|
Battle Of Cape Kaliakra
The Battle of Cape Kaliakra (Kaliakria, Caliacria; ) was the last naval battle of the Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792). It took place on 11 August 1791 off the coast of Cape Kaliakra, Bulgaria, in the Black Sea. Neither side lost a ship, but the Ottomans retreated to Istanbul afterwards. The Russian fleet under Counter (Rear) Admiral Fyodor Ushakov, of 15 ships of the line and two frigates (990 guns), and several small craft sailed from Sevastopol on 8 August, and at midday on 11 August encountered the Ottoman– Algerian fleet under Hussein Pasha of 18 ships of the line and 17 frigates (1,500–1,600 guns) and some smaller craft at anchor just south of Cape Kaliakra. Ushakov sailed, in three columns, from the northeast, between the Ottomans and the cape, despite the presence on the cape of several guns. Admiral Said Ali, the commander of the Algerian ships, weighed anchor and sailed east, followed by Hussein Pasha with the 18 ships of the line. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1787–1792 involved an unsuccessful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to regain lands lost to the Russian Empire in the course of the previous Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774). It took place concomitantly with the Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791), the Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790), and the Theatre War. During the Russian-Turkish War of 1787–1792, on 25 September 1789, a detachment of the Imperial Russian Army under Alexander Suvorov and Ivan Gudovich, took Khadjibey and Yeni Dünya for the Russian Empire. In 1794, Odesa replaced Khadjibey by a decree of the Russian Empress Catherine the Great. Russia formally gained possession of the Sanjak of Özi ( Ochakiv Oblast) in 1792 and it became a part of Yekaterinoslav Viceroyalty. The Russian Empire retained full control of Crimea, as well as land between the Southern Bug and the Dniester. Background In May and June 1787, Catherine II of Russia made a triumphal procession through Novorossiya and the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of navy, naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest quality, best known, or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, early Christian Church. He appears repeatedly and prominently in Gospel#Canonical gospels, all four New Testament gospels, as well as the Acts of the Apostles. Catholic Church, Catholic and Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox tradition treats Peter as the first bishop of Rome – or List of popes, pope – and also as the first bishop of Antioch. Peter's History of the papacy, leadership of the early believers is estimated to have spanned from AD 30 or 33 to his death; these dates suggest that he could have been the longest-reigning pope, for anywhere from 31 to 38 years; however, this has never been verified. According to Apostolic Age, Christian tradition, Peter was crucified in Rome under Emperor Nero. The ancient Christian churches all venera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascension Of Jesus
The Ascension of Jesus (anglicized from the Vulgate ) is the Christianity, Christian and Islamic belief that Jesus entering heaven alive, ascended to Heaven. Christian doctrine, as reflected in the major Christian creeds and confessional statements, holds that Jesus ascended after his Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection, where he was exaltation of Jesus, exalted as Lord and Christ (title), Christ, session of Christ, sitting at the right hand of God. Schools of Islamic theology, Islamic doctrine holds that Jesus directly ascended to heaven without dying or resurrecting. The Gospels and other New Testament writings imply resurrection and exaltation as a single event. The ascension is "more assumed than described," and only Luke–Acts, Luke and Acts contain direct accounts of it, but with different chronologies. In Christian art, the ascending Jesus is often shown blessing an earthly group below him, signifying the entire Church. The Feast of the Ascension is celebrated on the 40t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navarch
Navarch, Navarchus or Nauarchus (, ) is an Anglicisation of a Greek word meaning "leader of the ships", which in some states became the title of an office equivalent to that of a modern admiral. Also this status was very valuable in Ancient Greece. Historical usage Not all states gave their naval commanders such a title. Athens, for instance, placed its fleet under the command of generals ('' strategoi'') holding the same title as those who commanded its land forces. In Athens navarch called only the commander of the Athenian sacred ships. Such command structures reflected the fact that, especially early in the Classical period, fleets operated in close conjunction with land forces, and indeed, the title of navarch did not begin to appear until the time of the Peloponnesian War, when fleets began to operate more independently. This separate title was originally used in cities that lacked an established naval tradition, Sparta being the most prominent, but entered broader use l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John The Apostle
John the Apostle (; ; ), also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Saint John the Theologian, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Generally listed as the youngest apostle, he was the son of Zebedee and Salome (disciple), Salome. His brother James the Great, James was another of the Twelve Apostles. The Church Fathers identify him as John the Evangelist, John of Patmos, John the Presbyter, John the Elder, and the Disciple whom Jesus loved, Beloved Disciple, and claim that he outlived the remaining apostles and was the only one to die of natural causes, although modern scholars are divided on the veracity of these claims. John the Apostle is traditionally held to be the author of the Gospel of John, and many Christian denominations believe that he authored several other books of the New Testament (the three Johannine epistles and the Book of Revelation, together with the Gospel of John, are called the Johannine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
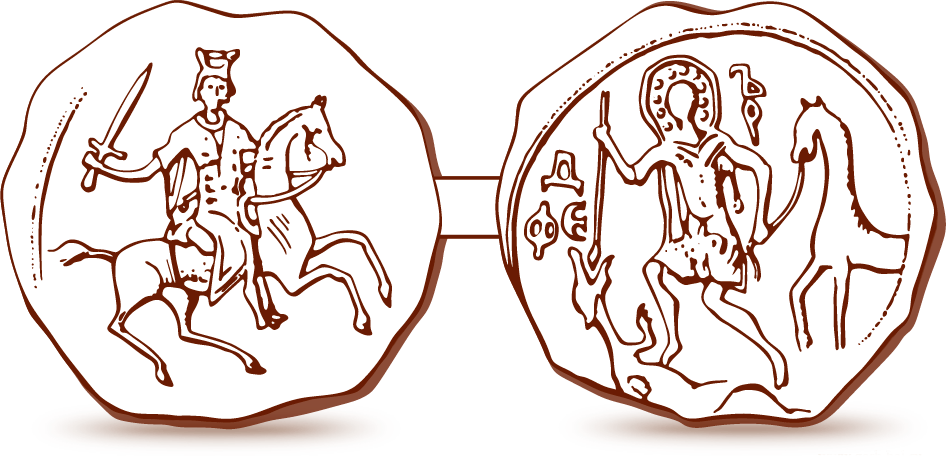
Theodore Stratelates
Theodore Stratelates (, ; ), also known as Theodore of Heraclea (; AD 281–319), was a martyr and warrior saint in the Eastern Orthodox, Catholic and Oriental Orthodox Churches. There is much confusion as to whether he and St. Theodore of Amasea were the same person, as the stories about their lives later diverged into two separate traditions. Life Of Greek origin, Theodore was born in the city of Euchaita in Asia Minor. He killed a giant serpent living on a precipice in the outskirts of Euchaita. The serpent had terrorised the countryside. Theodore armed himself with a sword and vanquished it. According to some of the legends, because of his bravery, Theodore was appointed military-commander (''stratelates'') in the city of Heraclea Pontica, during the time the emperor Licinius (307–324) began a fierce persecution of Christians. Theodore invited Licinius to Heraclea, having promised to offer a sacrifice to the pagan gods. He requested that all the gold and silver statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara (Lycia), Patara in Anatolia (in modern-day Antalya Province, Turkey) during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the many miracles attributed to his intercession, he is also known as Nicholas the Wonderworker. Saint Nicholas is the patron saint of sailors, merchants, archers, repentant thieves, children, brewers, pawnbrokers, toymakers, unmarried people, and students in various cities and countries around Europe. His reputation evolved among the pious, as was common for early Christian saints, and his legendary habit of secret gift-giving gave rise to the folklore of Santa Claus ("Saint Nick") through Sinterklaas. Little is known about the historical Saint Nicholas. The earliest accounts of his life were written centuries after his death and probably contain legendary elaborations. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Andrew
Andrew the Apostle ( ; ; ; ) was an apostle of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was a fisherman and one of the Twelve Apostles chosen by Jesus. The title First-Called () used by the Eastern Orthodox Church stems from the Gospel of John, where Andrew, initially a disciple of John the Baptist, follows Jesus and, recognising him as the Messiah, introduces his brother Simon Peter to him. According to Eastern Orthodox tradition, the apostolic successor to Andrew is the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople. Life Early life The name "Andrew" (meaning ''manly, brave'', from ), like other Greek names, appears to have been common among the Jews and other Hellenised people since the second or third century B.C.MacRory, Joseph; "Saint Andrew", The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 1, New York, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (; ; monastic name: ''Aleksiy''; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) was Prince of Novgorod (1236–1240; 1241–1256; 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249–1263), and Grand Prince of Vladimir (1252–1263). Commonly regarded as a key figure in medieval Russian history, Alexander was a grandson of Vsevolod the Big Nest and rose to legendary status on account of his military victories in northwestern Russia over Swedish invaders in the 1240 Battle of the Neva, as well as German crusaders in the 1242 Battle on the Ice. He preserved Eastern Orthodoxy, agreeing to pay tribute to the powerful Golden Horde. Metropolitan Macarius of Moscow canonized Alexander Nevsky as a saint of the Russian Orthodox Church in 1547. Early life Born in Pereslavl-Zalessky around the year 1220, Alexander was the second son of Prince Yaroslav Vsevolodovich. His mother was , daughter of Mstislav Mstislavich The Bold. From the ''Tales of the Life and Courage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir The Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych (; Christian name: ''Basil''; 15 July 1015), given the epithet "the Great", was Prince of Novgorod from 970 and Grand Prince of Kiev from 978 until his death in 1015. The Eastern Orthodox Church canonization, canonised him as Saint Vladimir. Vladimir's father was Sviatoslav I of the Rurik dynasty. After the death of his father in 972, Vladimir, who was then the prince of Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod, was forced to flee abroad after his brother Yaropolk I of Kiev, Yaropolk murdered his other brother Oleg of Drelinia, Oleg in 977 to become the sole ruler of Rus'. Vladimir assembled a Varangian army and returned to depose Yaropolk in 978. By 980, Vladimir had consolidated his realm to the Baltic Sea and solidified the frontiers against incursions of Bulgarians, Baltic tribes and Eastern nomads. Originally a follower of Slavic paganism, Vladimir converted to Christianity in 988, and Christianization of Kievan Rus', Christianized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul The Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is generally regarded as one of the most important figures of the Apostolic Age, and he also founded Early centers of Christianity, several Christian communities in Asia Minor and Europe from the mid-40s to the mid-50s AD. The main source of information on Paul's life and works is the Acts of the Apostles in the New Testament. Approximately half of its content documents his travels, preaching and miracles. Paul was not one of the Twelve Apostles, and did not know Jesus during his lifetime. According to the Acts, Paul lived as a Pharisees, Pharisee and participated in the Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, persecution of early Disciple (Christianity), disciples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |