|
Auricular Branch (other)
Auricular branch (in Latin, "ramus auricularis") can refer to any one of several different structures having to do with the ear or hearing: *Nerves **The auricular branch of the vagus nerve - "ramus auricularis nervi vagi" (also known as the Alderman's nerve) **The auricular branch of the posterior auricular nerve - "ramus auricularis nervus auricularis posterioris" *Arteries **The auricular branch of the occipital artery - "ramus auricularis arteriae occipitalis" **The auricular branch of the posterior auricular artery - "ramus auricularis arteriae auricularis posterioris" **The anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery - "rami auriculares anteriores arteriae temporalis superficialis" {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
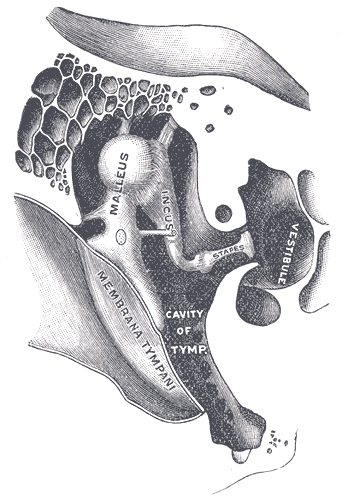
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Branch Of The Vagus Nerve
The auricular branch of the vagus nerve is often termed the Alderman's nerve or Arnold's nerve. The latter name is an eponym for Friedrich Arnold. The auricular branch of the vagus nerve supplies sensory innervation to the skin of the ear canal, tragus, and auricle. Path It arises from the superior ganglion of the vagus nerve, and is joined soon after its origin by a filament from the petrous ganglion of the glossopharyngeal; it passes behind the internal jugular vein, and enters the mastoid canaliculus on the lateral wall of the jugular fossa. Traversing the substance of the temporal bone, it crosses the facial canal about above the stylomastoid foramen, and here it gives off an ascending branch which joins the facial nerve. The nerve reaches the surface by passing through the tympanomastoid fissure between the mastoid process and the tympanic part of the temporal bone, and divides into two branches: * one joins the posterior auricular nerve. * the other is distributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Branch Of The Posterior Auricular Nerve
The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve (CN VII). It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle. Structure The posterior auricular nerve arises from the facial nerve (CN VII). It is the first branch outside of the skull. This origin is close to the stylomastoid foramen. It runs upward in front of the mastoid process. It is joined by a branch from the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X). It communicates with the posterior branch of the great auricular nerve, as well as with the lesser occipital nerve. As it ascends between the external acoustic meatus and mastoid process it divides into auricular and occipital branches. * The ''auricular branch'' travels to the posterior a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Branch Of The Occipital Artery
The auricular branch of occipital artery supplies the back of the concha and frequently gives off a branch, which enters the skull through the mastoid foramen and supplies the dura mater, the diploë, and the mastoid cells; this latter branch sometimes arises from the occipital artery The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery opposite the facial artery. Its path is below the posterior belly of digastric to the occipital region. This artery supplies blood to the back of the scalp and sternocleidomastoid musc ..., and is then known as the mastoid branch. References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Branch Of The Posterior Auricular Artery
The auricular branch of posterior auricular artery is a small artery in the head. It branches off the posterior auricular artery and ascends behind the ear, beneath the posterior auricular muscle, and is distributed to the back of the auricula, upon which it ramifies minutely, some branches curving around the margin of the cartilage, others perforating it, to supply the anterior surface. It anastomoses with the parietal and anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery. Its pulse can be felt above the zygomatic ar .... References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |