|
Aum Namah Shivaya
Om Namah Shivaya ( Hindi, Devanagari: ; IAST: Oṃ Namaḥ Śivāya) is one of the most popular Hindu mantras and the most important mantra in Shaivism. Namah Shivaya means "O salutations to the auspicious one!", or "adoration to Lord Shiva". It is called Siva Panchakshara, or Shiva Panchakshara or simply Panchakshara meaning the "five-syllable" mantra (viz., excluding the '' Om'') and is dedicated to Shiva. This Mantra appears as 'Na' 'Ma' 'Śi' 'Vā' and 'Ya' in the Shri Rudram Chamakam which is a part of the Krishna Yajurveda and also in the Rudrashtadhyayi which is a part of the Shukla Yajurveda. The five-syllabled mantra (excluding the Oṁ) may be chanted by all persons including śūdras and cāṇḍalas; however the six-syllabled mantra (with Oṁ included) may only be spoken by dvijas. Origin of the mantra The mantra without the initial Om was originally a verse in the eighth hymn of the ''Namakam'' section of the ''Shri Rudram'', (TS 4.5.8.1) itself taken fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaiva Siddhanta
Shaiva Siddhanta () is a form of Shaivism popular in a pristine form in South India and Sri Lanka and in a Tantrayana syncretised form in Indonesia (as Siwa Siddhanta). It propounds a devotional philosophy with the ultimate goal of experiencing union with Shiva. Tirumular, an aide of the prime Sangam age Vedic rishi Agastya, is considered to be the propounder of the term Siddhanta and its basic tenets in his ''magnum opus''. Pristine Shaiva Siddhanta draws primarily on the Tamil devotional hymns written by Shaiva saints from the 5th to the 9th century CE, known in their collected form as ''Tirumurai''. The Brahma Sutra Bhashya of Śrīkaṇṭhācārya Śivācārya is a further agamic philosophical foundation of the philosophy in a Srauta Vedic Vedantic Shiva advaita perspective. In the 12th century, Aghorasiva, the head of a branch monastery of the Amardaka order in Chidambaram, took up the task of formulating Shaiva Siddhanta. This is an earliest known Aghora Paddhati syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (, , , also written as ''Tamizhil'' according to linguistic pronunciation) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world,. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). attested since 300 BC, 300 BCE.: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900" at p. 610 Tamil was the lingua franca for early maritime traders in South India, with Tamil inscriptions found outside of the Indian subcontinent, such as Indonesia, Thailand, and Egypt. The language has a well-documented history wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchakshara Stotra
The ''Shiva Panchakshara Stotra'' () is a Hindu religious hymn (''stotra'') dedicated to god Shiva. Comprising five stanzas, it is regarded to have been composed by the philosopher Adi Shankara. Description The ''panchakshara'' (Sanskrit: पञ्चाक्षर) literally means "five syllables" in Sanskrit, referring to the five syllables of ''na, ma, śi, vā,'' and ''ya'' forming the mantra ''Om Namah Shivaya''. This hymn explains the significance of these five syllables and their affiliation with the deity. According to some texts, these five syllables are regarded to represent the five elements of the human body, the chanting of which is believed to energise them. ''Na'' is associated with ''prithvi'' (earth), ma is associated with ''jala'' (water) ''śi'' is associated with ''agni'' (fire) ''va'' is associated with ''vayu'' (air), and ''ya'' is associated with ''akasha'' (space). Hymn The first stanza of the Shiva Panchakshara Stotram is as follows: See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphemistic
A euphemism ( ) is when an expression that could offend or imply something unpleasant is replaced with one that is agreeable or inoffensive. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes to downplay. Euphemisms may be used to mask profanity or refer to topics some consider taboo such as mental or physical disability, sexual intercourse, bodily excretions, pain, violence, illness, or death in a polite way. Etymology ''Euphemism'' comes from the Greek word () which refers to the use of 'words of good omen'; it is a compound of (), meaning 'good, well', and (), meaning 'prophetic speech; rumour, talk'. '' Eupheme'' is a reference to the female Greek spirit of words of praise and positivity, etc. The term ''euphemism'' itself was used as a euphemism by the ancient Greeks; with the meaning "to keep a holy silence" (speaking well by not speaking at all). Purpose Avoidance Reasons for using euphemisms vary by cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudra
Rudra (/ ɾud̪ɾə/; ) is a Rigvedic deity associated with Shiva, the wind or storms, Vayu, medicine, and the hunt. One translation of the name is 'the roarer'. In the ''Rigveda'', Rudra is praised as the "mightiest of the mighty". Rudra means "who eradicates problems from their roots". Depending upon the period, the name Rudra can be interpreted as 'the most severe roarer/howler' or 'the most frightening one'. This name appears in the Shiva Sahasranama, and R. K. Sharma notes that it is often used as a name of Shiva in later languages. The " Shri Rudram" hymn from the ''Yajurveda'' is dedicated to Rudra and is important in the Shaivite sect.For an overview of the Śatarudriya see: . In the Prathama Anuvaka of Namakam ( Taittiriya Samhita 4.5), Rudra is revered as Sadasiva (meaning 'mighty Shiva') and Mahadeva. Sadashiva is the Supreme Being, Paramashiva, in the Siddhanta sect of Shaivism. Etymology The etymology of the theonym ''Rudra'' is uncertain.. It is usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
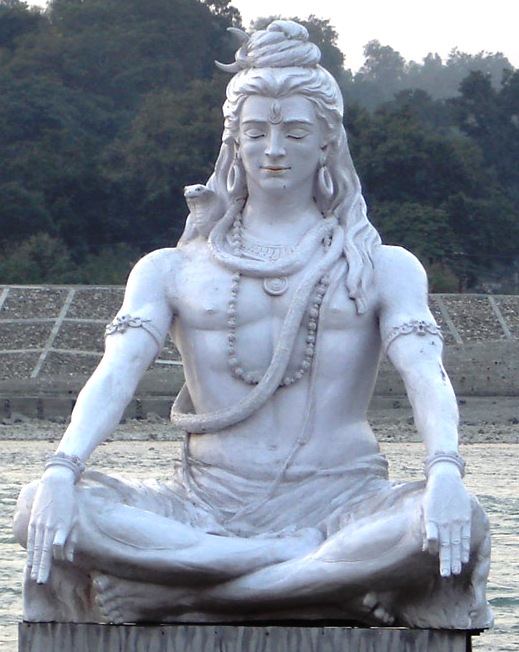
Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [mɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh]) and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism. Shiva is known as ''The Destroyer'' within the Trimurti, the Hinduism, Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shaktism, Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess (Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta Tradition, Smarta tradition of Hinduism. Shiva has many aspects, benevolent as well as fearsome. In benevolent aspects, he is depicted as an Omniscience, omniscient yogi who lives an Asceticism#Hinduism, ascetic life on Kailasa as well as a house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumantiram
The ''Tirumantiram'' () or ''Thirumantiram'' is a Tamil poetic work, written either in the 2nd century BCE and 4th century CE by Tirumular. It is the tenth of the twelve volumes of the ''Tirumurai'', the key texts of Shaiva Siddhanta and the first known Tamil work to use the term. The ''Tirumantiram'' is the earliest known exposition of the Shaiva Agamas in Tamil. It consists of over three thousand verses dealing with various aspects of spirituality, ethics and praise of Shiva. But it is more spiritual than religious and one can see the difference between Vedanta and Siddhanta from Tirumular's interpretation of the Mahavakyas.''The Encyclopaedia Of Indian Literature'' (Volume Two) (Devraj To Jyoti), Volume 2, page 1625''Saivism in Philosophical Perspective'', page 31 According to historian Venkatraman, the work covers almost every feature of the siddhar of the Tamils. According to another historian, Madhavan, the work stresses on the fundamentals of Siddha medicine and its he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ātman (Hinduism)
''Ātman'' (; ) is a Sanskrit word for the true or eternal Self or the self-existent essence or an impersonal (''it'') witness-consciousness within each individual. Atman is conceptually different from Jīvātman, which persists across multiple bodies and lifetimes. Some schools of Indian philosophy regard the ''Ātman'' as distinct from the material or mortal ego ('' Ahankara''), the emotional aspect of the mind ('' Citta''), and existence in an embodied form ('' Prakṛti''). The term is often translated as soul, but is better translated as "Self", as it solely refers to pure consciousness or witness-consciousness, beyond identification with phenomena. In order to attain moksha (liberation), a human being must acquire self-knowledge ('' Atma Gyaan or Brahmajnana''). ''Ātman'' is a central concept in the various schools of Indian philosophy, which have different views on the relation between ''Atman'', individual Self ('' Jīvātman''), supreme Self ('' Paramātmā'') a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiv Lingam Tripundra
The word Shiv or shiv may refer to: People with the name * Shivnarine Chanderpaul, a West Indies cricketer nicknamed Shiv Arts, entertainment, and media * Shiv, a fictional location in Magic: The Gathering, see Dominaria * Shiv, a villain in the animated series ''Static Shock'' * Shiv Roy, a character in the drama series ''Succession'' * Shiv (comics), a fictional villain from DC Comics Other uses * Shiv (weapon), a type of sharp weapon * Shiv, a shortened form of the name Siobhan * Shiv, a local Marathi name for Sion, Mumbai * Shiv, or Shiva Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ..., a Hindu deity * Hemp shiv, the woody waste material from flax, hemp, and linseed plants * Simian human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) See also * Shiva (other) * Siva (disambigua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Om Namah Shivaya In Panchakshara Form
''Om'' (or ''Aum''; ; , ISO 15919: ''Ōṁ'') is a polysemous symbol representing a sacred sound, seed syllable, mantra, and invocation in Hinduism. Its written form is the most important symbol in the Hindu religion. It is the essence of the supreme Absolute, consciousness,James Lochtefeld (2002), "Om", ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism'', Vol. 2: N-Z, Rosen Publishing. , page 482Om . ''Merriam-Webster'' (2013), Pronounced: \ˈōm\ ''Ātman (Hinduism), Ātman,'' ''Brahman,'' or the cosmic world.David Leeming (2005), ''The Oxford Companion to World Mythology'', Oxford University Press, , page 54Hajime Nakamura, ''A History of Early Vedānta Philosophy'', Part 2, Motilal Banarsidass, , page 318Annette Wilke and Oliver Moebus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
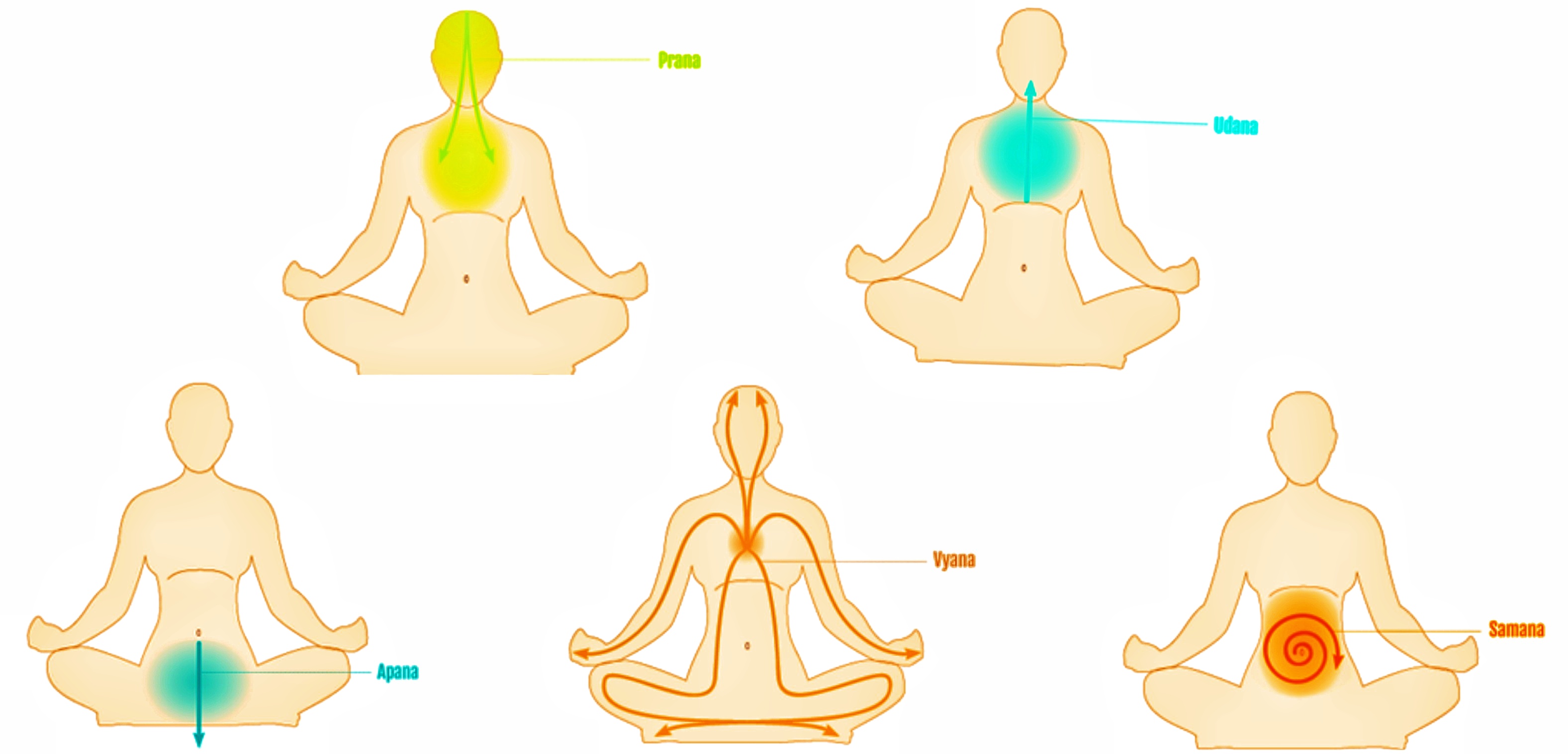
Pranic
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five ''vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |