|
Badr Shaker Al-Sayyab
Badr Shakir al-Sayyab () (December 24, 1926 in Jaykur, Basra – December 24, 1964 in Kuwait) was an Iraqi poet, regarded as one of the most important contemporary Arab poets. Alongside Nazik Al Malaika, he is considered one of the founders of Arab free-verse poetry. Early life and career Badr Shakir al-Sayyab was born in Jaykur, a town south of Basra, the eldest child of a date grower and shepherd. His mother passed away when he was six years old. He graduated from the Higher Teacher Training College of Baghdad in 1948 but was later dismissed from his teaching position for being a member of the Iraqi Communist Party. Banned from teaching because of his political views, he next found employment as a taster, working for the Iraqi Date Company in Basra. However, he soon returned to Baghdad, where he worked as a security guard for a road paving company. He was actively involved in the 1952 Iraqi Intifada, in which he joined his fellow workers in sacking the offices of the US Infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
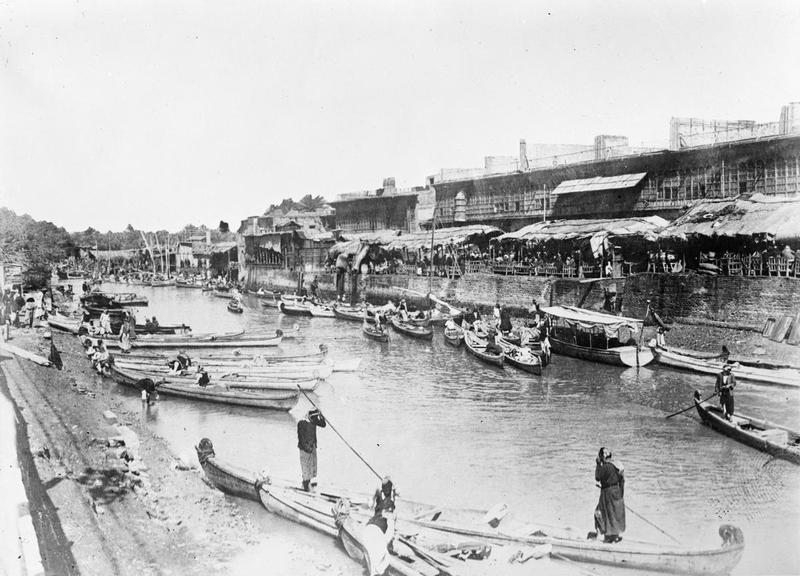
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq border at the north-easternmost extent of the Arabian Peninsula, the city is situated along the banks of the Shatt al-Arab that empties into the Persian Gulf. It is consistently one of the hottest cities in Iraq, with summer temperatures regularly exceeding . Built in 636 as a military camp, Basra played an important role as a regional hub of knowledge, trade and commerce during the Islamic Golden Age and is home to the first mosque built outside the Arabian Peninsula. It was a center of the History of slavery, slave trade in Mesopotamia, until the Zanj Rebellion, Zanj rebellion in Battle of Basra (871), 871. Historically, Basra is one of the ports from which the fictional Sinbad the Sailor embarked on his journeys. It has experienced numerou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain Song (al-Sayyab)
''Rain Song'' (انشودة المطر “Unshūdat almaṭar”) is a famous 1960 poetry collection and Arabic poem by Badr Shakir al-Sayyab One of the "great poems in modern Arabic poetry", it has been compared to T.S. Eliot's ''The Waste Land ''The Waste Land'' is a poem by T. S. Eliot, widely regarded as one of the most important English-language poems of the 20th century and a central work of modernist poetry. Published in 1922, the 434-line poem first appeared in the United ...''. Song The poem was set to music by Saudi singer and composer Mohammed Abdu in 1992. References 1960 poems 1960 poetry books Iraqi poetry {{Iraq-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Wahhab Al-Bayati
Abd al-Wahhab al-Bayati (Arabic: عبد الوهاب البياتي) (December 19, 1926 – August 3, 1999) was an Iraqi Arab poet. Biography Al-Bayati was born in Baghdad. Al-Bayati was an Iraqi Turkmen poet. One of his friends, Ahmed Abdel-Moeti Hegazi, said urban centers of "hotels and institutions, cafés and airports" were actually his temporary residences. He attended Baghdad University, and became a teacher after graduating from Dar al-Mu'allimin (the Teacher's College) in 1950, the same year that he released his first collection of poems, ''Mala'ika wa Shayatin'' (''Angels and Devils''). In 1996, he published a poem "The Dragon". The translation by Farouk Abdel Wahab, Najat Rahman, and Carolina Hotchandani is from the volume ''Iraqi Poetry Today'' () (c) 2003, edited by Saadi Simawe. "The Dragon" is an example of al-Bayyati's frequent incorporation of mythological figures into his poetry. Critics have interpreted the poem as addressed to Saddam Hussein Saddam Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazik Al-Mala'ika
Nazik al-Malaika (; 23 August 1923 – 20 June 2007) was an Iraq, Iraqi poet. Al-Malaika is noted for being among the first Arabic poets to use free verse. Early life and career Al-Malaika was born in Baghdad to a cultured family. Her mother Salma al-Malaika was also a poet, and her father was a teacher. She wrote her first poem at the age of 10. During her life, she studied English and French literature, Latin, and Greek poetry. Al-Malaika graduated in 1944 from the College of Arts in Baghdad and later completed a master's degree in comparative literature at the University of Wisconsin–Madison with a Degree of Excellence. She entered the Institute of Fine Arts and graduated from the Department of Music in 1949. In 1959 she earned a Master of Arts in Comparative Literature from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in the United States, and she was appointed professor at the University of Baghdad, the University of Basrah, and Kuwait University. Career Al-Malaika taught at a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Verse
Free verse is an open form of poetry which does not use a prescribed or regular meter or rhyme and tends to follow the rhythm of natural or irregular speech. Free verse encompasses a large range of poetic form, and the distinction between free verse and other forms (such as prose) is often ambiguous. History Though individual examples of English free verse poetry surfaced before the 20th-century (parts of John Milton's '' Samson Agonistes'' or the majority of Walt Whitman's poetry, for example), free verse is generally considered an early 20th century innovation of the late 19th-century French ''vers libre''. T. E. Hulme and F. S. Flint first introduced the form to the London-based Poets' Club in 1909. This later became the heart of the Imagist movement through Flint's advocacy of the genre. Imagism, in the wake of French Symbolism (i.e. vers libre of French Symbolist poets) was the wellspring out of which the main current of Modernism in English flowed. T. S. Eliot later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edith Sitwell
Dame Edith Louisa Sitwell (7 September 1887 – 9 December 1964) was a British poet and critic and the eldest of the three literary Sitwells. She reacted badly to her eccentric, unloving parents and lived much of her life with her governess. She never married but became passionately attached to Russian painter Pavel Tchelitchew, and her home was always open to London's poetic circle, to whom she was generous and helpful. Sitwell published poetry continuously from 1913, some of it abstract and set to music. With her dramatic style and exotic costumes, she was sometimes labelled a poseur, but her work was praised for its solid technique and painstaking craftsmanship. She was a recipient of the Benson Medal of the Royal Society of Literature. Early life Edith Louisa Sitwell was born in Scarborough, North Riding of Yorkshire, the oldest child and only daughter of Sir George Sitwell, 4th Baronet, of Renishaw Hall; he was an expert on genealogy and landscaping. Her mother w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazim Hikmet
Subahdar, also known as Nazim, was one of the designations of a governor of a Subah (province) during the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, Mamluk dynasty, Khalji dynasty, Tughlaq dynasty, and the Mughal era who was alternately designated as Sahib-i-Subah or Nazim. The word, ''Subahdar'' is of Persian origin. The Subahdar was the head of the Mughal provincial administration. He was assisted by the provincial ''Diwan'', '' Bakhshi'', ''Faujdar'', ''Kotwal'', ''Qazi'', ''Sadr'', ''Waqa-i-Navis'', ''Qanungo'' and '' Patwari''. The Subahdars were normally appointed from among the Mughal princes or the officers holding the highest ''mansabs'' (ranks). Nazim A ''nazim'' (, ; from the Arabic word for "organizer" or "convenor"), similar to a mayor, was the coordinator of cities and towns in Pakistan. Nazim is the title in Urdu of the chief elected official of a local government in Pakistan, such as a district, tehsil, union council, or village council. Likewise, a deputy mayor is known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Aragon
Louis Aragon (; 3 October 1897 – 24 December 1982) was a French poet who was one of the leading voices of the Surrealism, surrealist movement in France. He co-founded with André Breton and Philippe Soupault the surrealist review ''Littérature''. He was also a novelist and editor, a long-time member of the French Communist Party, Communist Party and a member of the Académie Goncourt. After 1959, he was a frequent nominee for the Nobel Prize in Literature. Early life (1897–1939) Louis Aragon was born in Paris. He was raised by his mother and maternal grandmother, believing them to be his sister and foster mother, respectively. His biological father, :fr:Louis Andrieux, Louis Andrieux, a former senator for Forcalquier, was married and thirty years older than Aragon's mother, whom he seduced when she was seventeen. Aragon's mother passed Andrieux off to her son as his godparent, godfather. Aragon was only told the truth at the age of 19, as he was leaving to serve in the Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Poetry
Arabic poetry ( ''ash-shi‘r al-‘arabīyy'') is one of the earliest forms of Arabic literature. Pre-Islamic Arabic poetry contains the bulk of the oldest poetic material in Arabic, but Old Arabic inscriptions reveal the art of poetry existed in Arabic writing in material as early as the 1st century BCE, with oral poetry likely being much older still. Arabic poetry is categorized into two main types, rhymed or measured, and prose, with the former greatly preceding the latter. The rhymed poetry falls within fifteen different meters collected and explained by al-Farahidi in ''The Science of ‘ Arud''. Al-Akhfash, a student of al-Farahidi, later added one more meter to make them sixteen. The meters of the rhythmical poetry are known in Arabic as "seas" (''buḥūr''). The measuring unit of seas is known as "''taf‘īlah''," and every sea contains a certain number of taf'ilas which the poet has to observe in every verse ('' bayt'') of the poem. The measuring procedure of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
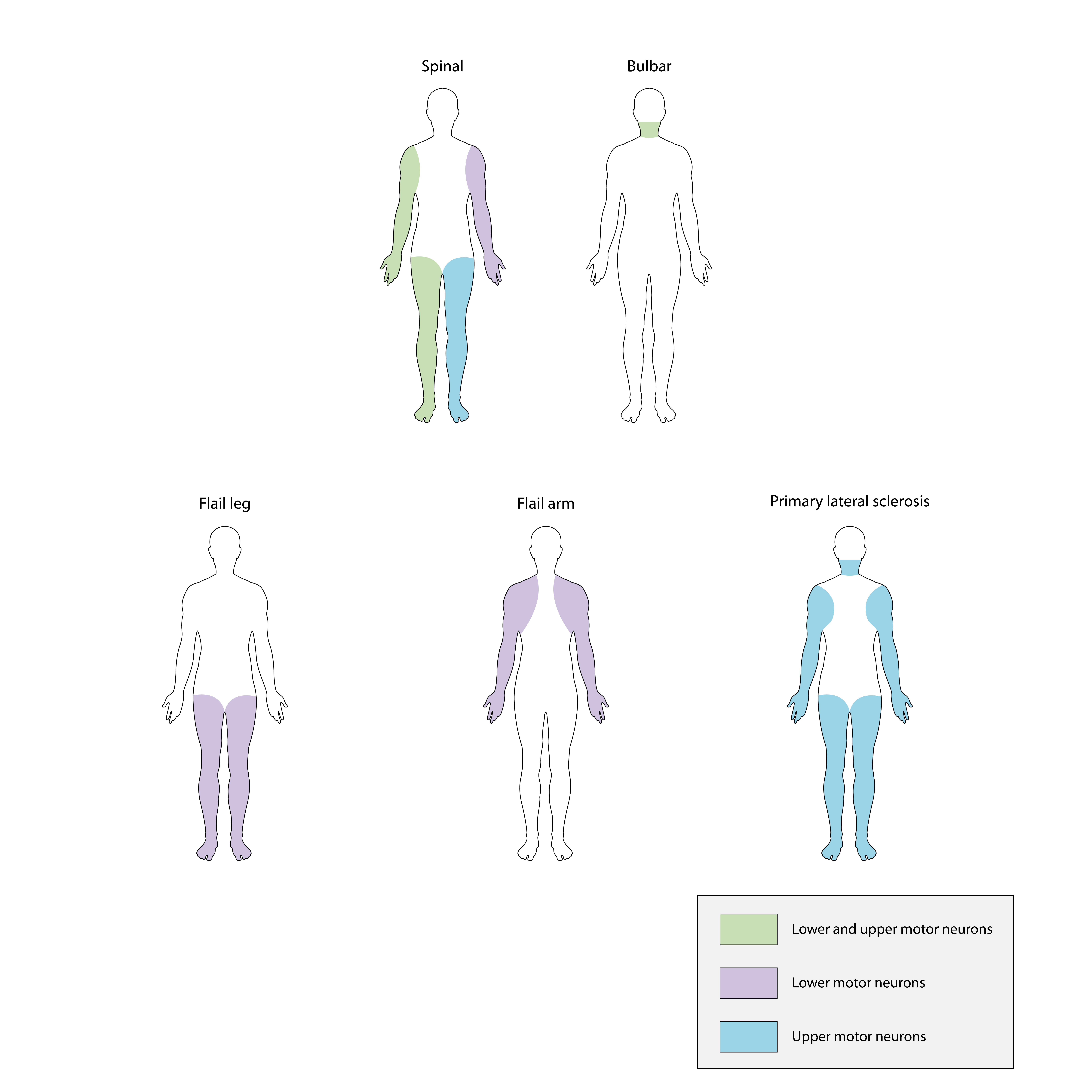
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Hospital, London
St Mary's Hospital is a teaching hospital in Paddington, in the City of Westminster, London, founded in 1845. Since the UK's first academic health science centre was created in 2008, it has been operated by Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, which also operates Charing Cross Hospital, Hammersmith Hospital, Queen Charlotte's and Chelsea Hospital and the Western Eye Hospital. Until 1988 the hospital ran St Mary's Hospital Medical School, part of the federal University of London. In 1988 it merged with Imperial College London, and then with Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School in 1997 to form Imperial College School of Medicine. In 2007 Imperial College became an independent institution when it withdrew from the University of London. History Development of the hospital The original block of St Mary's Hospital in Norfolk Place was designed by Thomas Hopper (architect), Thomas Hopper in the Classical architecture, classical style. It first opened its doors to patients i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are departments of the university, without their own royal charter). and a range of academic departments that are organised into four divisions. Each college ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |