|
Auxilia
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of infantry as the legions and, in addition, provided almost all of the Roman army's cavalry (especially light cavalry and archers) and more specialised troops. The ''auxilia'' thus represented three-fifths of Rome's regular land forces at that time. Like their legionary counterparts, auxiliary recruits were mostly volunteers, not conscripts. The Auxilia were mainly recruited from the '' peregrini'', free provincial subjects who did not hold Roman citizenship and constituted the vast majority of the population in the 1st and 2nd centuries (c. 90% in the early 1st century). In contrast to the legions, which only admitted Roman citizens, members of the Auxilia could be recruited from territories outside of Roman control. Reliance on the vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Roman Army
The Imperial Roman army was the military land force of the Roman Empire from about 30 BC to 476 AD, and the final incarnation in the long history of the Roman army. This period is sometimes split into the Principate (30 BC – 284 AD) and the Dominate (285–476) periods. Under Augustus (), the army consisted of '' legions'', eventually ''auxilia'' and also '' numeri''. By the end of Augustus' reign, the imperial army numbered some 250,000 men, equally split between 25 legions and 250 units of auxiliaries. The numbers grew to a peak of about 450,000 by 211, in 33 legions and about 400 auxiliary units. By then, auxiliaries outnumbered legionaries substantially. From this peak, numbers probably underwent a steep decline by 270 due to plague and losses during multiple major barbarian invasions. Numbers were restored to their early 2nd-century level of c. 400,000 (but probably not to their 211 peak) under Diocletian (r. 284–305). After the Empire's borders became settled (on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC – AD 476). Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 equites (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republican period of Rome (the infantry were split into 10 Cohort (military unit), cohorts each of four Maniple (military unit), maniples of 120 legionaries), to 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) during Caesar's age, to 5,280 men plus 120 auxiliaries in the Imperial period (split into 10 cohorts, nine of 480 men each, with the first cohort being double-strength at 960 men). It should be noted the above numbers are typical fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrian (Roman)
The ''equites'' (; literally "horse-" or "cavalrymen", though sometimes referred to as " knights" in English) constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an ''eques'' (). Description During the Roman kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six '' centuriae'' of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more ''centuriae'' of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians ( plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 ''centuriae''. These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Cavalry
Roman cavalry (Latin: ''equites Romani'') refers to the horse-mounted forces of the Roman army throughout the Regal, Republican, and Imperial eras. In the Regal era the Roman cavalry was a group of 300 soldiers called '' celeres'', tasked with guarding the king. Later their numbers were doubled to 600, then possibly 1,800. All of the cavalrymen were patricians. In the Republican era, the general name for the cavalry was Equites and consisted of the Equites class and the First Class, with a group of 300 cavalrymen in every legion. They were divided into 10 groups of 30 men. Each group elected three leaders known as ''decuriones''. Later the Roman cavalry stopped using Roman citizens as cavalrymen and relied on Auxilia and foreign recruits. Roman cavalrymen wore a Corinthian helmet, bronze chestplate, and bronze greaves. Later mail was adopted into the army. Their arms included a lance ('' lanceae''), a long sword ('' spatha''), and short throwing spears (''akontes''). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peregrinus (Roman)
In the early Roman Empire, from 30 BC to AD 212, a ''peregrinus'' (Latin: ) was a free provincial subject of the Empire who was not a Roman citizen. ''Peregrini'' constituted the vast majority of the Empire's inhabitants in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. In AD 212, all free inhabitants of the Empire were granted citizenship by the '' Constitutio Antoniniana'', with the exception of the '' dediticii'', people who had become subject to Rome through surrender in war, and freed slaves.Giessen Papyrus, 40,7-9 "I grant to all the inhabitants of the Empire the Roman citizenship and no one remains outside a civitas, with the exception of the dediticii" The Latin '' peregrinus'' "foreigner, one from abroad" is related to the Latin adverb ''peregre'' "abroad", composed of ''per-'' "through" and an assimilated form of ''ager'' "field, country", i.e., "over the lands"; the ''-e'' () is an adverbial suffix. During the Roman Republic, the term ''peregrinus'' simply denoted any person who did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
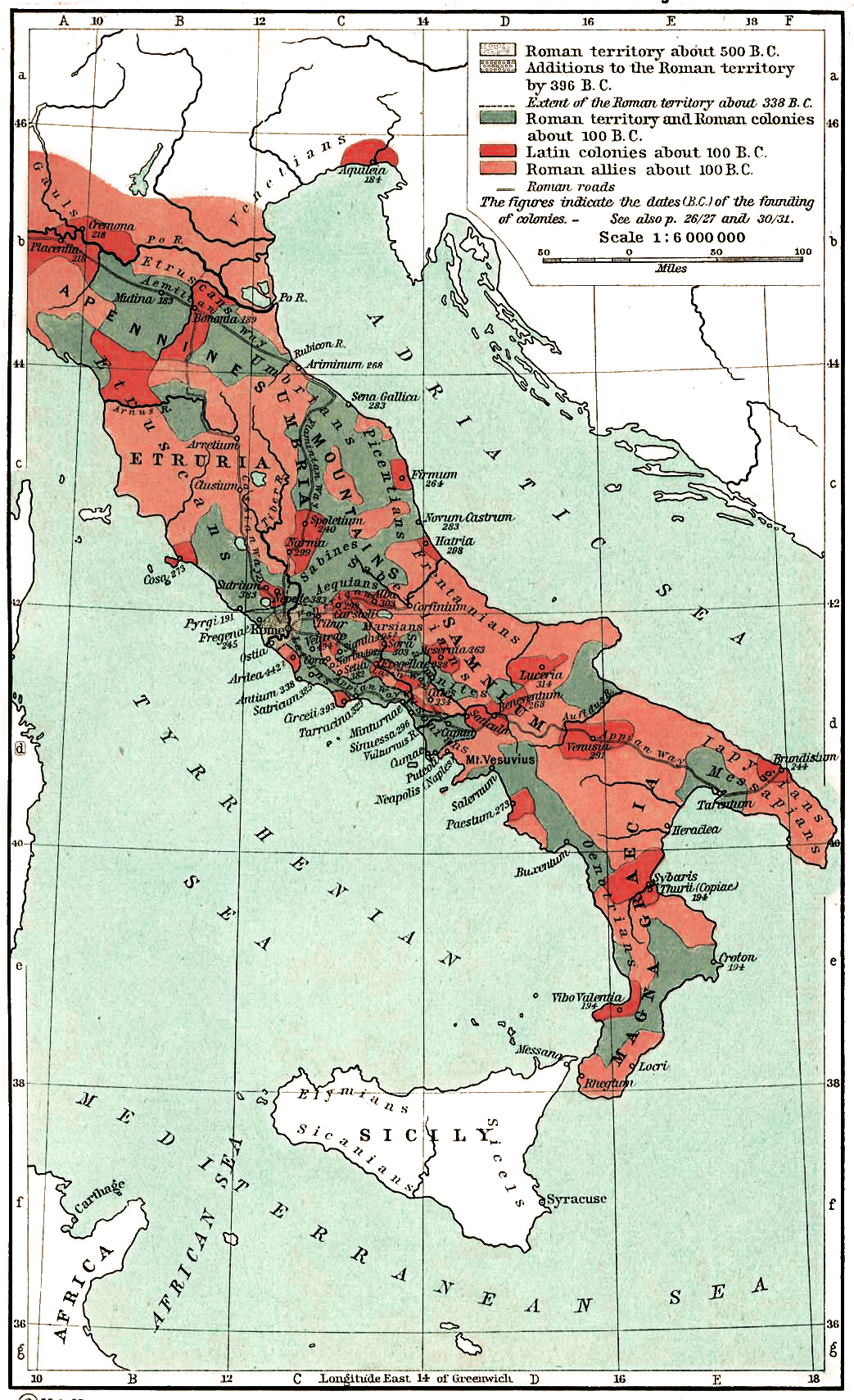
Roman Military Confederation
The ''socii'' ( in English) or '' foederati'' ( in English) were confederates of Rome and formed one of the three legal denominations in Roman Italy (''Italia'') along with the Roman citizens (''Cives'') and the '' Latini''. The ''Latini'', who were simultaneously special confederates (''Socii Latini'') and semi-citizens (''Cives Latini''), should not be equated with the homonymous Italic people of which Rome was part (the Latins). This tripartite organisation lasted from the Roman expansion in Italy (509-264 BC) to the Social War (91–87 BC), when all peninsular inhabitants were awarded Roman citizenship. Treaties known as ''foedus'' served as the basic template for Rome's settlement with the large array of tribes and city-states of the whole Italian peninsula. The confederacy had its origin in the ''foedus Cassianum'' ("Treaty of Cassius", 493 BC) signed by the fledgling Roman republic with its neighbouring Latin city-states shortly after the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ala (Roman Allied Military Unit)
An ''ala'' (Latin for "wing", plural: ''alae'') was the term used during the middle of the Roman Republic (338–88 BC) to denote a military formation composed of conscripts from the ''socii'', Rome's Italian military allies. A normal consular army during the period consisted of two legions, composed of only Roman citizens, and two allied ''alae''. The ''alae'' were somewhat larger than normal legions, 5,400 or 5,100 men against the legion's 4,500 men, and it contained a greater quantity of cavalry, usually 900 horsemen against the 300 supplied by the Romans. From the time of the first Roman emperor, Augustus (ruled 27 BC – AD 14), the term ''ala'' was used in the professional imperial army to denote a much smaller (ca. 500), purely cavalry unit of the non-citizen auxilia corps: see ala (Roman cavalry unit). History When the Roman armies started being composed partly of Roman citizens and partly of ''socii'' (allies from the rest of the Italian mainland), either Latini or I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily raiding, reconnaissance, screening, skirmishing, patrolling and tactical communications. Prior to the early 17th century they were usually armed with swords, spears, javelins, or bows, and later on with sabres, pistols, shotguns, or carbines. Light cavalry was used infrequently by Ancient Greeks (who used hippeis such as prodromoi or sarissophoroi) and Ancient Romans (who used auxiliaries such as equites Numidarum or equites Maurorum), but were more common among the armies of Eastern Europe, North Africa, West Asia, Central Asia and East Asia. The Arabs, Cossacks, Hungarians, Huns, Kalmycks, Mongols, Turks, Parthians, and Persians were all adept light cavalrymen and horse archers. With the decline of feudalism and knight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe. * The first of these wars was the result of Rome's intervention to rescue the Campanian city of Capua from a Samnite attack. * The second one was the result of Rome's intervention in the politics of the city of Naples and developed into a contest over the control of central and southern Italy. * Similarly the third war also involved a struggle for control of this part of Italy. The wars extended over half a century, and also drew in the peoples to the east, north, and west of Samnium (land of the Samnites) as well as those of central Italy north of Rome (the Etruscans, Umbri, and Picentes) and the Senone Gauls, but at different times and levels of involvement. Background By the time of the First Samnite War (343 BC), the southward expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization (cultural)
Romanization or Latinization (Romanisation or Latinisation), in the historical and cultural meanings of both terms, indicate different historical processes, such as acculturation, integration and assimilation of newly incorporated and peripheral populations by the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. The term was used in Ancient Roman historiography and Italian historiography until the fascist period, when the various processes were called the " civilizing of barbarians". Characteristics Acculturation proceeded from the top down, with the upper classes adopting Roman culture first and the old ways lingering for the longest among peasants in outlying countryside and rural areas. Hostages played an important part in this process, as elite children, from Mauretania to Gaul, were taken to be raised and educated in Rome. Ancient Roman historiography and traditional Italian historiography confidently identified the different processes involved with a "civilization of barbarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Corps Traian S Column River Crossing
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized List of engineering branches, fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cultural practices. There existed several different types of citizenship, determined by one's gender, class, and political affiliations, and the exact duties or expectations of a citizen varied throughout the history of the Roman Empire. History The oldest document currently available that details the rights of citizenship is the Twelve Tables, ratified c. 449 BC. Much of the text of the Tables only exists in fragments, but during the time of Ancient Rome the Tables would be displayed in full in the Roman Forum for all to see. The Tables detail the rights of citizens in dealing with court proceedings, property, inheritance, death, and (in the case of women) public behavior. Under the Roman Republic, the government conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_31.jpg)



