|
BRCC3
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCC3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a subunit of the BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex (BRCC), which is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. This protein is also thought to be involved in the cellular response to ionizing radiation and progression through the G2/M checkpoint. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Repair of DNA damage BRCC36, the protein product of the ''BRCC3'' gene, is a deubiquitinating enzyme and a core component of the deubiquitin complex BRCA1-A. BRCA1, as distinct from BRCA1-A, is employed in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free homologous recombinational (HR) repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Sequestration of BRCA1 away from the DNA damage site suppresses homologous recombination and redirects the cell in the direction of repair by the process of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The role of BRCA1-A appears to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRE (gene)
BRCA1-A complex subunit BRE is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRE'' gene. Repair of DNA damage BRE, the protein product of the BRE (gene), is a core component of the deubiquitin complex BRCA1-A. Other core components of the BRCA1-A complex are the BRCC36 protein ( BRCC3 gene), MERIT40 protein ( BABAM1 gene), and RAP80 protein ( UIMC1 gene). BRCA1, as distinct from BRCA1-A, is employed in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free homologous recombinational (HR) repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Sequestration of BRCA1 away from the DNA damage site suppresses homologous recombination and redirects the cell in the direction of repair by the process of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The role of BRCA1-A appears to be to bind BRCA1 with high affinity and withdraw it away from the site of DNA damage to the periphery where it remains sequestered, thus promoting NHEJ in preference to HR. Protein-protein interactions BRE (gene) h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
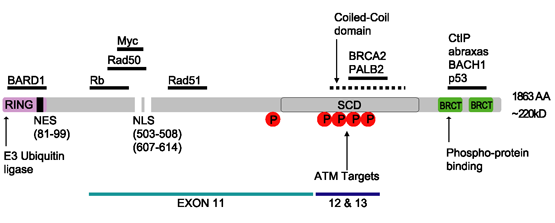
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are human genes and their protein products, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are gene nomenclature, maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC proteins, FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosome, chromosomal damage with an important role in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAD51
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene ''RAD51''. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA, Archaeal RadA, and yeast Rad51. The protein is highly conserved in most eukaryotes, from yeast to humans. The name RAD51 derives from ''radiation sensitive protein 51''. Variants Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been reported, which encode distinct proteins. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyA signals also exist. Family In mammals, seven recA-like genes have been identified: Rad51, Rad51L1/B, Rad51L2/C, Rad51L3/D, XRCC2, XRCC3, and DMC1/Lim15. All of these proteins, with the exception of meiosis-specific DMC1, are essential for development in mammals. Rad51 is a member of thRecA-like NTPases Function In humans, RAD51 is a 339-amino acid protein that plays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissues, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair, repair harmful DNA breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and ovum, egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to Adaptation, adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage (naturally Occurring)
Natural DNA damage is an alteration in the chemical structure of DNA, such as a break in a strand of DNA, a nucleobase missing from the backbone of DNA, or a chemically changed base such as 8-OHdG. DNA damage can occur naturally or via environmental factors, but is distinctly different from mutation, although both are types of error in DNA. DNA damage is an abnormal chemical structure in DNA, while a mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs. DNA damages cause changes in the structure of the genetic material and prevents the replication mechanism from functioning and performing properly. The DNA damage response (DDR) is a complex signal transduction pathway which recognizes when DNA is damaged and initiates the cellular response to the damage. DNA damage and mutation have different biological consequences. While most DNA damages can undergo DNA repair, such repair is not 100% efficient. Un-repaired DNA damages accumulate in non-replicating cells, such as cells in the brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-homologous End Joining
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. It is called "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair (HDR), which requires a homologous sequence to guide repair. NHEJ is active in both non-dividing and proliferating cells, while HDR is not readily accessible in non-dividing cells. The term "non-homologous end joining" was coined in 1996 by Moore and Haber. NHEJ is typically guided by short homologous DNA sequences called microhomologies. These microhomologies are often present in single-stranded overhangs on the ends of double-strand breaks. When the overhangs are perfectly compatible, NHEJ usually repairs the break accurately. Imprecise repair leading to loss of nucleotides can also occur, but is much more common when the overhangs are not compatible. Inappropriate NHEJ can lead to translocations and telomere fusion, hallmarks of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |