|
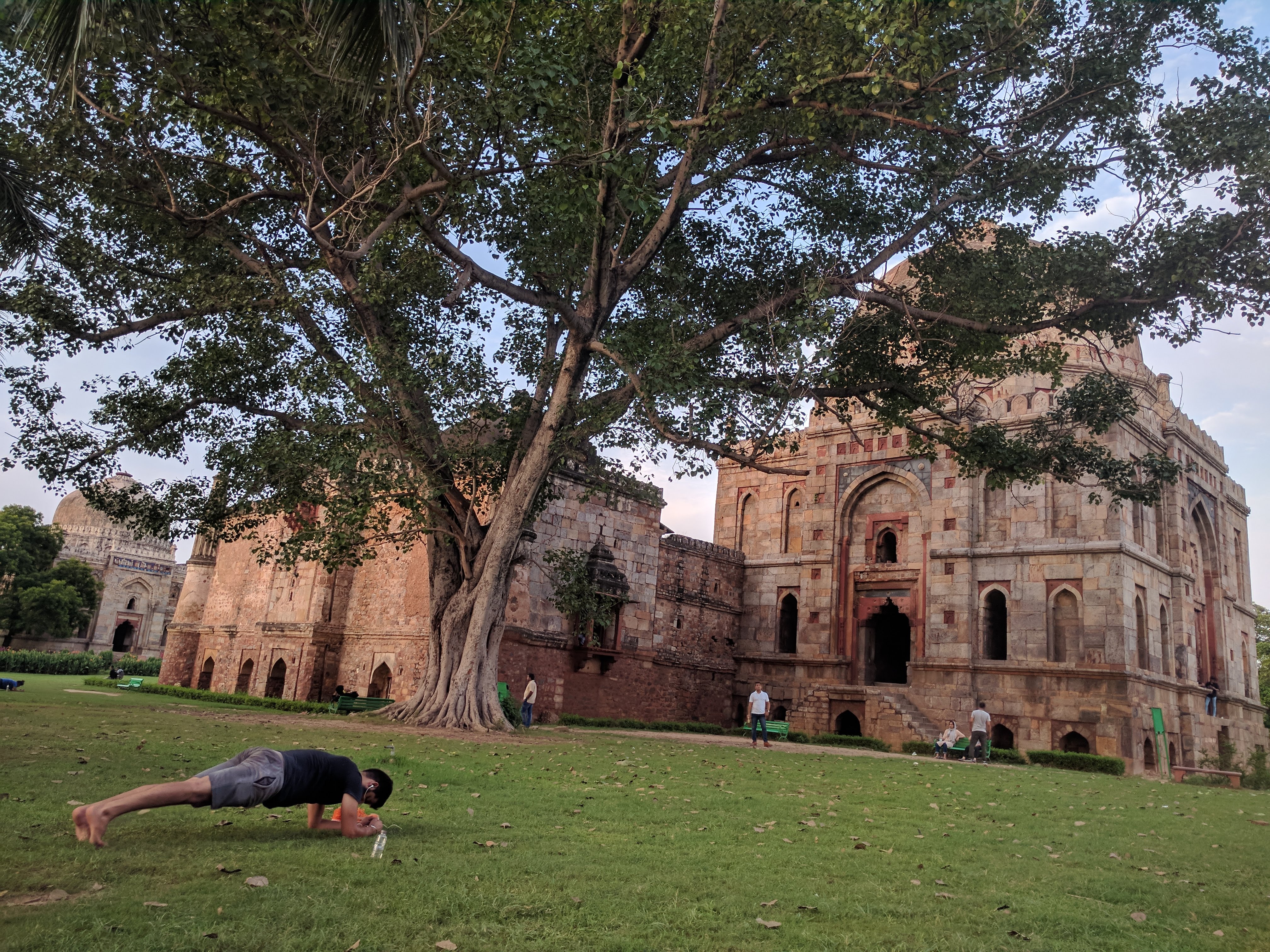
Bara Gumbad Mosque
The Bara Gumbad () is a medieval monument located in Lodi Gardens in Delhi, India. It is part of a group of monuments that include a Friday mosque (Jama Masjid) and the "''mehman khana''" (guest house) of Sikandar Lodi, the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate. The Bara Gumbad was constructed in 1490 Common Era, CE, during the reign of the Lodi dynasty. Its construction is generally attributed to Sikandar Lodi, and it is believed to have the earliest constructed full dome of any building in Delhi. The monument is situated near the Tomb of Sikandar Lodi and Shisha Gumbad. Although the three structures, which share a common raised platform, were all built during the Lodi reign, they were not constructed at the same time. The intended purpose of the builders of Bara Gumbad is unclear: it may have been intended as a free-standing tomb, but no tombstone has been identified, or as a gateway. The area in which Bara Gumbad is situated was formally called Khairpur village. Bara Gumbad and the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodi Gardens
Lodi Gardens is a city park situated in New Delhi. Spread over , it contains Muhammad Shah IV, Muhammad Shah's tomb, the tomb of Sikandar Lodi, the Shisha Gumbad and the Bara Gumbad. These monuments date from the late Delhi Sultanate, during the Sayyid dynasty () and Lodi dynasty (). At this time, the Delhi Sultanate's territory included parts of present-day North India and the Pakistani provinces of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. As there is little architecture dating to the Sayyid and the Lodi periods still standing, Lodi Gardens is an important archaeological site, and is protected by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). The gardens are situated between Khan Market and Safdarjung's Tomb on Lodi Road and are a popular spot for morning walks for Delhiites. Architecture In the middle of the gardens is the Bara Gumbad (), consisting of a large rubble-construct dome and is not a tomb but was constructed as a gateway to either the attached three domed (mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
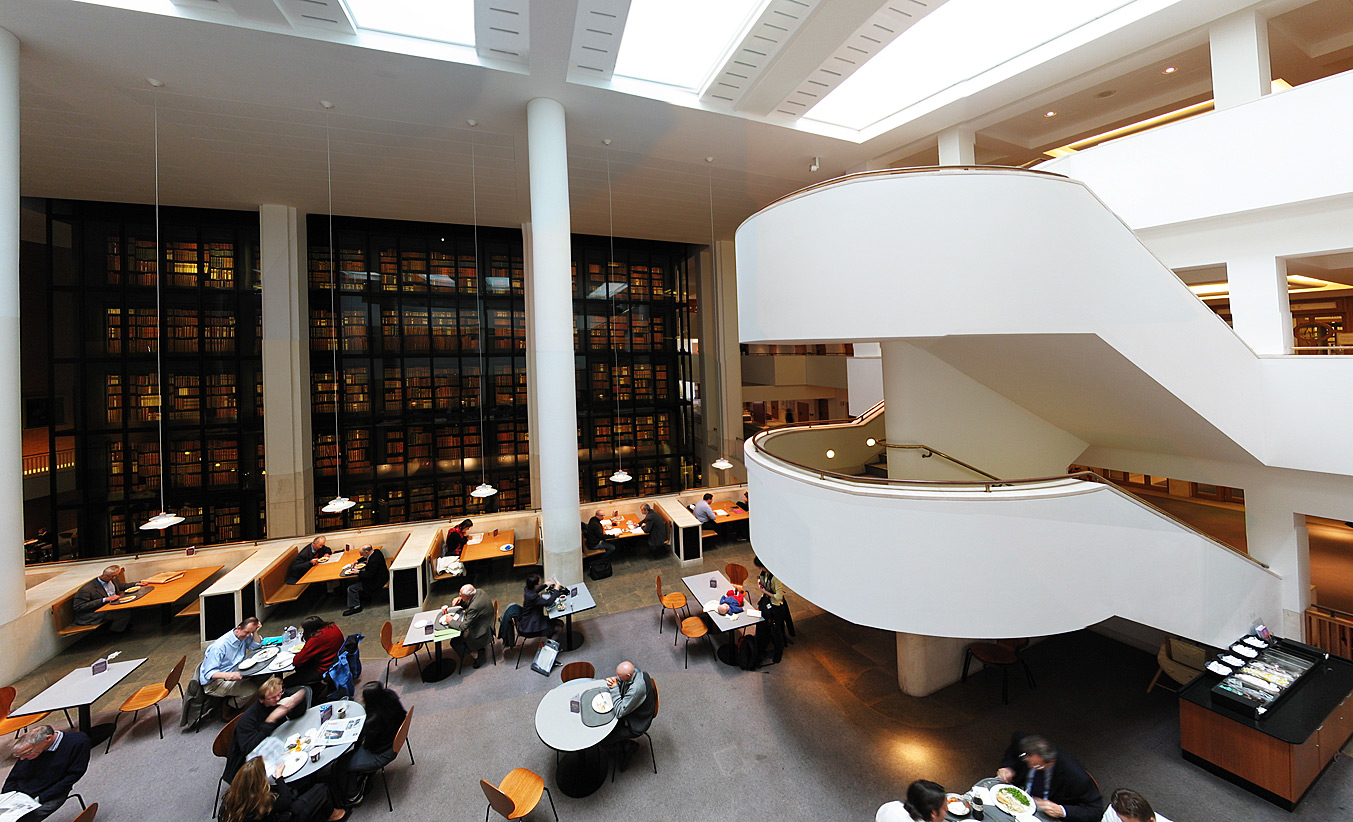
British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom. Based in London, it is one of the largest libraries in the world, with an estimated collection of between 170 and 200 million items from multiple countries. As a legal deposit library, it receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, as well as a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the United Kingdom. The library operates as a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The British Library is a major research library, with items in many languages and in many formats, both print and digital: books, manuscripts, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, videos, play-scripts, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings. The Library's collections include around 14 million books, along with substantial holdings of manuscripts and items dating as far back as 2000 BC. The library maintains a programme for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyid Dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See: * M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill * The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion into South Asia, Journal of South Asian Studies, 4(1), pp. 91–109 * Sookoohy M., Bhadreswar – Oldest Islamic Monuments in India, , Brill Academic; see discussion of earliest raids in Gujarat The first ruler of the dynasty, Khizr Khan, who was the Timurid vassal of Multan, conquered Delhi in 1414, while the rulers proclaimed themselves the Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate under Mubarak Shah, which succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled the Sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty in 1451. Origins A contemporary writer Yahya Sirhindi mentions in his ''Tarikh-i-Mubarak Shahi'' that Khizr Khan was a descendant of Muhammad. Members of the dynasty derived their title, Sayyid, or the descendants of the Islamic prophet Muh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihrab
''Mihrab'' (, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "''qibla'' wall". The '' minbar'', which is the raised platform from which an imam (leader of prayer) addresses the congregation, is located to the right of the ''mihrab''. Etymology The origin of the word ''miḥrāb'' is complicated, and multiple explanations have been proposed by different sources and scholars. It may come from Old South Arabian (possibly Sabaic) ''mḥrb'' meaning a certain part of a palace, as well as "part of a temple where ''tḥrb'' (a certain type of visions) is obtained," from the root word ''ḥrb'' "to perform a certain religious ritual (which is compared to combat or fighting and described as an overnight retreat) in the ''mḥrb'' of the temple." It may also possibly be related to Ethiopic ''məkʷrab'' "temple, sanctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Monuments Fund
World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a private, international, non-profit organization dedicated to the preservation of historic architecture and cultural heritage sites around the world through fieldwork, advocacy, grantmaking, education, and training. Founded in 1965, WMF is headquartered in New York, and has offices and affiliates around the world, including Cambodia, France, Peru, Portugal, Spain, and the United Kingdom. In addition to hands-on management, the affiliates identify, develop, and manage projects, negotiate local partnerships, and attract local support to complement funds provided by donors. History International Fund for Monuments (1965–1984) The International Fund for Monuments (IFM) was an organization created by Colonel James A. Gray (1909–1994) after his retirement from the U.S. Army in 1960. Gray had conceived of a visionary project to arrest the settlement of the Leaning Tower of Pisa by freezing the soil underneath, and he formed the organization in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monuments Of National Importance (India)
This article contains lists of Monuments of National Importance in India. An Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 defines an "Ancient Monument" as follows: A "Monument of National Importance" is designated by the Archaeological Survey of India and includes the following: #The remains of an ancient monument #The site of an ancient monument #The land on which there are fences or protective covering structures for preserving the monument #Land by means of which people can freely access the monument #monument is something that show our history our strength and our power. Table of monuments The Monuments of National Importance are designated by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). The union government of India is authorised to maintain, protect and promote the Monuments of National Importance. See also * State Protected Monuments of India * National Geological Monuments of India * List of World Heritage Sites in India * List of Water Heritage Sites in India * List o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb
A tomb ( ''tumbos'') or sepulchre () is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called '' immurement'', although this word mainly means entombing people alive, and is a method of final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial. Overview The word is used in a broad sense to encompass a number of such types of places of interment or, occasionally, burial, including: * Architectural shrines – in Christianity, an architectural shrine above a saint's first place of burial, as opposed to a similar shrine on which stands a reliquary or feretory into which the saint's remains have been transferred * Burial vault – a stone or brick-lined underground space for multiple burials, originally vaulted, often privately owned for specific family groups; usually beneath a religious building such as a * Church * Cemetery * Churchyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shisha Gumbad
Shish Gumbad ("glazed dome"), also spelt Shisha Gumbad, is a tomb from the Lodi dynasty and is thought to have possibly been constructed between 1489 and 1517 CE; the historian Simon Digby has argued on the basis of an inscription in the adjoining mosque that it was completed in 1494 CE. Simon Digby, ''The Tomb of Buhlul Lodi'', The Bulletin of SOAS, Vol. 38, No. 3, 1975, pp. 550–61. The Shish Gumbad (glass dome) houses graves, whose occupants are not unequivocally identifiable. Historians have suggested, the structure might have been dedicated either to an unknown family, which was part of the Lodi family and of Sikandar Lodi's court, or to Bahlul Lodi (died 12 July 1489) himself, who was chief of the Afghan Lodi tribe, founder and Sultan of the Lodi dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate. Simon Digby, ''The Tomb of Buhlul Lodi'', The Bulletin of SOAS, Vol. 38, No. 3, 1975, pp. 550–61. Shish Gumbad is situated in the Lodi Gardens in Delhi and the area where the tomb is situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Sikandar Lodi
The Tomb of Sikandar Lodi is the tomb of the second ruler of the Lodi Dynasty, Sikandar Lodi (reign: 1489–1517 CE) situated in New Delhi, India. The tomb is situated in Lodi Gardens in Delhi and was built in 1517–1518 CE by his son Ibrahim Lodi. The monument is situated 100 meters away from the Bara Gumbad and the area in which it is situated was formerly a village called Khairpur. History Sikandar Khan Lodi (born Nizam Khan), was the Sultan of Delhi between 1489 and 1517 CE and was the son of Bahlul Lodi. After the death of his father in 1489, Sikandar Lodi assumed the reign the same year and ruled until his death in 1517 CE. Upon Sikandar Lodi's death in 1517 CE, his son Ibrahim Lodi built the tomb. The Tomb of Sikandar Lodi was inspired in part by the tomb of Muhammad Shah which is also situated in the Lodi Gardens. Construction and Architecture The Tomb of Sikandar Lodi was inspired in parts by the tomb of Muhammad Shah. It has octagonal design and the architectural s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
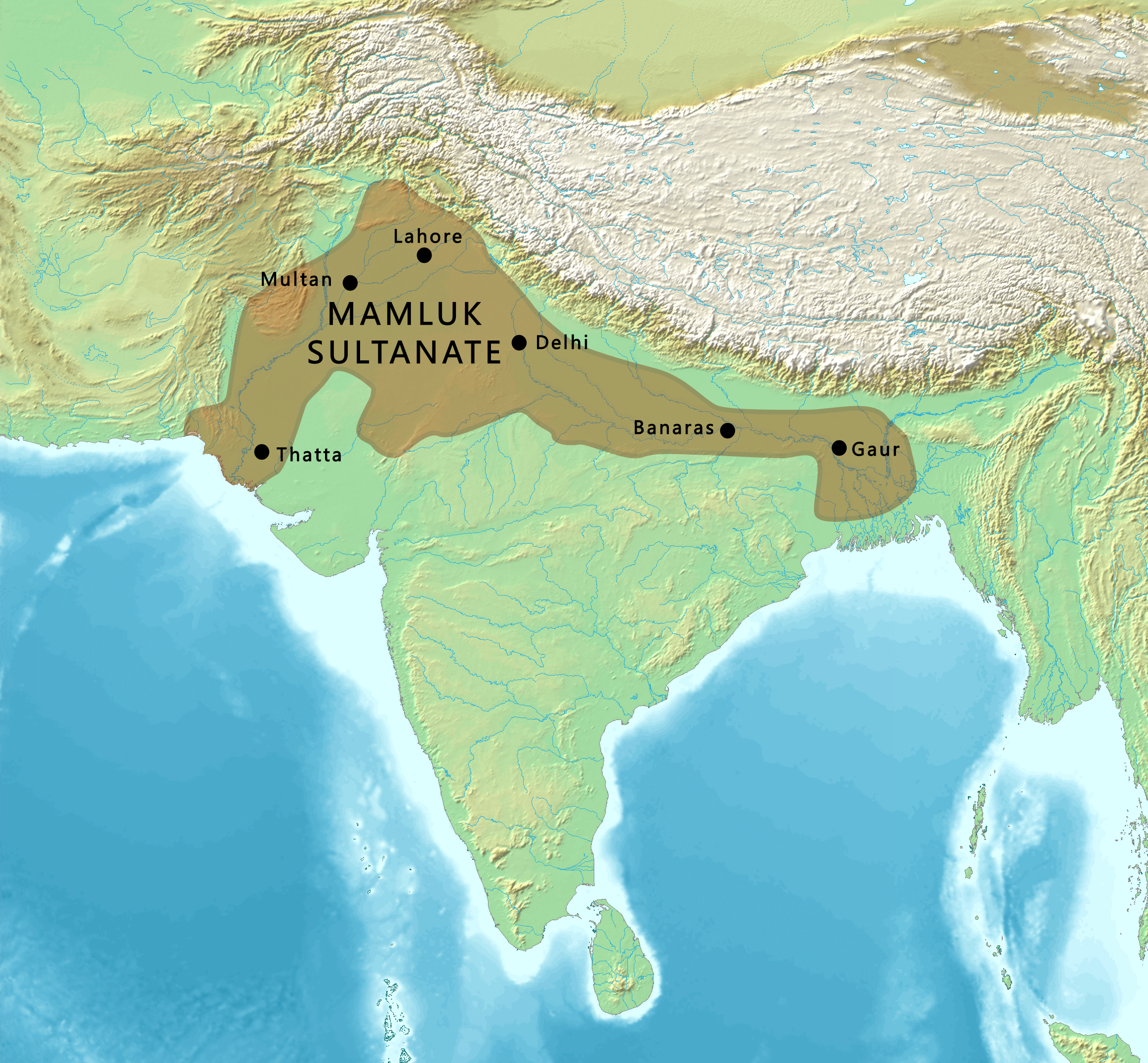
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friday Mosque
A congregational mosque or Friday mosque (, ''masjid jāmi‘'', or simply: , ''jāmi‘''; ), or sometimes great mosque or grand mosque (, ''jāmi‘ kabir''; ), is a mosque for hosting the Friday noon prayers known as ''jumu'ah''.See: * * * * * * * * * It can also host the Eid prayers in situations when there is no '' musalla'' or '' eidgah'' available nearby to host the prayers. In early Islamic history, the number of congregational mosques in one city was strictly limited. As cities and populations grew over time, it became more common for many mosques to host Friday prayers in the same area. Etymology The full Arabic term for this kind of mosque is ''masjid jāmi‘'' (), which is typically translated as "mosque of congregation" or "congregational mosque". "Congregational" is used to translate ''jāmi‘'' (), which comes from the Arabic root "ج - م - ع" which has a meaning ‘to bring together’ or ‘to unify’ (verbal form: and ). In Arabic, the term is typically s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |