|
Aurelian And The Third Century
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in modest circumstances, most likely in Moesia Superior, he entered the Roman army in 235 and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus then ruled for three months, before Aurelian took the empire for himself. Aurelian was chosen Roman emperor by the Illyriciani as one of themselves. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi. Aurelian restored the Empire's eastern provinces after his conques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius Gothicus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – August/September 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle of Naissus. He died after succumbing to a "pestilence", possibly the Plague of Cyprian that had ravaged the provinces of the Empire. Early life and origin The most significant source for Claudius II (and the only one regarding his early life) is the collection of imperial biographies called the ''Historia Augusta''. However, his story, like the rest of the ''Historia Augusta'', is riddled with fabrications and obsequious praises. In 4th century, Claudius was declared a relative of Constantine the Great's father, Constantius Chlorus, and, consequently, of the ruling dynasty. The ''Historia Augusta'' should be used with extreme caution and supplemented with information from other sources: the works of Aurelius Victor, Pseudo-Aurelius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrians
The Illyrians (, ; ) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Ancient Greece, Greeks. The territory the Illyrians inhabited came to be known as Illyria to later Greek and Roman Republic, Roman authors, who identified a territory that corresponds to most of Albania, Montenegro, Kosovo, much of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, western and central Serbia and some parts of Slovenia between the Adriatic Sea in the west, the Drava river in the north, the Great Morava, Morava river in the east and the Ceraunian Mountains in the south. The first account of Illyrian people dates back to the 6th century BC, in the works of the ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus. The name "Illyrians", as applied by the ancient Greeks to their northern neighbors, may have referred to a broad, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Roman Senate, Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed. Domitian had a minor and largely ceremonial role during the reigns of his father and brother. After the death of his brother, Domitian was declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard. His 15-year reign was the longest since Tiberius. As emperor, Domitian strengthened the economy by revaluing the Roman currency, Roman coinage, expanded the border defenses of the empire, and initiated a massive building program to restore the damaged city of Rome. Significant wars were fought in Britain, where his general Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola made significant gains in his attempt to conquer Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Currency
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum#Numismatics, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction during the Roman Republic, Republic, in the third century BC, through Roman Empire, Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denomination, and composition. A feature was the inflationary debasement and replacement of coins over the centuries. Notable examples of this followed the reforms of Diocletian. This trend continued with Byzantine currency. Due to the economic power and longevity of the Roman state, Roman currency was widely used throughout western Eurasia and northern Africa from classical times into the Middle Ages. It served as a model for the currencies of the List of Muslim states and dynasties, Muslim caliphates and the European states during the Middle Ages and the Modern Era. Roman currency names survive today in many countries via the Carolingian monetary system, such as the dinar (from the ''denari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelian Walls
The Aurelian Walls () are a line of city walls built between 271 AD and 275 AD in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman Emperor Aurelian. They superseded the earlier Servian Wall built during the 4th century BC. The walls enclosed all the seven hills of Rome plus the Campus Martius and, on the right bank of the Tiber, the Trastevere district. The river banks within the city limits appear to have been left unfortified, although they were fortified along the Campus Martius. The size of the entire enclosed area is . The wall cut through populated areas: in reality the city at the time embraced . Pliny the Elder in the first century AD suggested that the densely populated areas, ''extrema tectorum'' ("the limits of the roofed areas") extended from the Golden Milestone in the Forum (Natural History 3.67). Construction The full circuit ran for surrounding an area of . The walls were constructed in brick-faced concrete, thick and high, with a square tower every 100 Roman fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Empire
The Gallic Empire or Gallo-Roman Empire are names used in modern historiography for a secession, breakaway part of the Roman Empire that functioned ''de facto'' as a separate state from 260 to 274. It originated during the Crisis of the Third Century, when a series of Roman military leaders and aristocrats Roman usurpers, declared themselves emperors and took control of Roman Gaul, Gaul and adjacent provinces without attempting to conquer Roman Italy, Italy or otherwise seize the central Roman administrative apparatus. The Gallic Empire was established by Postumus in 260 in the wake of barbarian invasions and instability in Rome, and at its height included the territories of Germania, Gaul, Roman Britain, Britannia, and (for a time) Hispania. After Postumus' assassination in 269 it lost much of its territory, but continued under a number of emperors and usurpers. It was retaken by Roman emperor Aurelian after the Battle of Châlons (274), Battle of Châlons in 274. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
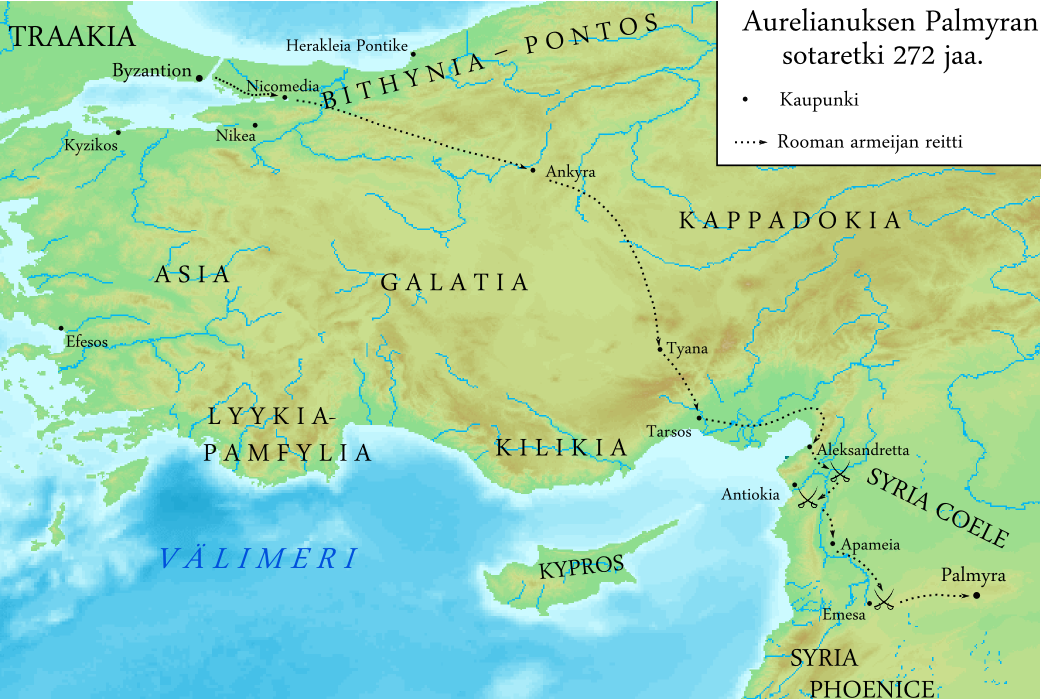
Palmyrene Empire
The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt (Roman province), Egypt, as well as large parts of Anatolia, Asia Minor. The Palmyrene Empire was ruled by Queen Zenobia, officially as regent for her son Vaballathus, who inherited the throne in 267 at age ten. In 270, Zenobia rapidly conquered most of the Roman east, attempting to maintain relations with Rome as a legitimate power. In 271, she claimed the imperial title for both herself and her son, fighting a short war with the Roman emperor Aurelian, who conquered Palmyra and captured Zenobia. A year later the Palmyrenes rebelled, which led Aurelian to raze Palmyra. Despite its brief existence, the Palmyrene Empire is remembered for having been ruled by one of the most ambitious and powerful women in antiquity. It is also hailed in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpi (people)
The Carpi or Carpiani were a tribe that resided in the eastern parts of modern Romania in the historical region of Moldavia from no later than c. AD 140 and until at least AD 318. The ethnic affiliation of the Carpi remains disputed, as there is no direct evidence in the surviving ancient literary sources. A strong body of modern scholarly opinion considers that the Carpi were a tribe of the Dacian nation. Other scholars have linked the Carpi to a variety of ethnic groups, including Sarmatians, Thracians, Slavs, Germanic peoples, Balts and Celts. About a century after their earliest mention by Ptolemy, during which time their relations with Rome appear to have been peaceful, the Carpi emerged in c. 238 as among Rome's most persistent enemies. In the period AD 250–270, the Carpi were an important component of a loose coalition of transdanubian barbarian tribes that also included Germanic and Sarmatian elements. These were responsible for a series of large and devastating inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4th century CE. The earliest known reference to the Sarmatians occurs in the Avesta, where they appear as ''Sairima-'', which in later Iranian sources becomes ''*Sarm'' and Salm (Shahnameh), ''Salm''. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BCE, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BCE. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BCE, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black Sea, Black and Caspian Sea, Caspian seas and the Caucasus to the south. In the first century CE, the Sarmatians beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juthungi
The Juthungi (, ) were a Germanic tribe in the region north of the rivers Danube and Altmühl in what is now the modern German state of Bavaria. The tribe was mentioned by a few Roman historians, including Publius Herennius Dexippus and Ammianus Marcellinus, stretching from the 3rd to the 5th century CE. Tribal name The Juthungi only appear in Roman records for a few centuries. They are only known to have been referred by the ''Juthungi'' name twice before the Laterculus Veronensis, an Imperial record of provinces and peoples of the Empire written around 314 CE, and the last listing of the tribal name occurred around 430 CE. There are conflicting accounts as to whether the Juthungi were a tribe of their own, a subtribe of the Alemanni, or a separate tribe that merged into the Alemanni. Their name appears together with that of the Semnoni, leading some people to believe that they might have been one and the same. This, however, there is no etymological or historical proofs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |