|
Baku–Rostov Highway Bombing
The Baku–Rostov highway bombing was an incident which occurred near the village of Shaami-Yurt in Chechnya, on October 29, 1999. Two low-flying Russian aircraft carried out repeated rocket attacks on a large convoy of refugees trying to enter the Russian republic of Ingushetia through a supposed "safe exit" route. The attacks killed or injured scores of people. Incident The incident took place after it was officially announced that the border between Chechnya and Ingushetia would re-open following a week's closure. However, the convoy of more than 1,000 vehicles heading to safety was not permitted to cross the border and ordered to turn back by an unidentified senior Russian military officer (the area was under responsibility of Gen. Vladimir Shamanov), and subsequently attacked on their way back to the besieged Chechen capital Grozny. According to the Amnesty International report, "at the time of the Russian attacks there were no legitimate military targets in the area. Eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
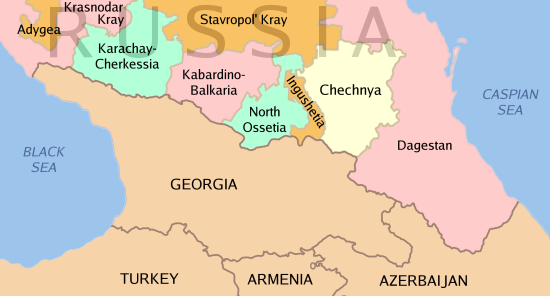
Chechnya
Chechnya, officially the Chechen Republic, is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia. It is situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, between the Caspian Sea and Black Sea. The republic forms a part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with Georgia (country), Georgia to its south; with the Russian republics of Dagestan, Ingushetia, and North Ossetia–Alania to its east, north, and west; and with Stavropol Krai to its northwest. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Chechnya and Ingushetia in the Soviet Union, Checheno-Ingush ASSR split into two parts: the Republic of Ingushetia and the Chechen Republic. The latter proclaimed the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, which declared independence, while the former sided with Russia. Following the First Chechen War of 1994–1996 with Russia, Chechnya gained ''de facto'' independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, although ''de jure'' it remained a part of Russia. Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grozny (1999–2000)
The 1999–2000 battle of Grozny or Operation Wolf Hunt was the siege and assault of the Chechnya, Chechen capital Grozny by Russian forces, lasting from late 1999 to early 2000. The siege and assault on the city resulted in the near total destruction of the urban area. In 2003, the United Nations designated Grozny as the most destroyed city on Earth. The battle had a devastating impact on the civilian population. It is estimated that between 5,000 and 8,000 civilians were killed during the siege, making it the bloodiest episode of the Second Chechen War. Prelude On 15 October 1999, after mounting an intense tank and artillery Barrage (artillery), barrage against Chechen separatists, Russian forces took control of a strategic ridge within artillery range of Grozny. They then made several abortive attempts to seize positions on the outskirts of the city. On 4 December, the commander of Russian forces in the North Caucasus, General Viktor Kazantsev, claimed that Grozny was fully b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Bombing Operations And Battles
Aerial may refer to: Music * ''Aerial'' (album), by Kate Bush, and that album's title track * "Aerials" (song), from the album ''Toxicity'' by System of a Down Bands * Aerial (Canadian band) * Aerial (Scottish band) * Aerial (Swedish band) Recreation and sport * Aerial (dance move) * Aerial (skateboarding) * Front aerial, gymnastics move performed in acro dance * Aerial cartwheel * Aerial silk, a form of acrobatics * Aerial skiing Technology *Aerial (radio), a radio ''antenna'' or transducer that transmits or receives electromagnetic waves **Aerial (television), an over-the-air television reception antenna *Aerial photography Other uses *Aerial, Georgia, a community in the United States * ''Aerial'' (magazine), a poetry magazine * ''Aerials'' (film), a 2016 Emirati science-fiction film *''Aerial'', a TV ident for BBC Two from 1997 to 2001 See also * Arial * Ariel (other) * Airiel * Area (other) * Airborne (other) * Antenna (disambigua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Chechen War
Names The Second Chechen War is also known as the Second Chechen Campaign () or the Second Russian Invasion of Chechnya from the Chechens, Chechen insurgents' point of view.Федеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 1995 (в редакции от 27 ноября 2002) "О ветеранах" Historical basis of the conflict Russian Empire Chechnya is an area in the North Caucasus, Northern Caucasus which has constantly fought against foreign rule, including the Ottoman Turks in the 15th century. The Russian Terek Cossacks, Terek Cossack Host was established in lowland Chechnya in 1577 by free Cossacks who were resettled from the Volga to the Terek River. In 1783, the Russian Empire and the Georgia (country), Georgian Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti signed the Treaty of Georgievsk, under which Kartli-Kakheti became a Russian protectorate. To secure communications with Georgia (country), Georgia and other regions of the Transcaucasia, the Russian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Murder In Russia
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh less than it d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service has over 5,500 journalists working across its output including in 50 foreign news bureaus where more than 250 foreign correspondents are stationed. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutatis Mutandis
''Mutatis mutandis'' is a Medieval Latin phrase meaning "with things changed that should be changed" or "once the necessary changes have been made", literally: having been changed, going to be changed. It continues to be seen as a foreign-origin phrase (and thus, unnaturalized, meaning not integrated as part of native vocabulary) in English and is therefore usually italicized in writing. It is used in many countries to acknowledge that a comparison being made requires certain obvious alterations, which are left unstated. It is not to be confused with the similar ''ceteris paribus'', which excludes any changes other than those explicitly mentioned. ''Mutatis mutandis'' is still used in law, economics, mathematics, linguistics and philosophy. In particular, in logic, it is encountered when discussing counterfactuals, as a shorthand for all the initial and derived changes which have been previously discussed. Latin The phrase '—now sometimes written ' to show vowel length—do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bataysk
Bataysk () is a city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Rostov-on-Don. Population: History It was founded in 1769, and was granted town status in 1938. The reconstructed Church of the Ascension was built between 1990 and 2006. The former Bataysk (air base) is located nearby. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Bataysk Urban Okrug—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts.Law #340-ZS As a municipal division, this administrative unit also has urban okrug status.Law #235-ZS Trivia Bataysk has gained international attention since unveiling a "monument that shows a man's hand gripping a nubile female breast", which officials say "will bring family happiness to men who touch it". Arts and culture Libraries *Maxim Gorky Central State Library *Nadezhda Krupskaya Central State *Children's Library *Mayakovsky Library *Chekhov Library *Pushkin Library *Leo Tolstoy Libr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crimes against humanity, Child labour, child labor, torture, human trafficking, and Women's rights, women's and LGBTQ rights. It pressures governments, policymakers, companies, and individual abusers to respect human rights, and frequently works on behalf of refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners. The organization was founded in 1978 as Helsinki Watch, whose purpose was to monitor the Soviet Union's compliance with the 1975 Helsinki Accords. Its separate global divisions merged into Human Rights Watch in 1988. The group publishes annual reports on about 100 countries with the goal of providing an overview of the worldwide state of human rights. In 1997, HRW shared the Nobel Peace Prize as a founding member of the International C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-24 Rocket
The S-24 is a rocket (weapon), rocket weapon designed and used by the Soviet Air Force. It remains in use by the Russian Aerospace Forces, Ukrainian Air Force and many export countries. The name is based on the diameter of the rocket, . The Soviet Union was an enthusiastic user of rocket weapons, employing them as early as the 1930s. The S-24/S-24B is a very large, powerful unguided weapon and one of a handful of successors to the earlier World War II-era BETAB-750DS rockets. The S-24B differs from the S-24 in that it uses BN-K low smoke motor powder for a low-smoke flight. The S-24 is long, with a launch weight of . It has a blast-fragmentation (weaponry), fragmentation warhead. Its range is about . The S-24 is carried individually on weapon hardpoints, rather than in pods. Proximity fuze RV-24 is also available, in which the warhead detonate 3 meters above ground, creating 300–400 m radius of fragmentation casualty zone. The body is mesh-texture shape-hardened by elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlovo Bus Factory
Pavlovo Bus Factory (, formerly , Pavlovsky Avtobusny Zavod or PAZ) is a manufacturer of buses in Russia, in the city of Pavlovo, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast. PAZ is a subsidiary of Russian Buses which is a division of GAZ. The production of buses since 2005 has been carried out by PAZ, a 100% subsidiary of PAO Pavlovsky Avtobus. Pavlovo Bus Factory specializes in designing and manufacturing buses of the small/medium class (length 9.7 m). Buses are the most common plant in Russia, their annual output is over 10,000 units, almost 80% of small buses in Russia. The small PAZ buses have long been used by Russian "fixed-route taxi" (''marshrutka'') operators. Starting in 2015, the GAZ Group introduced a single brand for all its bus manufacturing subsidiaries, and newly manufactured vehicles now feature the deer badge of the GAZ Gaz may refer to: Geography *Gaz, Kyrgyzstan Iran * Gaz, Darmian, village in South Khorasan province * Gaz, Golestan, a village in Bandar-e Gaz County * Gaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |