|
Attributive Adjective
An adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as determiners. Examples: * That's a ''funny'' idea. (Prepositive attributive) * That idea is ''funny''. ( Predicative) * * The ''good'', the ''bad'', and the ''funny''. (Substantive) * Clara Oswald, completely ''fictional'', died three times. ( Appositive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were inflected for gender, number, and case like nouns (a process called declension), they were considered a ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbreviations
An abbreviation () is a shortened form of a word or phrase, by any method including shortening, contraction, initialism (which includes acronym), or crasis. An abbreviation may be a shortened form of a word, usually ended with a trailing period. For example, the term ''etc.'' is the usual abbreviation for the Latin phrase . Types A '' contraction'' is an abbreviation formed by replacing letters with an apostrophe. Examples include ''I'm'' for ''I am'' and ''li'l'' for ''little''. An ''initialism'' or ''acronym'' is an abbreviation consisting of the initial letter of a sequence of words without other punctuation. For example, FBI ( ), USA ( ), IBM ( ), BBC ( ). When initialism is used as the preferred term, acronym refers more specifically to when the abbreviation is pronounced as a word rather than as separate letters; examples include SWAT and NASA. Initialisms, contractions and crasis share some semantic and phonetic functions, and are connected by the term ''abbreviat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantive
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an object or subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category ( part of speech) defined according to how its members com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Noun
In linguistics, a mass noun, uncountable noun, non-count noun, uncount noun, or just uncountable, is a noun with the syntactic property that any quantity of it is treated as an undifferentiated unit, rather than as something with discrete elements. Uncountable nouns are distinguished from count nouns. Given that different languages have different grammatical features, the actual test for which nouns are mass nouns may vary between languages. In English, mass nouns are characterized by the impossibility of being directly modified by a numeral without specifying a unit of measurement and by the impossibility of being combined with an indefinite article (''a'' or ''an''). Thus, the mass noun "water" is quantified as "20 litres of water" while the count noun "chair" is quantified as "20 chairs". However, both mass and count nouns can be quantified in relative terms without unit specification (e.g., "so much water", "so many chairs", though note the different quantifiers "much" a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation, also known as nouning, is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head (linguistics), head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivation (linguistics), derivational affix (e.g., the noun "legalization" from the verb "legalize"), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion (word formation), conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphology (linguistics), morphological transformation. English language, English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural language, natural part of language, but some insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elision
In linguistics, an elision or deletion is the omission of one or more sounds (such as a vowel, a consonant, or a whole syllable) in a word or phrase. However, these terms are also used to refer more narrowly to cases where two words are run together by the omission of a final sound. An example is the elision of word-final /t/ in English if it is preceded and followed by a consonant: "first light" is often pronounced "firs' light" (). Many other terms are used to refer to specific cases where sounds are omitted. Citation forms and contextual forms A word may be spoken individually in what is called the citation form. This corresponds to the pronunciation given in a dictionary. However, when words are spoken in context, it often happens that some sounds that belong to the citation form are omitted. Elision is not an all-or-nothing process: elision is more likely to occur in some styles of speaking and less likely in others. Many writers have described the styles of speech in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominalized Adjective
A nominalized adjective is an adjective that has undergone nominalization, and is thus used as a noun. In ''the rich and the poor'', the adjectives ''rich'' and ''poor'' function as nouns denoting people who are rich and poor respectively. In English The most common appearance of the nominalized adjective in English is when an adjective is used to indicate a collective group. This happens in the case where a phrase such as ''the poor people'' becomes ''the poor''. The adjective ''poor'' is nominalized, and the noun ''people'' disappears. Other adjectives commonly used in this way include ''rich'', ''wealthy'', ''homeless'', ''disability, disabled'', ''blind'', ''deaf'', etc., as well as certain demonyms such as ''English'', ''Welsh'', ''Irish'', ''French'', ''Dutch''. Another case is when an adjective is used to denote a single object with the property, as in "you take the long route, and I'll take the ''short''". Here ''the short'' stands for "the short route". A much more common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Complement
In grammar, an object complement is a predicative expression that follows a direct object of an attributive ditransitive or resultative verb and that complements the direct object of the sentence by describing it. Object complements are constituents of the predicate. Noun phrases and adjective phrases most frequently function as object complements.Quirk, Randolph, Sidney Greenbaum, Jan Svartvik, & Geoffrey Leech. 1985. A comprehensive grammar of the English language. London: Longman. Examples The object complement is bold in the following examples: ::*She painted the barn red. – Adjective as object complement Here, ''painted'' is an attributive ditransitive verb. The direct object is ''the barn''. The object complement construction allows for the combination of the sentences ''She painted the barn'' and ''The barn was painted red''. ::*He considers you a friend. – Noun phrase as object complement Here, ''considers'' is an attributive ditransitive verb. The direct object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject Complement
In traditional grammar, a subject complement is a predicative expression that follows a copula (commonly known as a linking verb), which complements the subject of a clause by means of characterization that completes the meaning of the subject. When a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun functions as a subject complement, it is called a predicative nominal. When an adjective or analogous phrase functions as subject complement, it is called a predicative adjective. In either case the predicative complement corresponds to the subject. Within the small class of copulas that preface a subject complement, the verb ''be'', or one of its concomitant forms, is the most common. Because a copula is an intransitive verb, subject complements are not customarily construed to be the object of the verb. They are often deemed to be neither arguments nor adjuncts of a predicate. A plural or singular subject, rather than a subject complement determines the grammatical number expressed by a copula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
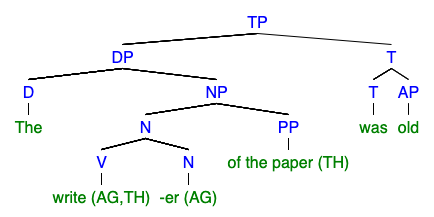
Predicative Adjective
A predicative expression (or just predicative) is part of a clause predicate, and is an expression that typically follows a copula or linking verb, e.g. ''be'', ''seem'', ''appear'', or that appears as a second complement (object complement) of a certain type of verb, e.g. ''call'', ''make'', ''name'', etc. The most frequently acknowledged types of predicative expressions are predicative adjectives (also predicate adjectives) and predicative nominals (also predicate nominals). The main trait of all predicative expressions is that they serve to express a property that is assigned to a "subject", whereby this subject is usually the clause subject, but at times it can be the clause object. A primary distinction is drawn between predicative (also ''predicate'') and attributive expressions. Further, predicative expressions are typically ''not'' clause arguments, and they are also typically ''not'' clause adjuncts. There is hence a three-way distinction between predicative expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resultative
In linguistics, a resultative (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a form that expresses that something or someone has undergone a change in state as the result of the completion of an event. Resultatives appear as Predicate (grammar), predicates of sentences, and are generally composed of a verb (denoting the event), a post-verbal noun phrase (denoting the entity that has undergone a change) and a so-called resultative phrase (denoting the state achieved as the result of the action named by the verb) which may be represented by an adjective, a prepositional phrase, or a grammatical particle, particle, among others.Goldberg, A. E. & Jackendoff, R. (2004). The English Resultative as a Family of Constructions. Language, 80, 532-568. For example, in the English sentence ''The man wiped the table clean'', the adjective ''clean'' denotes the state achieved by ''the table'' as a result of the event described as ''the man wiped''. Resultative constructions Resultative const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (; : copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being cooperative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula (in English, the verb "to be"), although some (such as Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attributive Expression
In grammar, an attributive expression is a word or phrase within a noun phrase that modifies the head noun. It may be an: * attributive adjective * attributive noun * attributive verb or other part of speech, such as an attributive numeral. See also * Property Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ... (attribute) * Attribution (other) {{SIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |