|
Battle At The Village
The Battle at The Village, also known as the Second Battle of Mobile, fought on January 7, 1781, was a failed British attempt to recapture a Spanish fortification at "The Village," during the American Revolutionary War. The attack was led by Waldecker Colonel Johann von Hanxleden who was killed in the attempt. Background After Spain declared war on Great Britain in 1779, Bernardo de Gálvez, the governor of Louisiana, immediately began offensive operations to gain control of neighboring West Florida, which included parts of today's Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. In September 1779 he gained complete control over the lower Mississippi River by capturing Fort Bute and shortly afterwards obtaining the surrender of the remaining enemy forces in the region following the Battle of Baton Rouge. He followed up these successes with the capture of Mobile on March 14, 1780, following a brief siege. (In the spring of 1781, Gálvez would go on to capture Pensacola, West Florida's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Coast Campaign
The Gulf Coast campaign or the Spanish conquest of West Florida in the American Revolutionary War, was a series of military operations primarily directed by the governor of Spanish Louisiana, Bernardo de Gálvez, against the British province of West Florida. Begun with operations against British positions on the Mississippi River shortly after Britain and Spain went to war in 1779, Gálvez completed the conquest of West Florida in 1781 with the successful siege of Pensacola. Background Spain officially entered the American Revolutionary War on May 8, 1779, with a formal declaration of war by King Charles III.This was after the Treaty of Aranjuez (1779) . This declaration was followed by another on 8 July that authorized his colonial subjects to engage in hostilities against the British. Gayarré (1867), p. 121 When Bernardo de Gálvez, the colonial Governor of Spanish Louisiana, received word of this on 21 July, he immediately began to secretly plan offensive operations. Gál ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the southwest, and Arkansas to the northwest. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River, or its historical course. Mississippi is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 32nd largest by area and List of U.S. states by population, 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income. Jackson, Mississippi, Jackson is both the state's List of capitals in the United States, capital and largest city. Jackson metropolitan area, Mississippi, Greater Jackson is the state's most populous Metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan area, with a population of 591,978 2020 United States census, in 2020. Other major cities include Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Southaven, Mississippi, South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were refugee colonists from Thirteen Colonies, thirteen of the 20 British American colonies who remained loyal to the British Crown, British crown during the American Revolution, often referred to as Tories, Royalists, or King's Men at the time. They were opposed by the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriots or Whigs, who supported the revolution and considered them "persons inimical to the liberties of America." Prominent Loyalists repeatedly assured the Government of the United Kingdom, British government that many thousands of them would spring to arms and fight for the Crown. The British government acted in expectation of that, especially during the Southern theater of the American Revolutionary War, Southern campaigns of 1780 and 1781. Britain was able to effectively protect the people only in areas where they had military control, thus the number of military Loyalists was significantly lower than what had been expected. Loyalists were often under suspicion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenadiers
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word ''grenade'') was historically an assault-specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in siege operation battles. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited from among the strongest and largest soldiers. By the 18th century, the grenadier dedicated to throwing hand grenades had become a less necessary specialist, yet in battle, the grenadiers were the physically robust soldiers who led vanguard assaults, such as storming fortifications in the course of siege warfare. Certain countries such as France ( Grenadiers à Cheval de la Garde Impériale) and Argentina ( Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers) established units of Horse Grenadiers, and for a time the British Army had Horse Grenadier Guards. Like their infantry grenadier counterparts, these horse-mounted soldiers were chosen for their size and strength (heavy cavalry). In modern warfare, a grenadier is a specially tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
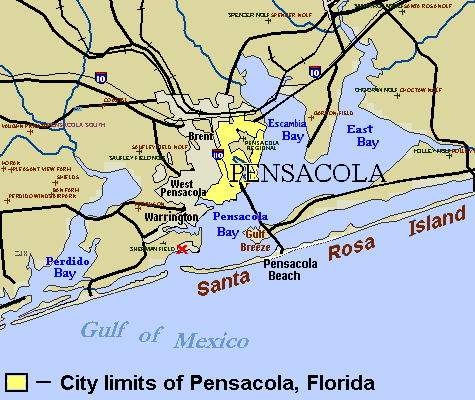
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only incorporated city, city in Escambia County, Florida, Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which had 509,905 residents in the 2020 census. Pensacola was first settled by the Spanish Empire in 1559, antedating the establishment of St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine by six years, but was abandoned due to a significant hurricane and not resettled until 1698. Pensacola is a Port of Pensacola, seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa Island (Florida), Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large Naval Air Station Pensacola, United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located in Pensacola. It is the base of the Blue Angels flight-demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The Mobile River and Tensaw River empty into the northern end of the bay, making it an estuary. Several smaller rivers also empty into the bay: Dog River, Deer River, and Fowl River on the western side of the bay, and Fish River on the eastern side. Mobile Bay is the fourth-largest estuary in the United States with a discharge of of water per second. Annually, and often several times during the summer months, the fish and crustaceans will swarm the shallow coastline and shore of the bay. This event, appropriately named a jubilee, draws a large crowd because of the abundance of fresh, easily caught seafood. Mobile Bay is in area. It is long by a maximum width of . The deepest areas of the bay are located within the shipping channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outpost (military)
In military terminology, an outpost is a location where detachments of military personnel are stationed at a distance from the main armed force or formation in a region. Outposts are usually located in remote or sparsely populated areas, positioned to observe and defend against unauthorized intrusions and surprise attacks, serving as the first line of defense. The station occupied by such troops, usually a small military base or settlement in an outlying frontier, limit, political boundary or in another country. Outposts can also be called miniature military bases based on size and number of troops it houses. Oldest known use is from the 16th century "station when on duty, a fixed position or place," 1590s, from French poste "place where one is stationed," Recent military use Military outposts, most recently referred to as combat outposts (COPs), served as a cornerstone of counterinsurgency doctrine in Iraq and Afghanistan. These permanent or semi-permanent structures, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which combatants are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. It became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front starting in September 1914.. Trench warfare proliferated when a Weapons of World War I, revolution in firepower was not matched by similar advances in mobility (military), mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. On the Western Front in 1914–1918, both sides constructed elaborate trench, underground, and dugout (shelter), dugout systems opposing each other along a front (military), front, protected from assault by barbed wire. The area between opposing trench lines (known as "no man's land") was fully exposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pensacola
The siege of Pensacola, fought from March 9 to May 10, 1781, was the culmination of Spain's conquest of West Florida during the Gulf Coast Campaign of the American Revolutionary War. The siege was commanded by Bernardo de Gálvez, whose nearly 8,000 troops ultimately overran the British forces in the region. The success of the siege resulted in Gálvez' promotion to governor of West Florida and Louisiana. Background When Spain entered the American Revolutionary War in 1779, Bernardo de Gálvez, the energetic governor of Spanish Louisiana, immediately began offensive operations to gain control of West Florida beginning with his assault at Fort Bute. In September 1779 he gained control over the lower Mississippi River by capturing Fort Bute and then shortly thereafter obtaining the surrender of the remaining forces following the Battle of Baton Rouge. He followed up these successes with the capture of Mobile on March 14, 1780, after a brief siege. Gálvez began planning an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fort Charlotte
The Battle of Fort Charlotte, also known as the siege of Fort Charlotte, was a two-week siege conducted by Spanish general Bernardo de Gálvez against the Kingdom of Great Britain, British fortifications guarding the port of Mobile, Alabama, Mobile, (which was then in the British province of British West Florida, West Florida, and now in Alabama) during the Spain in the American Revolutionary War, Anglo-Spanish War of 1779-1783. Fort Charlotte (Mobile), Fort Charlotte was the last remaining British frontier post capable of threatening New Orleans, Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana. Its fall drove the British from the western reaches of West Florida and reduced the British military presence in West Florida to its capital, Pensacola, Florida, Pensacola. Gálvez's army sailed from New Orleans aboard a small fleet of transports on January 28, 1780. On February 25, the Spaniards landed near Fort Charlotte. The outnumbered British garrison resisted stubbornly until Spanish bombardment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Baton Rouge (1779)
The Battle of Baton Rouge was a brief siege during the Anglo-Spanish War that was decided on September 21, 1779. Fort New Richmond (present-day Baton Rouge, Louisiana) was the second British outpost to fall to Spanish arms during Bernardo de Gálvez's march into West Florida. Background Spain officially entered the American Revolutionary War on May 8, 1779, with a formal declaration of war by King Charles III. This declaration was followed by another on July 8 that authorized his colonial subjects to engage in hostilities against the British. Gayarré (1867), p. 121 When Colonel Bernardo de Gálvez, the colonial Governor of Spanish Louisiana received word of this on July 21, he immediately began to plan offensive operations to take West Florida. Gayarré (1867), p. 122 Fort Bute On August 27, Gálvez set out by land toward Fort Bute, leading a force that consisted of 520 regulars, of whom about two-thirds were recent recruits, 60 militiamen, 80 free blacks and mulattoes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |