|
Bacterial Flora
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, mutualistic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or else the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product (short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
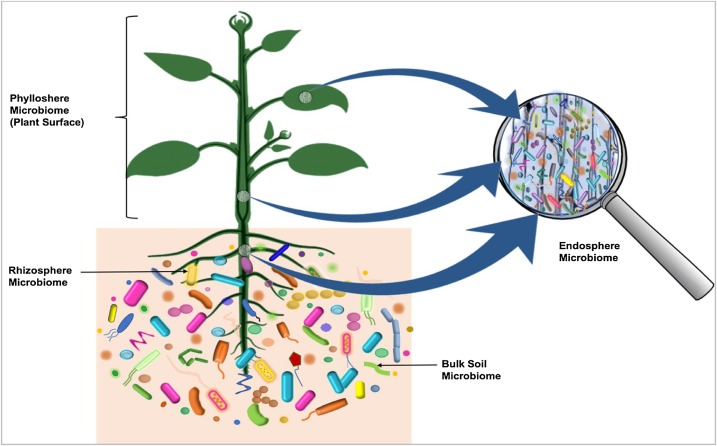
The Plant Microbiome
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying Behavioral ecology, behavioral adaptations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminium'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 million tonnes of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common building block for biosynthesis. Nomenclature and common formula When part of a salt, the formula of the acetate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-chain Fatty Acid
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are fatty acids of two to six carbon atoms. The SCFAs' lower limit is interpreted differently, either with one, two, three or four carbon atoms. Derived from intestine, intestinal microbe, microbial fermentation of indigestible foods, SCFAs in human gut are acetic, propionic and butyric acid. They are the main energy source of colonocytes, making them crucial to gastrointestinal health. SCFAs all possess varying degrees of water solubility, which distinguishes them from longer chain fatty acids that are immiscible. List of SCFAs Functions SCFAs are produced when dietary fiber is fermented in the Colon (anatomy), colon. Macronutrient composition (carbohydrate, protein or fat) of diets affects circulating SCFAs. Acetate, propionate and butyrate are the three most common SCFAs. Butyric acid, Butyrate is particularly important for large intestine, colon health because it is the primary energy source for Gastrointestinal tract#Mucosa, colonocytes (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 9.4. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the past, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open-access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMC Biology
''BMC Biology'' is an online open access scientific journal that publishes original, peer-reviewed research in all fields of biology, together with opinion and comment articles. The publication was established in 2003. The journal is part of a series of BMC journals published by the UK-based publisher BioMed Central, owned by Springer Nature. The journal has an international editorial board of researchers and editorial offices in London and New York. Since 2010 it has incorporated what was previously the separate ''Journal of Biology''. Video abstracts associated with the BMC Biology articles are collected on the BMC YouTube Channel. Abstracting and Indexing BMC Biology is indexed in PubMed, MEDLINE (added in 2005), BIOSIS Previews, Chemical Abstracts Service, EMBASE, Scopus, Zoological Record, CAB International, Institute for Scientific Information and Google Scholar. The journal has a (2019) impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Microbiology
''International Microbiology'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media and the official journal of the . It covers all aspects of microbiology. The journal was established in 1947 as ''Microbiología Española'' and renamed ''Microbiología SEM'' in 1985 before obtaining its current title in 1998. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Science Citation Index Expanded, Scopus, Biological Abstracts, MEDLINE, and Excerpta Medica. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.3. References External links * English-language journals Open access journals Microbiology journals Academic journals established in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Reviews In Microbiology
''Critical Reviews in Microbiology'' is an international, peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes comprehensive review articles covering all areas of medical microbiology. Areas covered by the journal include bacteriology, virology, microbial genetics, epidemiology, and diagnostic microbiology. It is published by Taylor and Francis Group. As of 2024, the impact factor is 6.0. Core research areas Expert reviewers address the following disciplines: * Molecular biology * Microbial genetics * Microbial physiology * Microbial biochemistry * Microbial structure * Medical microbiology * Epidemiology * Public health * Diagnostic microbiology Diagnostic microbiology is the study of microbial identification. Since the discovery of the germ theory of disease, scientists have been finding ways to harvest specific organisms. Using methods such as differential media or Whole genome sequencing ... Editor-in-chief Publication format ''Critical Reviews in Microbiology'' publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holobiont
A holobiont is an assemblage of a Host (biology), host and the many other species living in or around it, which together form a discrete ecological unit through symbiosis, though there is controversy over this discreteness. The components of a holobiont are individual species or wikt:biont, bionts, while the combined genome of all bionts is the Hologenome theory of evolution, hologenome. The holobiont concept was initially introduced by the German theoretical biologist :de:Adolf Meyer-Abich, Adolf Meyer-Abich in 1943, and then apparently independently by Lynn Margulis, Dr. Lynn Margulis in her 1991 book ''Symbiosis as a Source of Evolutionary Innovation''. The concept has evolved since the original formulations. Holobionts include the Host (biology), host, virome, microbiome, and any other organisms which contribute in some way to the functioning of the whole. Well-studied holobionts include Coral#Holobiont, reef-building corals and humans. Overview A holobiont is a collection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional (DNA sequence based) genetic mechanism of inheritance. Epigenetics usually involves a change that is not erased by cell division, and affects the regulation of gene expression. Such effects on cellular and physiological traits may result from environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Further, non-coding RNA sequences have been shown to play a key role in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synergy
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts (i.e., a non-linear addition of force, energy, or effect). The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' from ', , meaning "working together". Synergy is similar in concept to emergence. History The words ''synergy'' and ''synergetic'' have been used in the field of physiology since at least the middle of the 19th century: SYN'ERGY, ''Synergi'a'', ''Synenergi'a'', (F.) ''Synergie''; from ''συν'', 'with', and ''εργον'', 'work'. A correlation or concourse of action between different organs in health; and, according to some, in disease. :—Dunglison, Roble''Medical Lexicon''Blanchard and Lea, 1853 In 1896, Henri Mazel applied the term "synergy" to social psychology by writing ''La synergie sociale'', in which he argued that Darwinian theory failed to account of "social synergy" or "social love", a collective evolutionary drive. The hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |