|
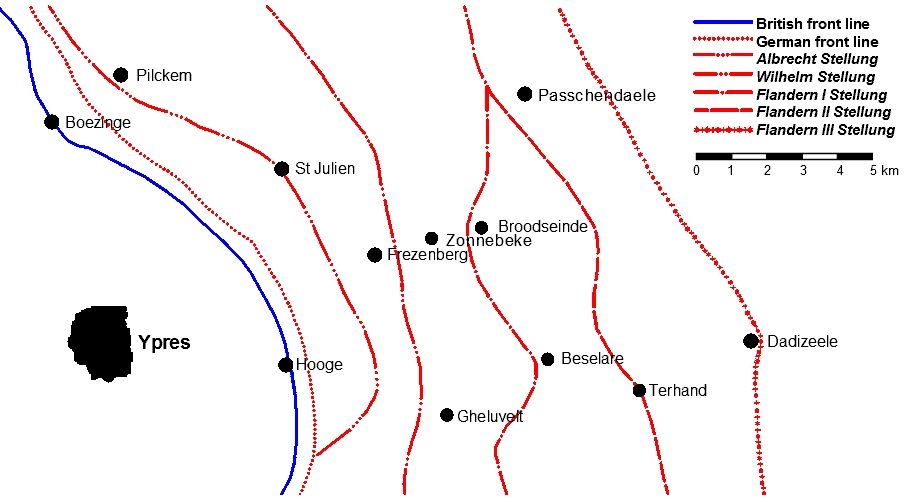
Battle Of Broodseinde
The Battle of Broodseinde was fought on 4 October 1917 near Ypres in Belgium, at the east end of the Gheluvelt plateau, by the British Second and Fifth armies against the German 4th Army. The battle was the most successful Allied attack of the Third Battle of Ypres. Using ''bite-and-hold'' tactics, with objectives limited to what could be held against German counter-attacks, the British devastated the German defence, prompted a crisis among the German commanders and caused a severe loss of morale in the 4th Army. Preparations were made by the Germans for local withdrawals and planning began for a greater withdrawal, which would entail the abandonment by the Germans of the Belgian coast, one of the strategic aims of the Flanders Offensive. After the period of unsettled but drier weather in September, heavy rain began again on 4 October and affected the remainder of the campaign, working more to the advantage of the German defenders, being pushed back on to far less damaged gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of Ypres
The Third Battle of Ypres (; ; ), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele ( ), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Entente at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere ( Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuwpoort), combined with an amphibious landing ( Operation Hush), were to have reached Bruges and then the Dutch fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passendale
Passendale () or Passchendaele ( , ; ) is a rural Belgian village in the Zonnebeke municipality of West Flanders province. It is close to the town of Ypres, situated on the hill ridge separating the historical wetlands of the Yser and Leie valleys. It is also commonly known as a battlefield and the name of a campaign during World War I, the Battle of Passchendaele. History Early history In the pre-Roman and Roman times the area of the town was located along the border between the Menapii and Morini Belgic tribes of northern Gaul and later the border between the bishoprics of Tournai and Thérouanne. The town is first recorded in 844 as Pascandale, and may be named after an individual by the name of Paulus or Pasko. In the Middle Ages, most of the region was ruled by the Augustine abbey of Zonnebeke and the Benedictine convent of Nonnebossen. Both the abbey and the convent were destroyed during an iconoclasm ('' Beeldenstorm'') of 1580. First World War Passchendaele Ridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Bombardment
In warfare, infiltration tactics involve small independent light infantry forces advancing into enemy rear areas, bypassing enemy frontline strongpoints, possibly isolating them for attack by follow-up troops with heavier weapons. Soldiers take the initiative to identify enemy weak points and choose their own routes, targets, moments and methods of attack; this requires a high degree of skill and training, and can be supplemented by special equipment and weaponry to give them more local combat options. Forms of these infantry tactics were used by skirmishers and irregulars dating back to classical antiquity, but only as a defensive or secondary tactic; decisive battlefield victories were achieved by shock combat tactics with heavy infantry or heavy cavalry, typically charging ''en masse'' against the primary force of the opponent. By the time of early modern warfare, defensive firepower made this tactic increasingly costly. When trench warfare developed to its height i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eingreif
Eingreif division () is a term for a type of German Empire, German German Army (German Empire), Army formation of the First World War, which developed in 1917, to conduct immediate counterattack, counter-attacks () against enemy troops who broke into a defensive position being held by a front-holding division () or to conduct a methodical counter-attack () 24–48 hours later. Attacks by the French and British armies against the on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front had been met in 1915 and 1916 by increasing the number and sophistication of trench networks, the original improvised defences of 1914 giving way to a centrally-planned system of trenches in a trench-position and then increasing numbers of trench-positions, to absorb the growing firepower and offensive sophistication of the Entente armies. During the Battle of the Somme (1 July – 18 November 1916), the use of defensive lines began to evolve into the defence of the areas between them, using the local troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale () is a scale of temperature, temperature scale based on one proposed in 1724 by the German-Polish physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736). It uses the degree Fahrenheit (symbol: °F) as the unit. Several accounts of how he originally defined his scale exist, but the original paper suggests the lower defining point, 0 °F, was established as the freezing temperature of a solution of brine made from a mixture of water, ice, and ammonium chloride (a Salt (chemistry), salt). The other limit established was his best estimate of the average human body temperature, originally set at 90 °F, then 96 °F (about 2.6 °F less than the modern value due to a later redefinition of the scale). For much of the 20th century, the Fahrenheit scale was defined by two fixed points with a 180 °F separation: the temperature at which pure water freezes was defined as 32 °F and the boiling point of water was defined to be 212 °F, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westrozebeke
 Westrozebeke is a village in the Belgium, Belgian province of West Flanders. It is part of the municipality of Staden. It is located 6 miles (10 km) west of Roeselare and 9.5 miles (15 km) north-east of Ypres. It's a typical agricultural village with many farms.
The name ''Westrozebeke'' means 'west thatch brook'. The word 'roze' is also related to the 'roes' of the nearby city Roeselare.
It lies at the top of a hill, and has beautiful views, especially to the West.
It has two football fields and a local youth mouvement, the Chiro.
The village is also famous because of the Battle of Roosebeke, where a Flemish army under the guidance of Philip van Artevelde (son of the famous Jacob van Artevelde, Flemish people, Flemish statesman and political le ...
Westrozebeke is a village in the Belgium, Belgian province of West Flanders. It is part of the municipality of Staden. It is located 6 miles (10 km) west of Roeselare and 9.5 miles (15 km) north-east of Ypres. It's a typical agricultural village with many farms.
The name ''Westrozebeke'' means 'west thatch brook'. The word 'roze' is also related to the 'roes' of the nearby city Roeselare.
It lies at the top of a hill, and has beautiful views, especially to the West.
It has two football fields and a local youth mouvement, the Chiro.
The village is also famous because of the Battle of Roosebeke, where a Flemish army under the guidance of Philip van Artevelde (son of the famous Jacob van Artevelde, Flemish people, Flemish statesman and political le ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Hush
Operation Hush was a British plan for amphibious landings on the Belgian coast in 1917 during the First World War. The landings were to be combined with an attack from Nieuwpoort and the Yser bridgehead, left over since the Battle of the Yser in 1914. Plans were considered in 1915 and 1916, then shelved due to operations elsewhere. Operation Hush was intended to begin once the Third Battle of Ypres, the main offensive at Ypres, had advanced to Roulers, Koekelare and Thourout, with advances by the French and Belgians in between. On 10 July, conducted (Operation Beach Party) a spoiling attack by to forestall an Allied coastal operation. The Germans used mustard gas for the first time, captured part of the bridgehead over the Yser and annihilated two British infantry battalions. Operation Hush was cancelled on 14 October 1917, as the advance at Ypres was too far behind schedule. In April 1918, the Dover Patrol raided Zeebrugge to sink blockships in the canal entrance to tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XV Corps (United Kingdom)
XV Corps was a British infantry corps during World War I. World War I XV Corps was formed in Egypt on 9 December 1915 and then reformed in France on 22 April 1916 under Lieutenant-General Sir Henry Horne. It took part in the Battle of the Somme in 1916. Order of battle on 11 November 1918 Prior to the armistice, the corps halted on the Schelde on 10 November 1918. It was composed of the following units, the 36th Division having been transferred from the X Corps on 9 November 1918: *14th (Light) Division (Major General Skinner) * 40th Division (Major General Peyton) *36th (Ulster) Division The 36th (Ulster) Division was an infantry division of the British Army, part of Lord Kitchener's New Army, formed in September 1914. Originally called the ''Ulster Division'', it was made up of mainly members of the Ulster Volunteers, who f ... (Major General Coffin) * 3rd Cavalry Division (Major General Harmon) *Corps Troops **V/XV Heavy Trench Mortar Battery **15th Cyclist Bn **XV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Army (United Kingdom)
The Fifth Army was a field army of the British Army during World War I that formed part of the British Expeditionary Force on the Western Front between 1916 and 1918. The army originated as the Reserve Corps during the preparations for the British part of the Somme Offensive of 1916, was renamed Reserve Army when it was expanded and became the Fifth Army in October 1916. History The Fifth Army was created on 30 October 1916, by renaming the Reserve Army (General Hubert Gough). It participated in the Battle of the Ancre, which became the final British effort in the Battle of the Somme. In 1917,the Fifth Army was involved in the Battle of Arras and then the Third Battle of Ypres. The following year, the Fifth Army took over a stretch of front-line previously occupied by the French south of the River Somme and on 21 March, bore the brunt of the opening phase of the German Spring Offensive, known as Operation Michael. The failure of the Fifth Army to withstand the German advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Polygon Wood
The Battle of Polygon Wood (26 September to 3 October 1917) was fought during the second part of the Third Battle of Ypres in the First World War. The battle was fought near Ypres in Belgium, from the Menin road to Polygon Wood and thence north, to the area beyond St Julien. Much of the woodland had been destroyed by the huge bombardments from both sides since 16 July and the area had changed hands several times. General Herbert Plumer continued the British general attacks with limited objectives. Lines of skirmishers advanced ahead of small infantry columns in depth (as had been adopted by the Fifth Army in August) with a vastly increased amount of artillery support, five layers of creeping barrage on the Second Army front. An advance of was planned, to stop on reverse slopes, which were easier to defend, enclosing ground which gave observation of German reinforcement routes and counter-attack assembly areas. Preparations swiftly to defeat German counter-attacks were made, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Menin Road Ridge
The Battle of the Menin Road Ridge, sometimes called "Battle of the Menin Road", was the third British general attack of the Third Battle of Ypres in the First World War. The battle took place from 20 to 25 September 1917, in the Ypres Salient in Belgium on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front. During the pause in British and French general attacks from late August to 20 September, the British changed some infantry tactics, adopting the Bounding overwatch#Leapfrogging, leap-frog method of advance. Waves of infantry stopped once they reached their objective and consolidated the ground, while supporting waves passed through the objective to attack the next one and the earlier waves became the tactical reserve. General adoption of the method was made possible when more artillery was brought into the Salient (military), salient, by increasing the number of aircraft involved in close air support and by the Royal Flying Corps giving the tasks of air defence, contact-patrol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expeditionary Force (World War I)
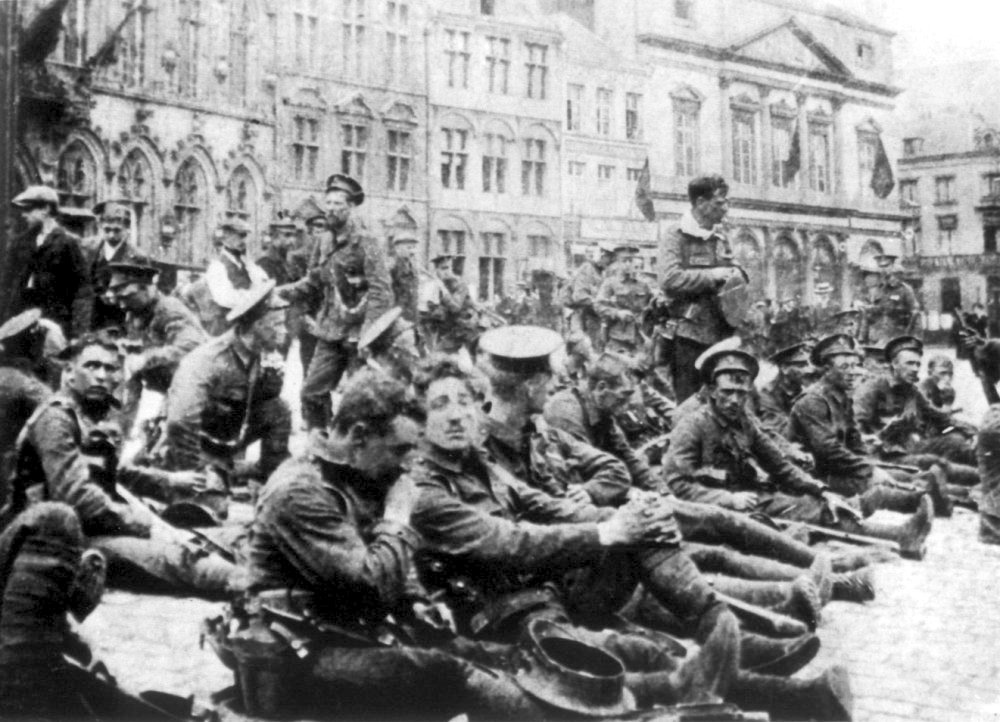
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the formation of British army on the Western Front during World War I. They were sent by Britain to France in 1914 to aid in resisting the German invasion. Originally sent as six divisions the British Army to the Western Front during the First World War. Planning for a British Expeditionary Force began with the 1906–1912 Haldane Reforms of the British Army carried out by the Secretary of State for War Richard Haldane following the Second Boer War (1899–1902). The term ''British Expeditionary Force'' is often used to refer only to the forces present in France prior to the end of the First Battle of Ypres on 22 November 1914. By the end of 1914—after the battles of Mons, Le Cateau, the Aisne and Ypres—the existent BEF had been almost exhausted, although it helped stop the German advance.An alternative endpoint of the BEF was 26 December 1914, when it was divided into the First and Second Armies (a Third, Fourth and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |