|
Barber's Pole
A barber's pole is a type of Signage, sign used by barbers to signify the place or shop where they perform their craft. The trade sign is, by a tradition dating back to the Middle Ages, a staff or :wikt:pole, pole with a helix of colored Stripe (pattern), stripes (often red and white in many countries, but usually red, white and blue in Canada, Japan, the Philippines, South Korea, Vietnam, and the United States). The pole may be stationary or may rotate, often with the aid of an electric motor. The consistent use of this advertising symbol can be seen as analogous to an apothecary's show globe, a tobacconist's cigar store IndianThe Freelance Star (Sep 11, 1982) ''Cigar Store Indian was Early Advertising Sign'' Ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Lighthouses mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, rocks, and safe entries to harbors; they also assist in aerial navigation. Once widely used, the number of operational lighthouses has declined due to the expense of maintenance and the advent of much cheaper, more sophisticated, and more effective electronic navigational systems. History Ancient lighthouses Before the development of clearly defined ports, mariners were guided by fires built on hilltops. Since elevating the fire would improve visibility, placing the fire on a platform became a practice that led to the development of the lighthouse. In antiquity, the lighthouse functioned more as an entrance marker to ports than as a warning signal for reefs and promontory, prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Innocent II
Pope Innocent II (; died 24 September 1143), born Gregorio Papareschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 February 1130 to his death in 1143. His election as Pope was controversial, and the first eight years of his reign were marked by a struggle for recognition against the supporters of Anacletus II. He reached an understanding with King Lothair III of Germany, who supported him against Anacletus, and whom he crowned as Holy Roman Emperor. Innocent went on to preside over the Second Council of the Lateran. Early years Gregorio Papareschi came from a Roman family, probably of the ''rione'' Trastevere. Formerly a Cluniac monk, he was made cardinal deacon of Sant'Angelo in 1116 by Pope Paschal II. Gregorio was selected by Pope Callixtus II for various important and difficult missions, such as the one to Worms for the conclusion of the Concordat of Worms, the peace accord made with Holy Roman Emperor Henry V in 1122, and also the one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical and religious tradition rooted in the teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, a syncretism, syncretic figure combining elements of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth. This system encompasses a wide range of Western esotericism, esoteric knowledge, including aspects of alchemy, astrology, and theurgy, and has significantly influenced various mystical and occult traditions throughout history. The writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, often referred to as the ''Hermetica'', were produced over a period spanning many centuries () and may be very different in content and scope. One particular form of Hermetic teaching is the religio-philosophical system found in a specific subgroup of Hermetic writings known as the Hermetica#Religio-philosophical Hermetica, 'religio-philosophical' ''Hermetica''. The most famous of these are the ''Corpus Hermeticum'', a collection of seventeen Ancient Greek, Greek treatises written b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Mercurius Van Helmont
Franciscus Mercurius van Helmont (baptised 20 October 1614 – December 1698) was a Flemish alchemist and writer, the son of Jan Baptist van Helmont. He is now best known for his publication in the 1640s of his father's pioneer works on chemistry, which link the origins of the science to the study of alchemy. From his early work as a physician, he became a kabbalist and together with Henry More of the Cambridge Platonists he annotated Christian Knorr von Rosenroth's translations of kabbalist texts. Contacts and movement He led an itinerant life in wanderings in Europe, an adjective already applied to him by Anthony Ashley-Cooper, 3rd Earl of Shaftesbury in his 1711 '' Characteristicks of Men, Manners, Opinions, Times''. He self-identified as a "wandering eremite". Franciscus van Helmont had important groups of contacts in the Netherlands, where he knew Adam Boreel and Serrarius, and later in life, in 'the Lantern', the circle around the Rotterdam merchant Benjamin Furly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes
Hermes (; ) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife. In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. He is regarded as "the divine trickster", about which the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' offers the most well-known account. Hermes's attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, talaria (winged sandals), and winged helmet or simple petasos, as well as the palm tree, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. However, his main symbol is the ''caduceus'', a wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; , ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was borne by other heralds like Iris (mythology), Iris, the messenger of Hera. The short staff is entwined by two serpent (mythology), serpents, sometimes surmounted by wings. In Roman iconography, it was depicted being carried in the left hand of Mercury (mythology), Mercury, the messenger of the gods. Some accounts assert that the oldest imagery of the caduceus is rooted in Mesopotamia with the Sumerian god Ningishzida; his symbol, a staff with two snakes intertwined around it, dates back to 4000 BC to 3000 BC. This iconography may have been a representation of two snakes copulating. As a symbol, it represents Hermes (or the Roman Mercury), and by extension trades, occupations, or undertakings associated with the god. In later Classical antiquity, Antiquity, the caduceus provided the basis for the astronomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motif (visual Arts)
In art and iconography, a motif () is an element of an image. Motifs can occur both in figurative and narrative art, and in ornament and geometrical art. A motif may be repeated in a pattern or design, often many times, or may just occur once in a work. A motif may be an element in the iconography of a particular subject or type of subject that is seen in other works, or may form the main subject, as the Master of Animals motif in ancient art typically does. The related motif of confronted animals is often seen alone, but may also be repeated, for example in Byzantine silk and in other ancient textiles. Where the main subject of an artistic work - such as a painting - is a specific person, group, or moment in a narrative, that should be referred to as the "subject" of the work, not a motif, though the same thing may be a "motif" when part of another subject, or part of a work of decorative art - such as a painting on a vase. Ornament (art), Ornamental or decorative art ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid; the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels. The majority of leeches live in freshwater habitats, while some species can be found in terrestrial or marine environments. The best-known species, such as the medicinal leech, ''Hirudo medicinalis'', are hematophagous, attaching themselves to a host with a sucker and feeding on blood, having first secreted the pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wash Basin
A sink (also known as ''basin'' in the UK) is a bowl-shaped plumbing fixture for washing hands, dishwashing, and other purposes. Sinks have a tap (faucet) that supplies hot and cold water and may include a spray feature to be used for faster rinsing. They also include a drain to remove used water; this drain may itself include a strainer and/or shut-off device and an overflow-prevention device. Sinks may also have an integrated soap dispenser. Many sinks, especially in kitchens, are installed adjacent to or inside a counter. When a sink becomes clogged, a person will often resort to using a chemical drain cleaner or a plunger, though most professional plumbers will remove the clog with a ''drain auger'' (often called a "plumber's snake"). History United States The washstand was a bathroom sink made in the United States in the late 18th century. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. In use since prehistoric times, it is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure. Brass is similar to bronze, a copper alloy that contains tin instead of zinc. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other Chemical element, elements including arsenic, lead, phosphorus, aluminium, manganese and silicon. Historically, the distinction between the two alloys has been less consistent and clear, and increasingly museums use the more general term "list of copper alloys, copper alloy". Brass has long been a popular material for its bright gold-like appearance and is still used for drawer pulls and door handle, doorknobs. It has also been widely used to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
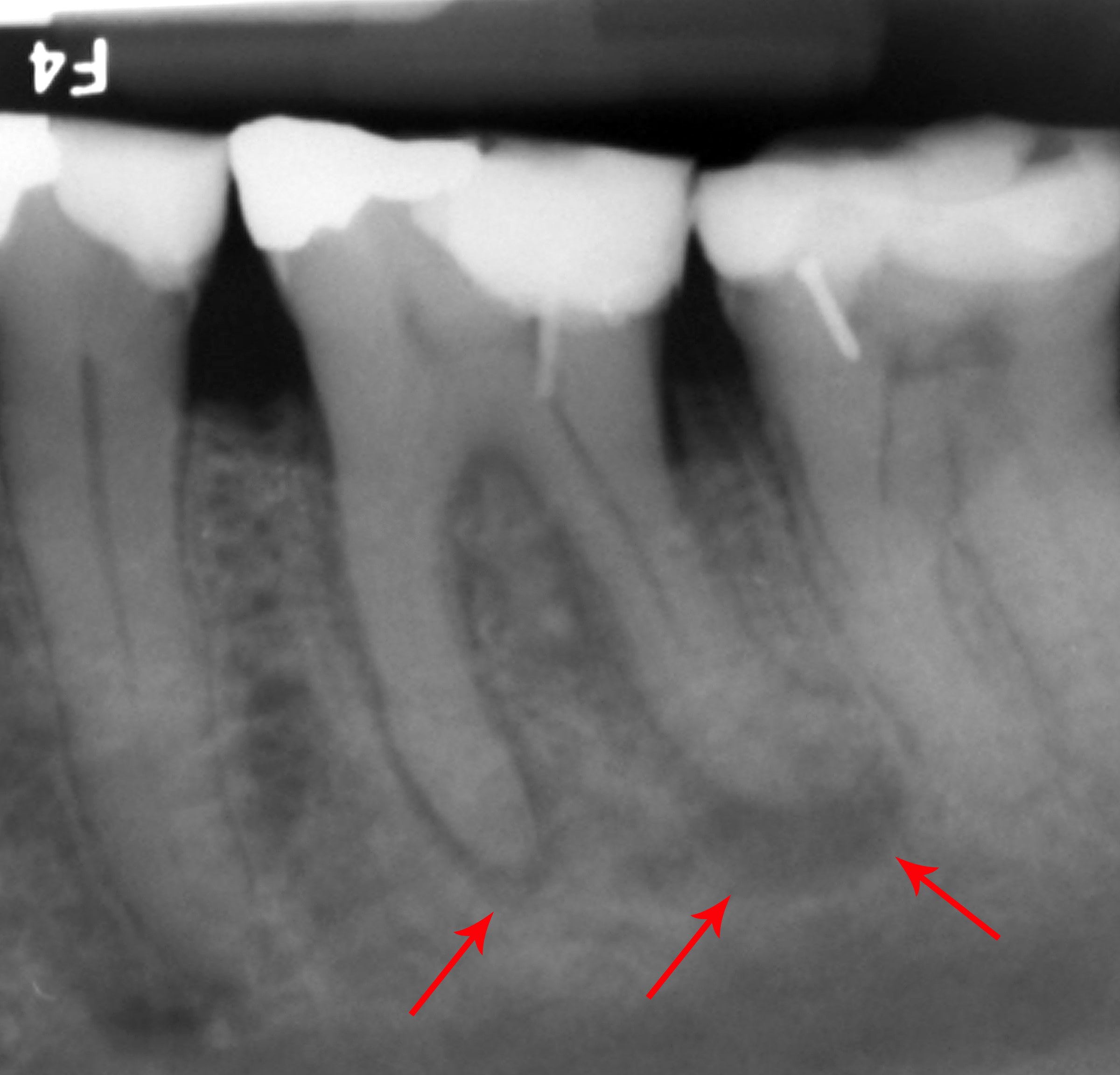
Tooth Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum ( pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |