|
Atomic Theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. The definition of the word "atom" has changed over the years in response to scientific discoveries. Initially, it referred to a hypothetical concept of there being some fundamental particle of matter, too small to be seen by the naked eye, that could not be divided. Then the definition was refined to being the basic particles of the chemical elements, when chemists observed that elements seemed to combine with each other in ratios of small whole numbers. Then physicists discovered that these particles had an internal structure of their own and therefore perhaps did not deserve to be called "atoms", but renaming atoms would have been impractical by that point. Atomic theory is one of the most important scientific developments in history, crucial to all the physical sciences. At the start of ''The Feynman Lectures on Physics'', physicist and Nobel laureate Richard Feynman offers the atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowercase Sigmabot
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''#Majuscule, majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally ''#Minuscule, minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Definite Proportions
In chemistry, the law of definite proportions, sometimes called Proust's law or the law of constant composition, states that a given chemical compound contains its constituent elements in a fixed ratio (by mass) and does not depend on its source or method of preparation. For example, oxygen makes up about 8/9 of the mass of any sample of pure water, while hydrogen makes up the remaining 1/9 of the mass: the mass of two elements in a compound are always in the same ratio. Along with the law of multiple proportions, the law of definite proportions forms the basis of stoichiometry. History The law of definite proportion was given by Joseph Proust in 1797. At the end of the 18th century, when the concept of a chemical compound had not yet been fully developed, the law was novel. In fact, when first proposed, it was a controversial statement and was opposed by other chemists, most notably Proust's fellow Frenchman Claude Louis Berthollet, who argued that the elements could combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
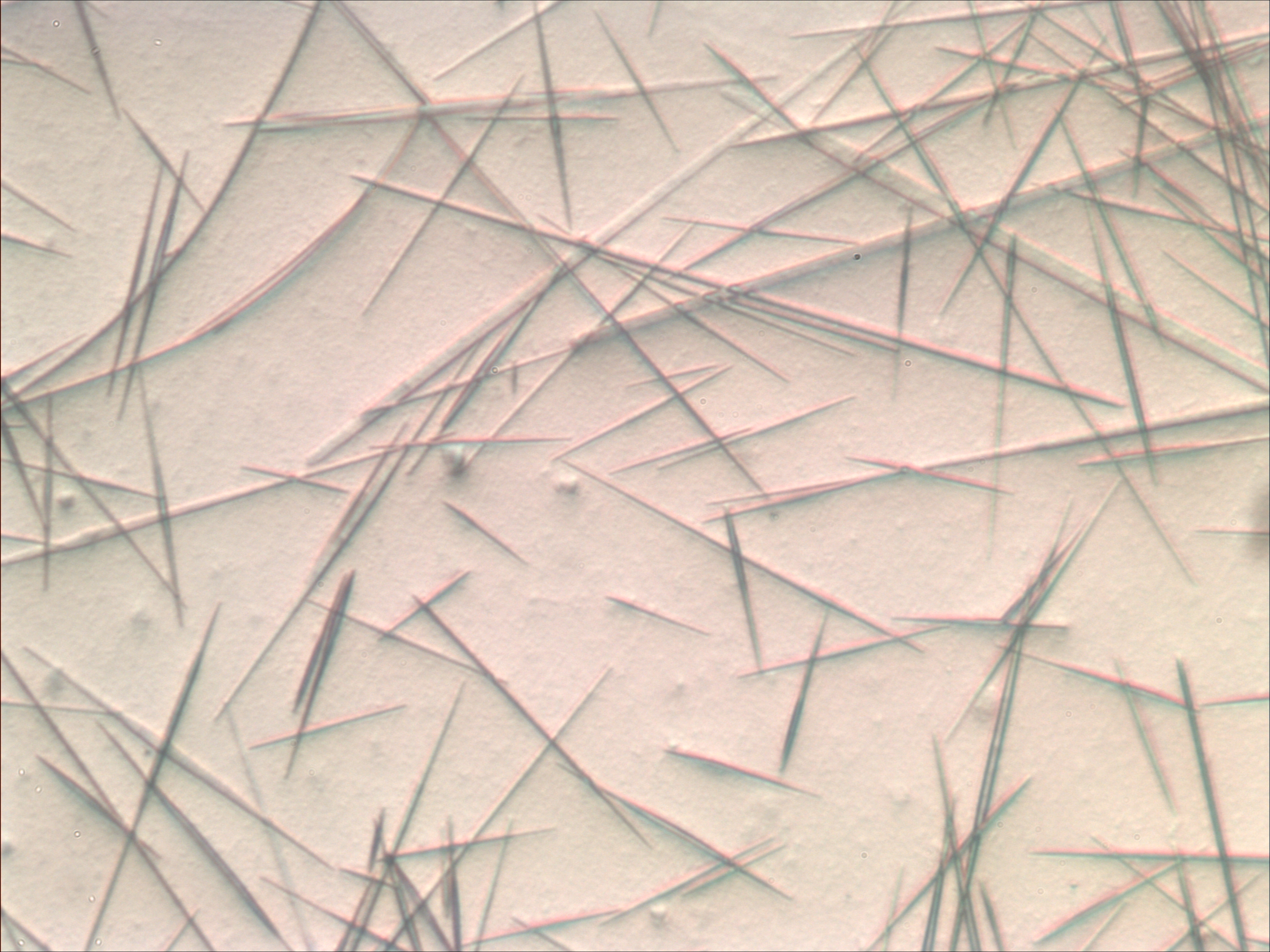
Iron(III) Oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It occurs in nature as the mineral hematite, which serves as the primary source of iron for the steel industry. It is also known as red iron oxide, especially when used in pigments. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, since rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as hydrous ferric oxide. Ferric oxide is readily attacked by even weak acids. It is a weak oxidising agent, most famously when reduced by aluminium in the thermite reaction. Structure can be obtained in various polymorphs. In the primary polymorph, α, iron adopts octahedral coordination geometry. That is, each Fe center is bound to six oxygen ligands. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Oxide
Iron(II) oxide or ferrous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula FeO. Its mineral form is known as wüstite. One of several iron oxides, it is a black-colored powder that is sometimes confused with rust, the latter of which consists of hydrated iron(III) oxide (ferric oxide). Iron(II) oxide also refers to a family of related non-stoichiometric compounds, which are typically iron deficient with compositions ranging from Fe0.84O to Fe0.95O. Preparation FeO can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of iron(II) oxalate. : The procedure is conducted under an inert atmosphere to avoid the formation of iron(III) oxide (). A similar procedure can also be used for the synthesis of manganous oxide and stannous oxide. Stoichiometric FeO can be prepared by heating Fe0.95O with metallic iron at 770 °C and 36 kbar.Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford University Press Reactions FeO is thermodynamically unstable below 575 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(IV) Oxide
Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid. Structure Tin(IV) oxide crystallises with the rutile structure. As such the tin atoms are six coordinate and the oxygen atoms three coordinate. SnO2 is usually regarded as an oxygen-deficient n-type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of SnO2 have been described as stannic acid. Such materials appear to be hydrated particles of SnO2 where the composition reflects the particle size. Preparation Tin(IV) oxide occurs naturally. Synthetic tin(IV) oxide is produced by burning tin metal in air. Annual production is in the range of 10 kilotons. SnO2 is reduced industrially to the metal with carbon in a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C. Reactions The reaction from tin(IV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(II) Oxide
Tin(II) oxide (stannous oxide) is a compound with the formula SnO. It is composed of tin and oxygen where tin has the oxidation state of +2. There are two forms, a stable blue-black form and a metastable red form. Preparation and reactions Blue-black SnO can be produced by heating the tin(II) oxide hydrate, (''x'' < 1) precipitated when a tin(II) salt is reacted with an alkali hydroxide such as NaOH.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier Metastable, red SnO can be prepared by gentle heating of the precipitate produced by the action of aqueous ammonia on a tin(II) salt. SnO may be prepared as a pure substance in the laboratory, by controlled heating of tin(II) oxalate ( stannous oxalate) in the absence of air or under a CO2 atmosphere. This method is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Oxide (other)
Tin oxide may refer to: * Tin(II) oxide (stannous oxide), a black powder with the formula SnO * Tin(IV) oxide Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in ti ... (tin dioxide, stannic oxide), a white powder with the formula SnO2 {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an Organic chemistry, organic Organic compound, compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward creating polyethylene, which is a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Production greenhouse gas emissions, emits greenhouse gases, including methane from feedstock production and carbon dioxide from any non-sustainable energy used. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to induce ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Thomson (chemist)
Thomas Thomson (12 April 1773 – 2 August 1852) was a Scottish chemist and mineralogist whose writings contributed to the early spread of Dalton's atomic theory. His scientific accomplishments include the invention of the saccharometer and he gave silicon its current name. He served as president of the Philosophical Society of Glasgow. Thomson was the father of the botanist Thomas Thomson, and the uncle and father-in-law of the Medical Officer of Health Robert Thomson. Life and work Thomas Thomson was born in Crieff in Perthshire, on 12 April 1773 the son of Elizabeth Ewan and John Thomson. He was educated at Crieff Parish School and Stirling Burgh School. He then studied for a general degree at the University of St Andrews to study in classics, mathematics, and natural philosophy from 1787 to 1790. He had a five year break then entered University of Edinburgh to study medicine in 1795, gaining his doctorate (MD) in 1799. During this latter period he was inspired by hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |