|
Auto Polarity (other)
{{disamb ...
Auto polarity or auto-polarity may refer to: * Auto polarity (digital multimeter), automatic polarity switching for signals in measurement devices * Auto polarity (differential signals), automatic polarity switching of differential signals * Auto polarity (Ethernet), automatic polarity of differential pairs in networking See also * Auto crossover * Bridge rectifier * Polarity inversion (other) * Polarity switch In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
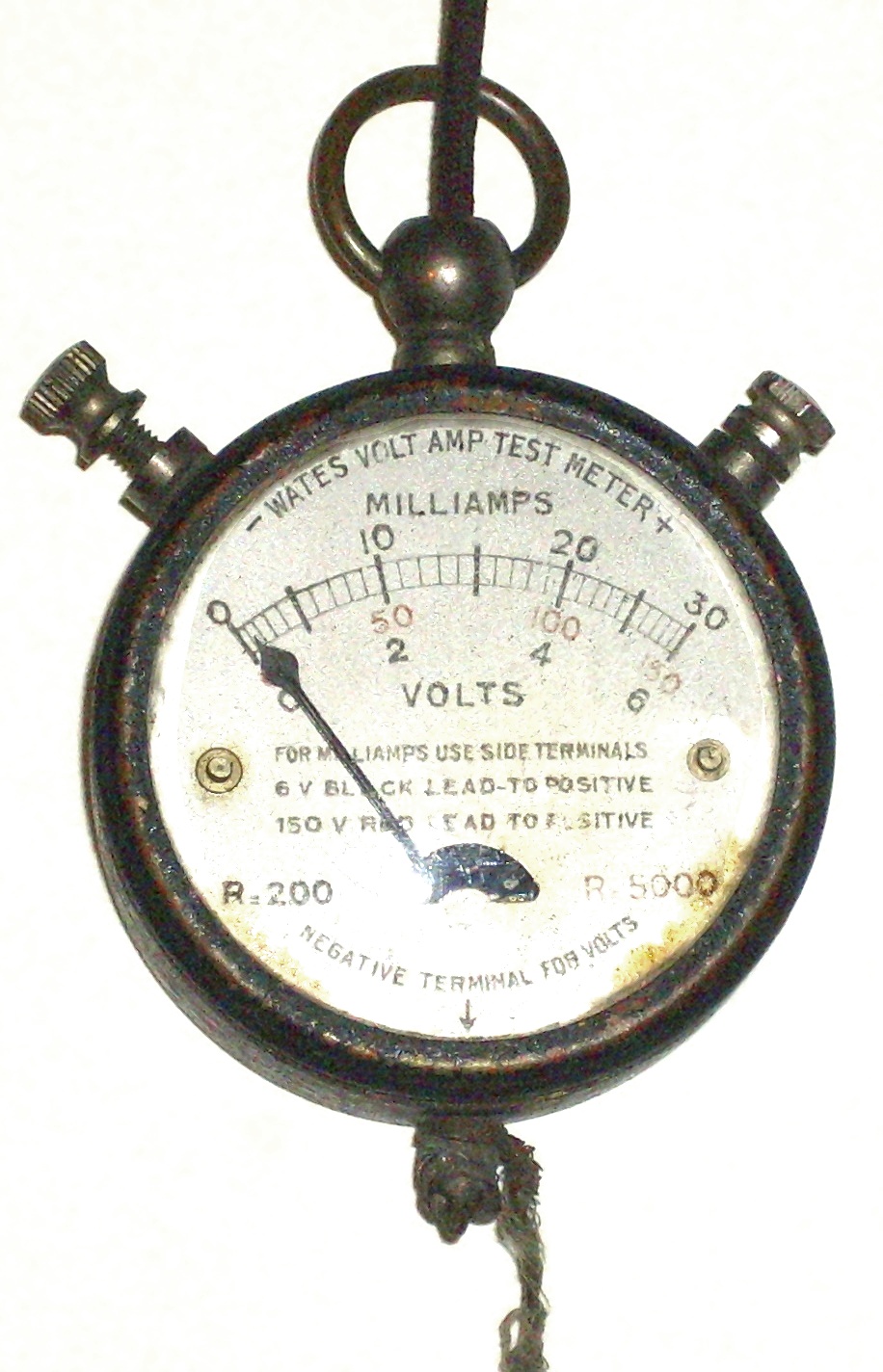
Auto Polarity (digital Multimeter)
A multimeter (also known as a multi-tester, volt-ohm-milliammeter, volt-ohmmeter or VOM, avometer or ampere-volt-ohmmeter) is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, electrical resistance, resistance, and electric current, current, in which case can be used as a voltmeter, ohmmeter, and ammeter. Some feature the measurement of additional properties such as temperature and capacitance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter with a moving pointer to display readings. Digital multimeters (DMMs) have numeric displays and are more precise than analog multimeters as a result. Meters will typically include probes that temporarily connect the instrument to the device or circuit under test, and offer some intrinsic safety features to protect the operator if the instrument is connected to high voltages that exceed its measurement capabilities. Multimeters vary in size, features, and price. They can be portable handh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto Polarity (differential Signals)
Differential signalling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conductors can be wires in a twisted-pair or ribbon cable or traces on a printed circuit board. Electrically, the two conductors carry voltage signals which are equal in magnitude, but of opposite polarity. The receiving circuit responds to the difference between the two signals, which results in a signal with a magnitude twice as large. The symmetrical signals of differential signalling may be referred to as ''balanced'', but this term is more appropriately applied to balanced circuits and balanced lines which reject common-mode interference when fed into a differential receiver. Differential signalling does not make a line balanced, nor does noise rejection in balanced circuits require differential signalling. Differential signalling is to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto Crossover
A medium-dependent interface (MDI) describes the interface (both physical and electrical/optical) in a computer network from a physical-layer implementation to the physical medium used to carry the transmission. Ethernet over twisted pair also defines a medium-dependent interfacecrossover (MDI-X) interface. Auto–MDI-X ports on newer network interfaces detect if the connection would require a crossover and automatically choose the MDI or MDI-X configuration to complement the other end of the link. Ethernet The popular Ethernet family defines common medium-dependent interfaces. For 10BASE5, connection to the coaxial cable was made with either a vampire tap or a pair of N connectors. For 10BASE2, the connection to the coaxial cable was typically made with a single BNC connector to which a T-piece was attached. For twisted-pair cabling 8P8C, modular connectors are used (often called ''RJ45'' in this context). For fiber, a variety of connectors are used depending on manufacturer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
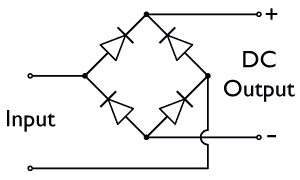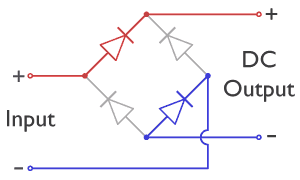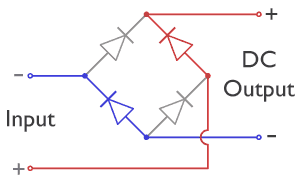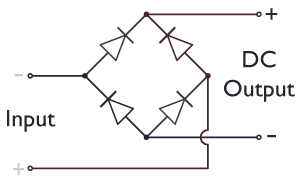
Bridge Rectifier
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four diodes that is used in the process of converting alternating current (AC) from the input terminals to direct current (DC, i.e. fixed polarity) on the output terminals. Its function is to convert the negative voltage portions of the AC waveform to positive voltage, after which a low-pass filter can be used to smooth the result into DC. When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating-current (AC) input into a direct-current (DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a three-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding. Prior to the availability of integrated circuits, a bridge rectifier was constructed from separate diodes. Since about 1950, a single four-terminal component containing the four diodes connected in a bridge con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarity Inversion (other)
Polarity inversion may refer to: * Polarity inversion (chemistry) (aka ), in organic chemistry * Polarity inversion (differential pairs), swapping of positive and negative wires in differential signal links See also * Polarity reversion * Auto polarity (other) {{disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |