|
Battle Of Alnwick (1174)
The Battle of Alnwick (1174) is one of two battles fought near the town of Alnwick, in Northumberland, England. In the battle, which took place on 13 July 1174, William I of Scotland, also known as William the Lion, was captured by a small English force led by Ranulf de Glanvill. Background William had inherited the title of Earl of Northumbria in 1152. However, he had to give up this title to King Henry II of England in 1157. He spent much of his reign trying to regain his lost territory. In 1173, whilst Henry II was occupied in fighting against his sons in the Revolt of 1173–1174, William saw his opportunity and invaded Northumbria. He advanced on Newcastle but found the partly built stone castle too strong to allow him to take the town. He also attacked Prudhoe Castle but found the defences too strong. Unwilling to undertake a lengthy siege, William returned to Scotland. In 1174, William again invaded Northumbria with an even larger army that included a contingent of Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolt Of 1173–74
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a portion of a state. A rebellion is often caused by political, religious, or social grievances that originate from a perceived inequality or marginalization. ''Rebellion'' comes from Latin ''re'' and ''bellum'', and in Lockian philosophy refers to the responsibility of the people to overthrow unjust government. Classification Uprisings which revolt, resisting and taking direct action against an authority, law or policy, as well as organize, are rebellions. An insurrection is an uprising to change the government. If a government does not recognize rebels as belligerents, then they are insurgents and the revolt is an insurgency. In a larger conflict, the rebels may be recognized as belligerents without their government being recognized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
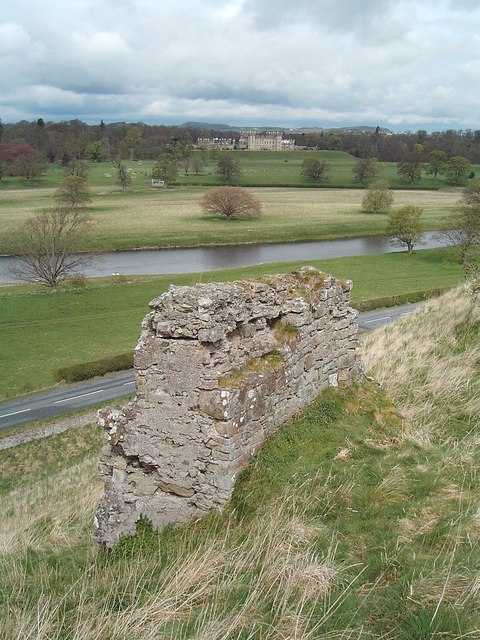
Prudhoe Castle
Prudhoe Castle is a ruined medieval English castle situated on the south bank of the River Tyne at Prudhoe, Northumberland, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and a Grade I listed building. The Umfravilles Archaeological excavations have shown that the first castle on the site was a Norman motte and bailey, built sometime in the mid 11th century. Following the Norman Conquest of England, the Umfraville family took over control of the castle. Robert d’Umfraville was formally granted the barony of Prudhoe by Henry I but it is likely that the Umfravilles had already been granted Prudhoe in the closing years of the 11th century. The Umfravilles (probably Robert) initially replaced the wooden palisade with a massive rampart of clay and stones and subsequently constructed a stone curtain wall and gatehouse. In 1173 William the Lion of Scotland invaded the North East to claim the earldom of Northumberland. The head of the Umfraville family, Odinel II, refused to suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of York
The Treaty of York was an agreement between the kings Henry III of England and Alexander II of Scotland, signed at York on 25 September 1237, which affirmed that Northumberland (which at the time also encompassed County Durham), Cumberland, and Westmorland were subject to English sovereignty. This established the Anglo-Scottish border in a form that remains almost unchanged to modern times (the only modifications have been regarding the Debatable Lands and Berwick-upon-Tweed). The treaty detailed the future status of several feudal properties and addressed other issues between the two kings, and historically marked the end of the Kingdom of Scotland's attempts to extend its frontier southward. The treaty was one of a number of agreements made in the ongoing relationship between the two kings. The papal legate Otto of Tonengo, Otho of Tonengo was already in the Kingdom of England at Henry's request, to attend a synod in London in November 1237. Otho was informed in advance by Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionally synonymous with what is known as the Land of Israel ( Zion) or the Promised Land in a biblical or religious context, or as Canaan or Palestine in a secular or geographic context—referring to a region that is mostly between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. Today, it chiefly overlaps with the combined territory of the modern states of Israel and Palestine. Most notable among the religions that tie substantial spiritual value to the Holy Land are Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. A considerable part of the Holy Land's importance derives from Jerusalem, which is regarded as extremely sacred in and of itself. It is the holiest city in Judaism and Christianity and the third-holiest city in Islam (behind Mecca and Medina in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard I Of England
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199), known as Richard the Lionheart or Richard Cœur de Lion () because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior, was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Duke of Aquitaine, Aquitaine, and Duchy of Gascony, Gascony; Lord of Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Cyprus; Count of Poitiers, Counts and dukes of Anjou, Anjou, Count of Maine, Maine, and Count of Nantes, Nantes; and was overlord of Brittany at various times during the same period. He was the third of five sons of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and was therefore not expected to become king, but his two elder brothers predeceased their father. By the age of 16, Richard had taken command of his own army, putting down rebellions in Poitou against his father. Richard was an important Christian commander during the Third Crusade, leading the campaign after the departure of Philip II of France and achieving sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stirling Castle
Stirling Castle, located in Stirling, is one of the largest and most historically and architecturally important castles in Scotland. The castle sits atop an Intrusive rock, intrusive Crag and tail, crag, which forms part of the Stirling Sill geological formation. It is surrounded on three sides by steep cliffs, giving it a strong defensive position. Its strategic location, guarding what was, until the 1890s, the lowest bridging point, farthest downstream crossing of the River Forth, has made it an important fortification in the region from the earliest times. Most of the principal buildings of the castle date from the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. A few structures remain from the fourteenth century, while the outer defences fronting the town date from the early eighteenth century. Before the union with England, Stirling Castle was also one of the most used of the many Scottish royal residences, very much a palace as well as a fortress. Several List of Scottish monarchs, Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle is a historic castle in Edinburgh, Scotland. It stands on Castle Rock (Edinburgh), Castle Rock, which has been occupied by humans since at least the Iron Age. There has been a royal castle on the rock since the reign of Malcolm III of Scotland, Malcolm III in the 11th century, and the castle continued to be a royal residence until 1633. From the 15th century, the castle's residential role declined, and by the 17th century it was principally used as a military garrison. Its importance as a part of Scotland's national heritage was recognised increasingly from the early 19th century onwards, and various restoration programmes have been carried out over the past century and a half. Edinburgh Castle has played a prominent role in History of Scotland, Scottish history, and has served variously as a Palace, royal residence, an arsenal, a treasury, a national archives, national archive, a Mints of Scotland, mint, a prison, a military fortress, and the home of the Honou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedburgh Castle
Jedburgh Castle was a castle at Jedburgh in Scotland. It was fought over during the Wars of Scottish Independence, and was demolished by the Scots commanded by James Douglas, 7th Earl of Douglas, Sir James Douglas of Balvenie in 1409. The site of the original castle was used to build the reform prison based on the John Howard (prison reformer), John Howard system, the construction of which started in 1820. Jedburgh Castle Jail In 1823 a jail was built on the site to designs by Archibald Elliot. It was modified in 1847 by Thomas Brown. This closed in 1868. The building was restored to an 1820s appearance in 1968 by Aitken and Turnbull. It opened to the public as Jedburgh Castle Jail and Museum. The museum features local history displays. On the Thursday after Shrove Tuesday, the town has played a Ba Game since 1704. The uppies team use the castle to record their victories. See also *List of places in the Scottish Borders *List of places in Scotland References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
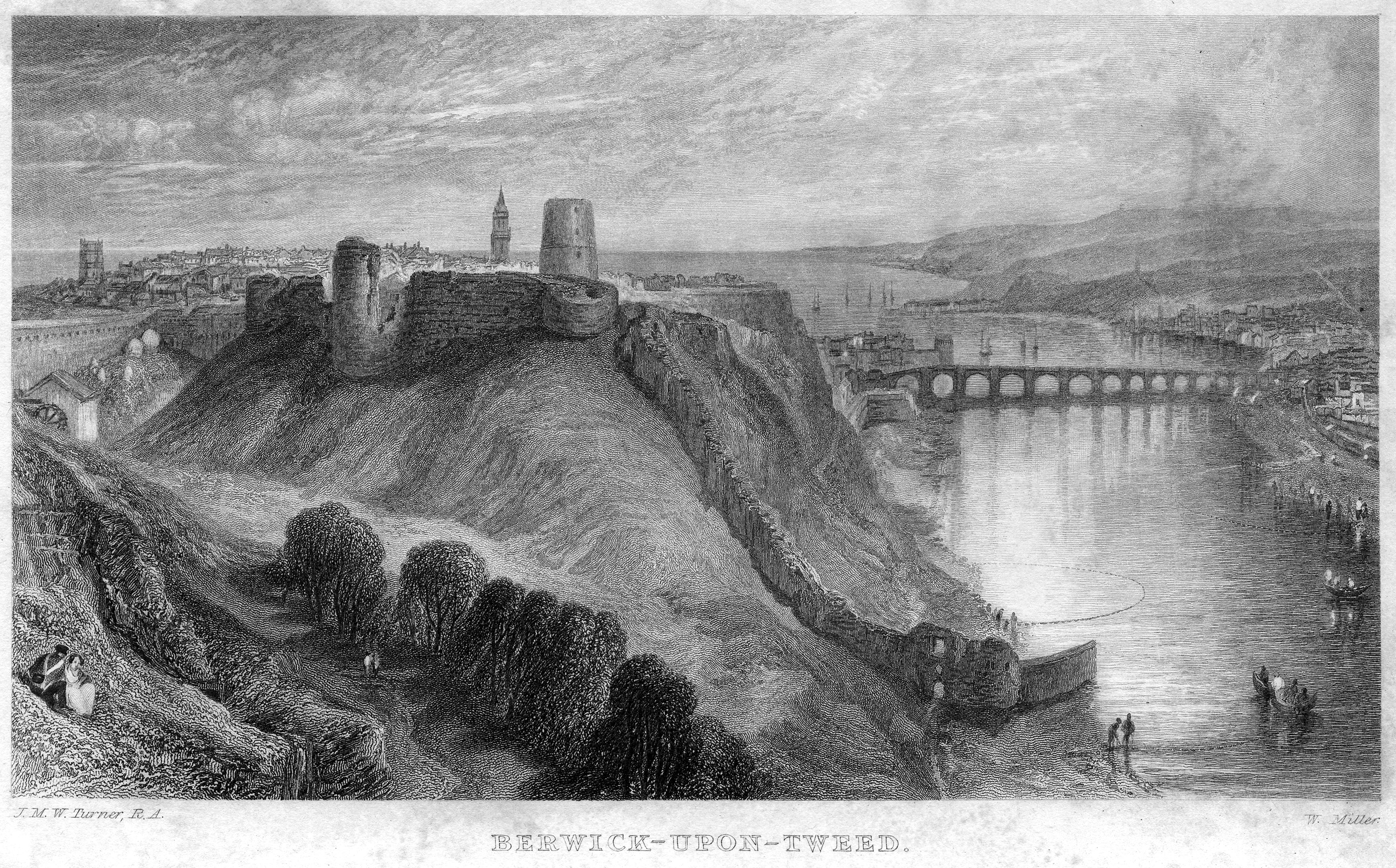
Berwick Castle
Berwick Castle is a ruined castle in Berwick-upon-Tweed, Northumberland, England. History The castle was commissioned by the Scottish King David I in the 1120s. It was taken by the English forces under the terms of the Treaty of Falaise in 1175 but then sold back to Scotland by the English King Richard I to fund the Third Crusade in around 1190. In November 1292, representatives of the English King Edward I arrived in Berwick and announced, in the great hall of the castle, King Edward's adjudication in favour of John Balliol of the dispute between him, Robert the Bruce and the count of Holland for the Crown of Scotland.Dunbar, Archibald H., ''Scottish Kings – A Revised Chronology of Scottish History 1005–1625'' (Edinburgh, 1899), p. 116 The castle was retaken by the forces of King Edward I in March 1296 during the First War of Scottish Independence. However, the forces of Robert the Bruce recovered the castle for Scotland in April 1318. In 1330, "Roberto de Lawedre" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
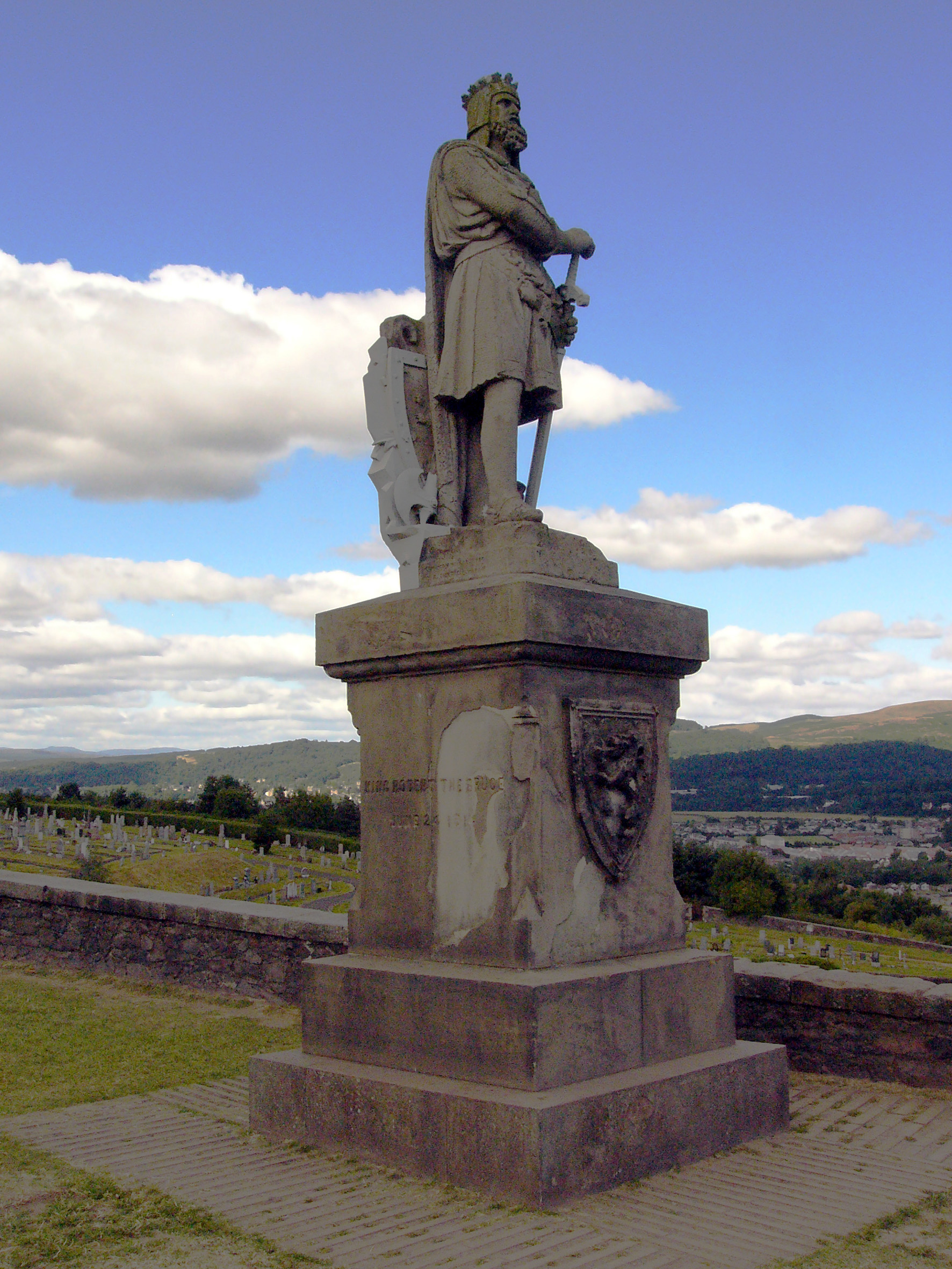
Roxburgh Castle
Roxburgh Castle is a ruined royal castle that overlooks the junction of the rivers Tweed and Teviot, in the Borders region of Scotland. The town and castle developed into the royal burgh of Roxburgh, which the Scots destroyed along with the castle after capturing it in 1460. Today the ruins stand in the grounds of Floors Castle, the seat of the Duke of Roxburghe, across the river from Kelso. History Tradition states that King David I founded the castle; it is first recorded in c.1128 during his reign. In 1174, it was surrendered to England after the capture of William I at Alnwick, and was often in English hands thereafter. The Scots made many attempts to regain the fortress. King Edward I of England imprisoned Mary Bruce in a cage hung outside the castle from 1306 to 1310. On 19 February 1314, it was retaken by Sir James Douglas (the "Black Douglas"), in a night attack. His men clothed in black cloaks were apparently mistaken for cattle. They then used rope and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy. Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular Normandy (mostly the British Channel Islands). It covers . Its population in 2017 was 3,499,280. The inhabitants of Normandy are known as Normans; the region is the historic homeland of the Norman language. Large settlements include Rouen, Caen, Le Havre and Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, Cherbourg. The cultural region of Normandy is roughly similar to the historical Duchy of Normandy, which includes small areas now part of the departments of Mayenne and Sarthe. The Channel Islands (French: ''Îles Anglo-Normandes'') are also historically part of Normandy; they cover and comprise two bailiwicks: Bailiwick of Guernsey, Guernsey and Jersey, which are British Crown Dependencies. Normandy's name comes from the settlement of the territory by Vikings ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
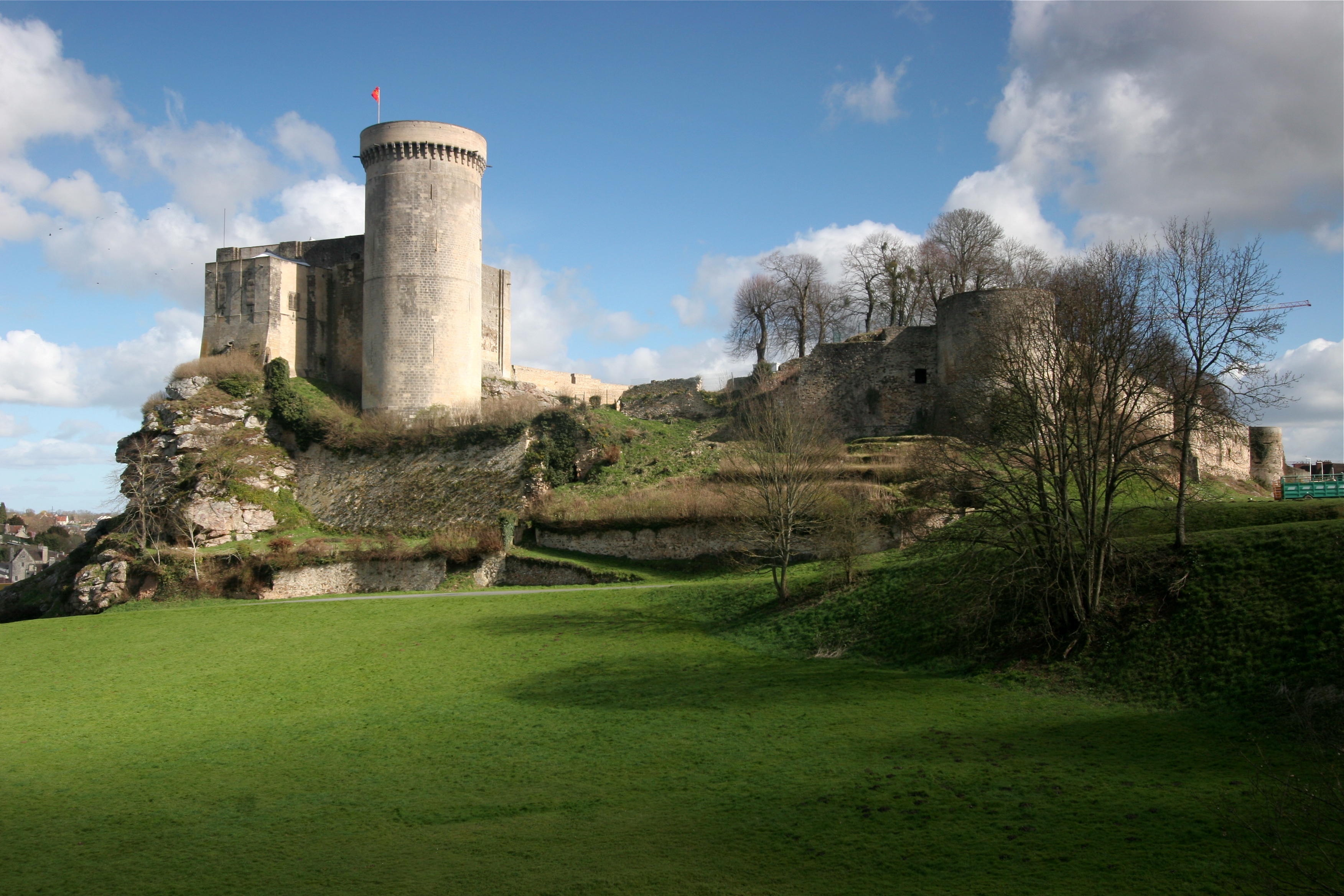
Falaise, Calvados
Falaise () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy Regions of France, region in northwestern France. The town is famous for being the birthplace of William I of England, William the Conqueror. It was also the centre of the area known as the Falaise pocket, the decisive engagement of the Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy in the World War II, Second World War. Geography Falaise lies at the eastern edge of the Armorican Massif, and the town has rocky outcrops on its edges such as the 173 metre high Mount Myrrha. The commune is spread over an area of with a maximum altitude of and minimum of Flowing through Falaise are the river Ante (river), Ante and the river Trainefeuille, both tributaries of the river Dives (river), Dives. Falaise borders the area known as Norman Switzerland, Suisse Normande, on its eastern side. Land distribution According to the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |