|
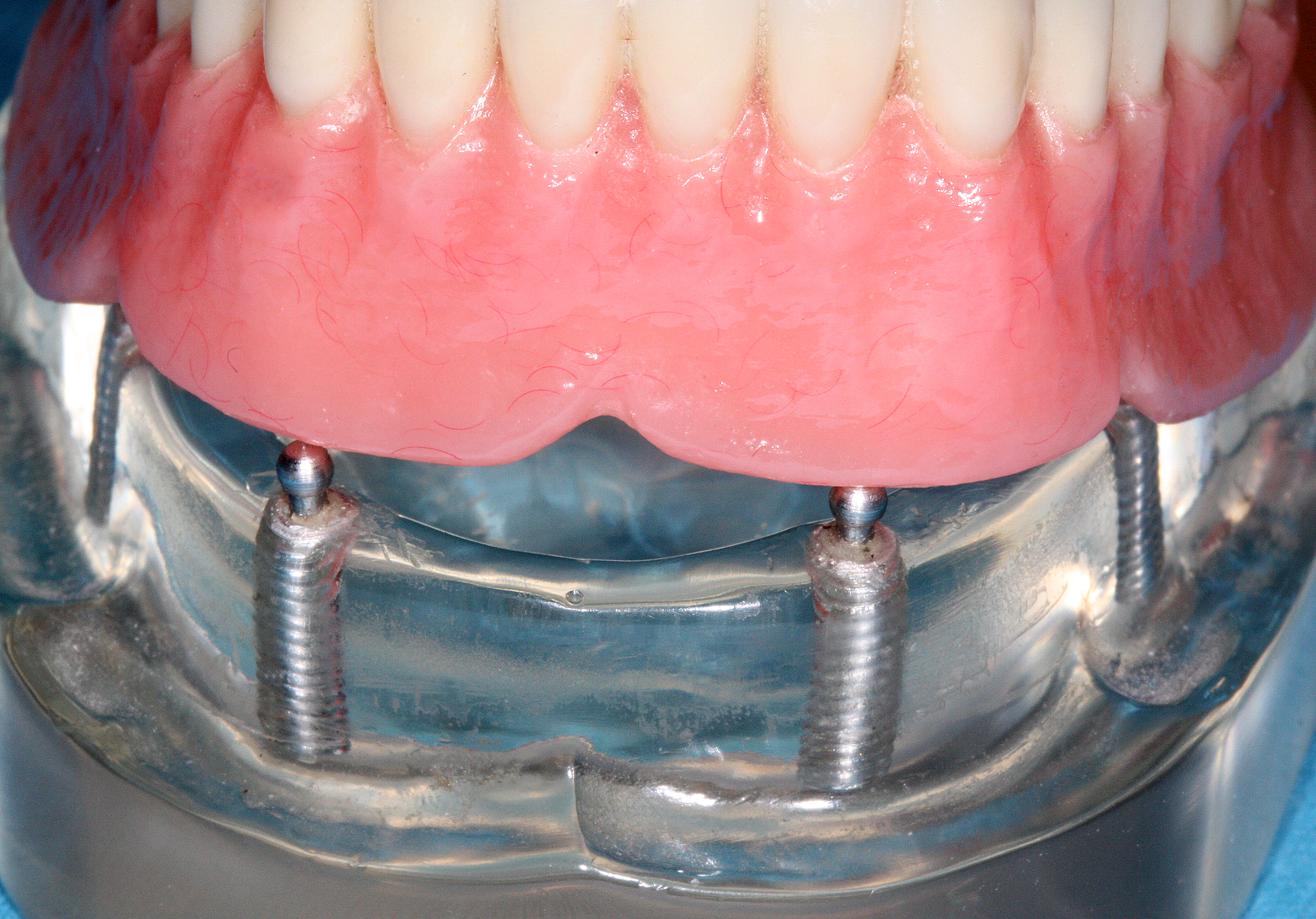
Ball Attachment (dentistry)
A ball attachment is a dental component commonly used in implant-retained and tooth-supported overdentures to enhance prosthetic retention, stability, and function. It consists of a ball-shaped male abutment that fits into a corresponding female housing, creating a mechanical connection that allows controlled movement while maintaining secure placement. Design and Components Ball attachments function as precision mechanical retention devices in dental prostheses. They typically consist of: * Male Component (Ball Abutment) – A spherical attachment fixed onto a dental implant, a natural tooth root, or a bar structure. It is available in various sizes and materials, including titanium and gold-plated alloys. * Female Component (Housing and Retentive Insert) – A socket-like structure embedded within the denture, often lined with a replaceable retentive insert made of nylon or other resilient materials. The insert provides flexibility and retention, gripping the ball abutment secure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdenture
Overdenture is any removable dental prosthesis that covers and rests on one or more remaining natural teeth, the roots of natural teeth, and/or dental implants. It is one of the most practical measures used in preventive dentistry. Overdentures can be either tooth supported (conventional / immediate) or implant supported. It is found to help in the preservation of alveolar bone and delay the process of complete edentulism. An overdenture is a denture, the base of which covers one or more teeth, prepared roots or implants. An overdenture is usually used for elderly patients that have lost some teeth but not all, rendering them suitable for a set of full dentures. The overdenture is not rigid in the mouth; it is removable. An advantage of overdentures compared to full dentures is that the roots left in the maxilla (upper jaw) help preserve bone of the upper jaw, preventing bone resorption. Another advantage is that the sensory aspect is improved. The nerves in the roots are still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes. These are the cells responsible for the resorption of bone. Osteoblasts are generally present on the outer layer of bone, just beneath the periosteum. Attachment of the osteoclast to the osteon begins the process. The osteoclast then induces an infolding of its cell membrane and secretes collagenase and other enzymes important in the resorption process. High levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphate and products of collagen will be released into the extracellular fluid as the osteoclasts tunnel into the mineralized bone. Osteoclasts are prominent in the tissue destruction found in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatological disorders. The human body is in a constant state of bone re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |