleet under Leptines, the brother of Dionysius I of Syracuse, engaged the Carthaginian fleet under Mago near the city of Catana in Sicily. While the Greek army under Dionysius was present near the city of Catana during the battle, the Carthaginian army under Himilco was away in the interior of Sicily, making a detour around the erupting Mount Etna. The Carthaginian fleet crushed the Greek fleet in the battle, leading to the Carthaginian siege of Syracuse later in 397 BC. Background Carthage had invaded Sicily in 406 BC in retaliation of Greek raids on Phoenician lands. The expedition, first commanded by Hannibal Mago, and, after the battle of Akragas, by his kinsman Himilco, had managed to capture and sack the cities of Akragas, Gela and Camarina by the summer of 405. These defeats had caused political turmoil in Syracuse, and had ultimately brought Dionysius I of Syracuse to power as tyrant. Himilco and Dionys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilian Wars
The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC. Carthage's economic success and its dependence on seaborne trade led to the creation of a powerful navy to discourage both pirates and rival nations. They had inherited their naval strength and experience from their forebears, the Phoenicians, but had increased it because, unlike the Phoenicians, the Punics did not want to rely on a foreign nation's aid. This, coupled with its success and growing hegemony, brought Carthage into increasing conflict with the Greeks, the other major power contending for control of the central Mediterranean. The Greeks, like the Phoenicians, were expert sailors who had established thriving colonies throughout the Mediterranean. These two rivals fought their wars on the island of Sicily, which lay close to Carthage. From th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of the leading cities of Magna Graecia during the golden age of Ancient Greece BC. History Akragas was founded on a plateau overlooking the sea, with two nearby rivers, the Hypsas and the Acragas, after which the settlement was originally named. A ridge, which offered a degree of natural fortification, links a hill to the north called Colle di Girgenti with another, called Rupe Atenea, to the east. According to Thucydides, it was founded around 582-580 BC by Greek colonists from Gela in eastern Sicily, with further colonists from Crete and Rhodes. The founders ( ''oikistai'') of the new city were Aristonous and Pystilus. It was the last of the major Greek colonies in Sicily to be founded. Archaic period The territory un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
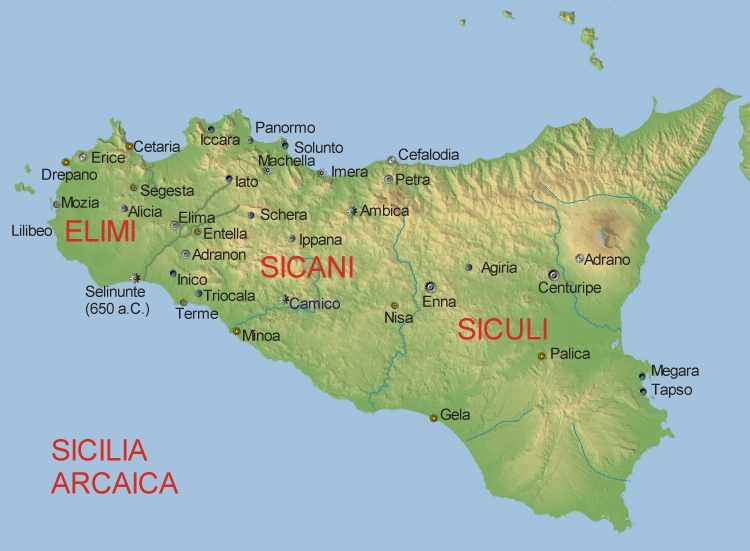
Eryx (Sicily)
Eryx ( grc-gre, Ἔρυξ, ''Éryx''; xpu, 𐤀𐤓𐤊, ) was an ancient city and a mountain in the west of Sicily, about 10 km from Drepana (modern Trapani), and 3 km from the sea-coast. It was located at the site of modern Erice. Mount Eryx The mountain, now called Monte Erice, is a wholly isolated peak, rising in the midst of a low undulating tract, which causes its elevation to appear much more considerable than it really is, so that it was regarded in ancient as well as modern times as the most lofty summit in the whole island next to Aetna, though its real elevation does not exceed 2184 English feet. Hence we find Eryx alluded to by Virgil and other Latin poets as a mountain of the first order of magnitude, and associated with Athos, Aetna, etc. On its summit stood a celebrated temple of Venus or Aphrodite, founded, according to the current legend, by Aeneas, whence the goddess derived the surname of Venus Erycina, by which she is often mentioned by Latin writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soluntum
Soluntum or Solus was an ancient city on the Tyrrhenian coast of Sicily near present-day in the comune of Santa Flavia, Italy. In antiquity, it was originally one of the three chief Phoenician settlements in the island and later flourished in the Greek and Roman periods. Names The Punic name of the town was simply ''Kapara'' (, ), meaning "Village". The Greek name appears in surviving coins as ''Solontînos'' () but appears variously in other sources as ''Solóeis'' (), ''Soloûs'' (), and ''Solountînos''. Some scholars contend that Soluntum and Solus were two different cities at close quarters, Soluntum, higher upon the hillside, being a later habitation displacing the earlier settlement of Solus, at a lower elevation. These were latinized as and , which became the modern Italian name Solunto. Geography Soluntum lay above sea level on the southeast side of Monte Catalfano (), commanding a fine view from a naturally-strong situation. It is immediately to the east of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. The city was founded in 734 BC by the Phoenicians as ("flower"). Palermo then became a possession of Carthage. Two Greek colonies were established, known collectively as ; the Carthaginians used this name on their coins after the 5th centuryBC. As , the town became part of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire, Empire for over a thousand years. From 831 to 1072 the city was under History of Islam in southern Italy, Arab rule in the Emirate of Sicily when the city became the capital of Sicily for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entella
Éntella (Greek: ), was an ancient city in the interior of Sicily, situated on the left bank of the river Hypsas (modern Belice), and nearly midway between the two seas, being about 40 km from the mouth of the Hypsas, and much about the same distance from the north coast of the island, at the Gulf of Castellamare. History It was apparently of Sicanian origin, though the traditions concerning its foundation connected it with the Elymi and the supposed Trojan colony. According to some writers it was founded by Acestes, and named after his wife Entella, a tradition to which Silius Italicus alludes, while others ascribed its foundation to Elymus, and Virgil represents Entellus (evidently the eponymous hero of the city) as a friend and comrade of Acestes. It was, together with Erice and Segesta, among the most important centres of the Elymians. Thucydides, however, says Eryx and Egesta were the only two cities of the Elymi, and does not notice Entella at all, any more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motya
Motya was an ancient and powerful city on San Pantaleo Island off the west coast of Sicily, in the Stagnone Lagoon between Drepanum (modern Trapani) and Lilybaeum (modern Marsala). It is within the present-day commune of Marsala, Italy. Many of the city's ancient monuments have been excavated and are visible today. Motya has become known for the marble statue of the Motya Charioteer, found in 1979 and on display at the local Giuseppe Whitaker museum. Names The Carthaginian settlement was written in their abjad as ( xpu, 𐤄𐤌𐤈𐤅𐤀) or ( xpu, 𐤌𐤈𐤅𐤀, possibly ''Motye''). The name seems to derive from the Phoenician triliteral root , which would give it the meaning of "a wool-spinning center". Motya is the latinization of the island's Greek name, variously written ''Motýa'' () or ''Motýē'' (). The Greeks claimed the place was named for a woman named Motya whom they connected with the myths around Hercules. The town's Italian name appears as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinquereme
From the 4th century BC on, new types of oared warships appeared in the Mediterranean Sea, superseding the trireme and transforming naval warfare. Ships became increasingly large and heavy, including some of the largest wooden ships hitherto constructed. These developments were spearheaded in the Hellenistic Near East, but also to a large extent shared by the naval powers of the Western Mediterranean, specifically Carthage and the Roman Republic. While the wealthy successor kingdoms in the East built huge warships ("polyremes"), Carthage and Rome, in the intense naval antagonism during the Punic Wars, relied mostly on medium-sized vessels. At the same time, smaller naval powers employed an array of small and fast craft, which were also used by the ubiquitous pirates. Following the establishment of complete Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean after the Battle of Actium, the nascent Roman Empire faced no major naval threats. In the 1st century AD, the larger warships were retained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
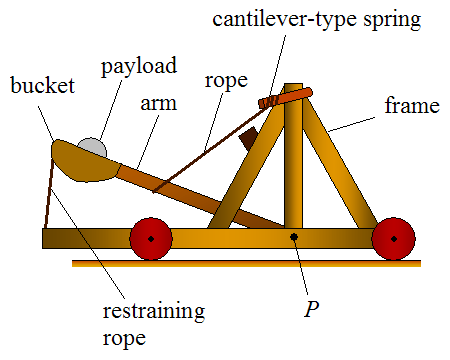
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert tension or torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms. In use since ancient times, the catapult has proven to be one of the most persistently effective mechanisms in warfare. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with King Uzziah, of Judah, recorded as equipping the walls of Jerusalem with machines that shot "great stones". Catapults are mentioned in Yajurv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
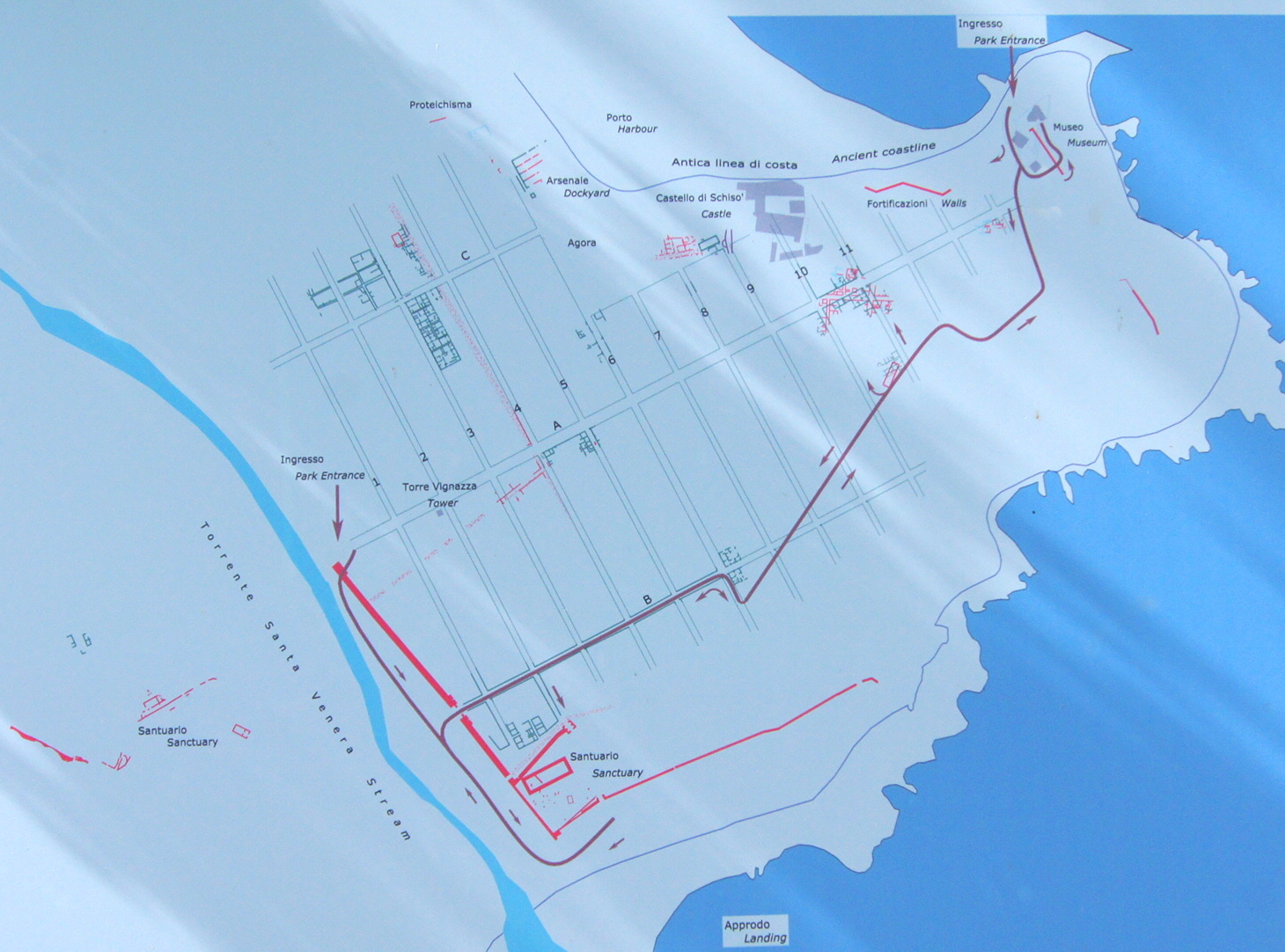
Naxos (Sicily)
Naxos or Naxus ( grc-gre, Νάξος) was an ancient Greek city, presently situated in modern Giardini Naxos near Taormina on the east coast of Sicily. Much of the site has never been built on and parts have been excavated in recent years. Its remains are open to the public and an on-site museum contains many finds. Location The city occupied a low rocky headland, now called Cape Schisò, formed by an ancient lava flow, immediately to the north of the Acesines (modern Alcantara) stream. Name There can be little doubt that the name was derived from the origin of the first colonists from Naxos in Greece. This has become even more definite since 1977 when the marble ''cippus'' (or sacred stone) inscribed with a dedication to the goddess Enyo was found in the large sanctuary west of the Santa Venera river. The characters are written in the unique 7th c. BC script of Greek Naxos. History Foundation Ancient writers agree that Naxos was the most ancient of all the Greek col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in the city proper and about 650,000 in the Metropolitan City. It is located near the northeast corner of Sicily, at the Strait of Messina and it is an important access terminal to Calabria region, Villa San Giovanni, Reggio Calabria on the mainland. According to Eurostat the Larger urban zone, FUA of the metropolitan area of Messina has, in 2014, 277,584 inhabitants. The city's main resources are its seaports (commercial and military shipyards), cruise ship, cruise tourism, commerce, and agriculture (wine production and cultivating lemons, oranges, mandarin oranges, and olives). The city has been a Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Messina-Lipari-Santa Lucia del Mela, Archdiocese and Archimandrite sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |