|
Aşıq Ümer
Aşıq Ümer (1621–1707) was a Crimean Tatar medieval poet of ashik and is one of the most famous representatives of the Turkic-speaking ashik poetry in general. Ashik poetry (; ) is a special kind of literary oeuvre, the representatives of which – folk poets-singers – accompany their performances with playing the string-plucked musical instrument ''bağlama''. Hence another name for this poetry – "bağlama poetry". He wrote mainly lyric poems (on mystical content and related to a soldier's theme) in the forms of Turkic folk poetry. Aşıq Ümer is also an author of poems that are traditional for classical oriental poetry – ghazals, rubaʿi A ''rubāʿī'' (, from Arabic language, Arabic ; plural: ) or ''chahārgāna(e)'' () is a poem or a verse of a poem in Persian poetry (or its derivative in English and other languages) in the form of a quatrain, consisting of four lines (four ... etcetera. He greatly influenced the later poets-improvisers (ashiks).''Mustafa Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevpatoria
Yevpatoria (; ; ; ) is a city in western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of History Greek settlement The first recorded settlement in the area, called ''Kerkinitis'' (), was built by Greek colonists around 500 BCE. Along with the rest of the Crimea, Kerkinitis formed part of the dominions of King Mithridates VI Eupator ( BCE). The name of the modern city derives from his nickname, ''Eupator'' ('of a noble father'). Khanate period From roughly the 7th through the 10th centuries, Yevpatoria was a Khazar settlement; its name in Khazar language was probably ''Güzliev'' (literally 'beautiful house'). It was later subject to the Cumans ( Kipchaks), the Mongols, and the Crimean Khanate. During this period the city was called ''Kezlev'' by Crimean Tatars and ''Gözleve'' by Ottoman Turks. The Russian medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kezlev
Yevpatoria (; ; ; ) is a city in western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of History Greek settlement The first recorded settlement in the area, called ''Kerkinitis'' (), was built by Greek colonists around 500 BCE. Along with the rest of the Crimea, Kerkinitis formed part of the dominions of King Mithridates VI Eupator ( BCE). The name of the modern city derives from his nickname, ''Eupator'' ('of a noble father'). Khanate period From roughly the 7th through the 10th centuries, Yevpatoria was a Khazar settlement; its name in Khazar language was probably ''Güzliev'' (literally 'beautiful house'). It was later subject to the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols, and the Crimean Khanate. During this period the city was called ''Kezlev'' by Crimean Tatars and ''Gözleve'' by Ottoman Turks. The Russian medieval name '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic peoples, Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Cumania, Desht-i-Kipchak. In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire, Russian Empire annexed the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance. Naming and geography The Crimean Khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of the Golden Horde and Desht-i Kipcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation of Crimea, Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the Classical antiquity, classical world and the Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppe. Greeks in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
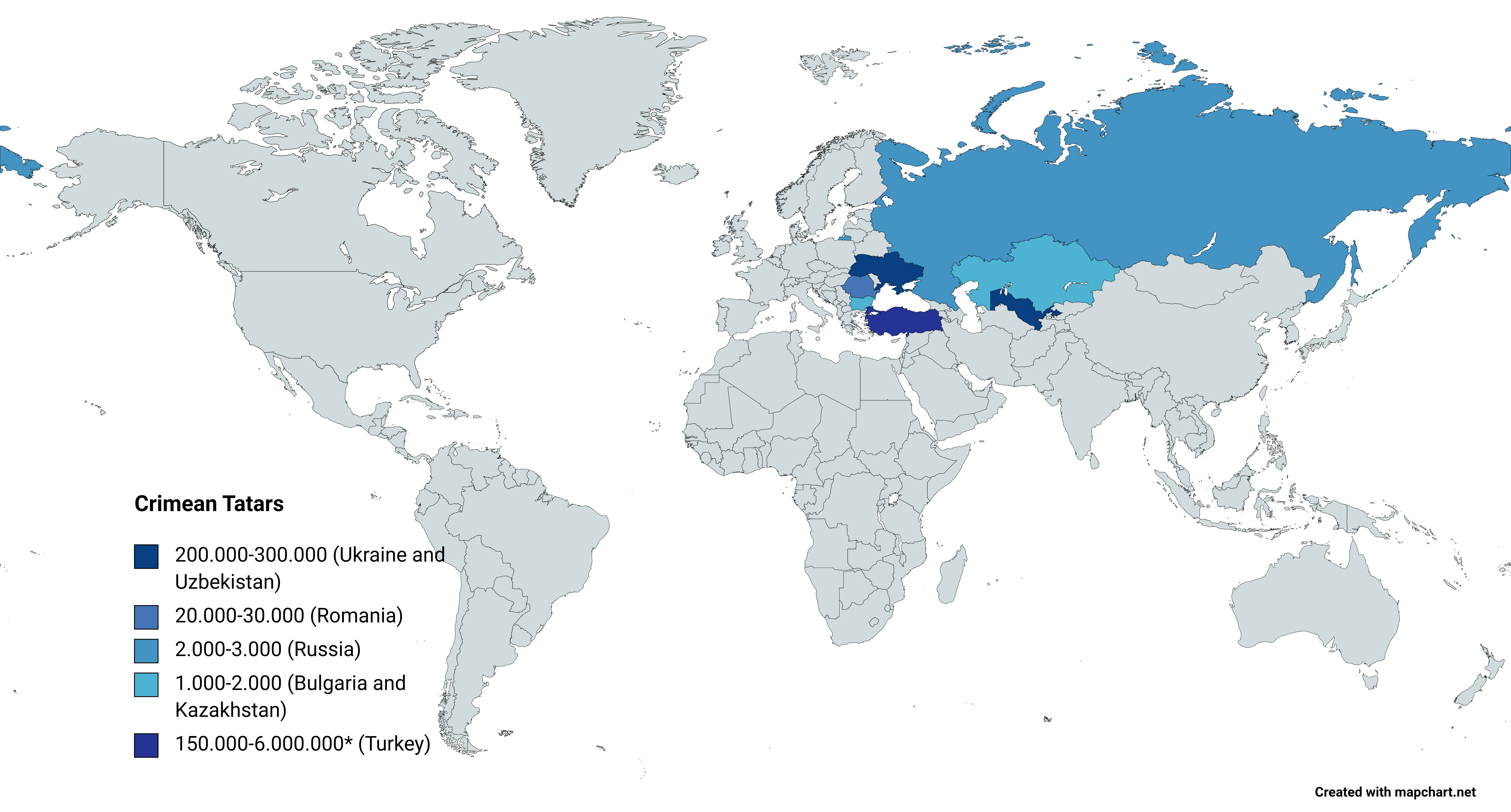
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Black Sea, uniting Mediterranean basin, Mediterranean populations with those of the Eurasian Steppe.''Агджоян А. Т., Схаляхо Р. А., Утевская О. М., Жабагин М. К., Тагирли Ш. Г., Дамба Л. Д., Атраментова Л. А., Балановский О. П.'Генофонд крымских татар в сравнении с тюркоязычными народами Европы, 2015 Genome-wide study of the Crimean Tatars unveiled connections between them and the genomes of individuals from the Steppe during the Bronze Age, specifically those associated with the Yamnaya culture, Yamnaya archaeological culture. Until the 20th century, Crimean Tatars were the most populous demographic cohort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashik
An ashik (; ) or ashugh (; ka, :ka:აშუღი, აშუღი) is traditionally a List of oral repositories, singer-poet and bard who accompanies his song—be it a dastan (traditional epic story, also known as ''Azeri hikaye, hikaye'') or a shorter original composition—with a long-necked lute (usually a bağlama or bağlama, saz) in Music of Azerbaijan, Azerbaijani culture, including Music of Turkey, Turkish and Iranian Azeri, South Azerbaijani and non-Turkic cultures of Transcaucasia, South Caucasus (primarily Music of Armenia, Armenian and Music of Georgia (country), Georgian). In Azerbaijan, the Ashiqs of Azerbaijan, modern ashik is a professional musician who usually serves an apprenticeship, masters playing the bağlama, and builds up a varied but individual repertoire of Turkic peoples, Turkic folk songs.Colin P. Mitchell (Editor), New Perspectives on Safavid Iran: Empire and Society, 2011, Routledge, 90–92 Etymology The word ''ashiq'' (, meaning "in love" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazal
''Ghazal'' is a form of amatory poem or ode, originating in Arabic poetry that often deals with topics of spiritual and romantic love. It may be understood as a poetic expression of both the pain of loss, or separation from the beloved, and the beauty of love in spite of that pain. The ghazal form is ancient, tracing its origins to 7th-century Arabic poetry. It spread into the Indian subcontinent in the 12th century due to the influence of Sufi mystics and the courts of the new Ghurid Sultanate, Islamic Sultanate, and is now most prominently a form of poetry of many languages of South Asia and Languages of Turkey, Turkey. A poem of ghazal commonly consists of five to fifteen couplets, which are independent, but are linked – abstractly, in their theme; and more strictly in their poetic form. The structural requirements of ghazal are similar in stringency to those of the Petrarchan sonnet. In style and content, due to its highly allusive nature, ghazal has proved capable of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubaʿi
A ''rubāʿī'' (, from Arabic language, Arabic ; plural: ) or ''chahārgāna(e)'' () is a poem or a verse of a poem in Persian poetry (or its derivative in English and other languages) in the form of a quatrain, consisting of four lines (four hemistichs). In classical Persian poetry, the ''ruba'i'' is written as a four-line (or two-couplet / two-distich) poem, with a rhyme-scheme AABA or AAAA. This is an example of a ''ruba'i'' from Rumi's ''Divan-e Shams'': : : : : :May the splendors of Salahuddin be roused, :And poured into the eyes and souls of the lovers. :May every soul that has become refined and has surpassed refinement :Be mingled with the dust of Salahuddin! Metre The usual metre of a Persian ''ruba'i'', which is used for all four lines of the above quatrain by Rumi, is, as follows: : – – u u – u – u – – u u – In the above scheme, quantitatively, "–" represents a long syllable, and "u" a short one. As variations of this scheme, any sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bağlama
The bağlama or saz is a family of plucked string instruments and long-necked lutes used in Europe, Balkans, Caucasus, Middle East, Khazar, Central Asia including Germany, France, Belgium, TRNC, Netherlands, Albania, Greece,Bosnia, Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Russia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and Turkey. It is commonly used by Ashik, ashiks. Name According to ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', "the terms 'bağlama' and 'saz' are used somewhat interchangeably in Turkey. 'Saz' is generally used interchangeably with 'enstrüman' (instrument) and it is used to refer single or group of musical instruments like 'üflemeli sazlar' (Wind instrument, wind instruments). Bağlama scale The scale (music), musical scale of the bağlama differs from that of many western instruments – such as the guitar – in that it features ratios that are close to quarter tones. The traditional ratios for bağla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writers From The Crimean Khanate
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles, genres and techniques to communicate ideas, to inspire feelings and emotions, or to entertain. Writers may develop different forms of writing such as novels, short stories, monographs, travelogues, plays, screenplays, teleplays, songs, and essays as well as reports, educational material, and news articles that may be of interest to the general public. Writers' works are nowadays published across a wide range of media. Skilled writers who are able to use language to express ideas well, often contribute significantly to the cultural content of a society. The term "writer" is also used elsewhere in the arts and music, such as songwriter or a screenwriter, but also a stand-alone "writer" typically refers to the creation of written language. Some writers work from an oral tradition. Writers can produce material across a number of genres, fictional or non-fictional. Other writers use multiple media such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |