|
Atmosphere Of Triton
The atmosphere of Triton is the layer of gases surrounding Triton. Like the atmospheres of Titan and Pluto, Triton's atmosphere is composed more than 95% of nitrogen, with smaller amounts of methane and carbon monoxide. It hosts a layer of organic haze extending up to 30 kilometers above its surface and a deck of thin bright clouds at about 4 kilometers in altitude. Due to Triton's low gravity, its atmosphere is loosely bound, extending over 800 kilometers from its surface. Triton, along with Saturn's moon Titan, is one of only two moons in the Solar System known to have significant, global atmospheres. The surface pressure is only 14 microbars (1.4 Pa or 0.0105mmHg), of the surface pressure on Earth. Similar to the atmosphere of Pluto, Triton's atmosphere is sensitive to seasonal changes; observations obtained in 1998 showed an increase in temperature, increasing the atmosphere's density. Composition and chemistry Nitrogen is the main gas in Triton's atmosphere. The two ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, as a part of the Voyager program. It was launched on a trajectory towards the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn) and enabled further encounters with the ice giants (Uranus and Neptune). The only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets, it was the List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System, third of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System#Farthest regions, Solar System. Launched 16 days before its twin ''Voyager 1'', the primary mission of the spacecraft was to study the outer planets and its extended mission is to study interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Exploration of Jupiter, Jovian system in 1979, the Exploration of Saturn, Saturnian system in 1981, Exploration of Uranus, Uranian system in 1986, and the Exploration of Neptune, Neptunian system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
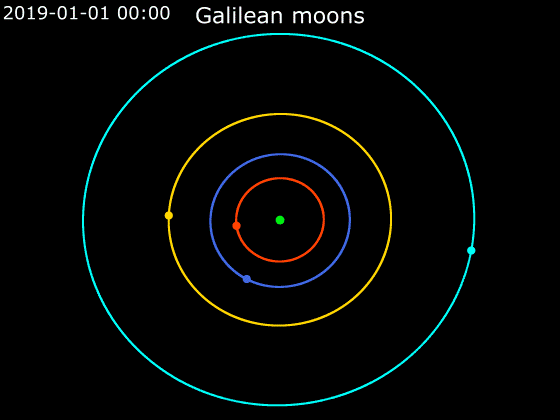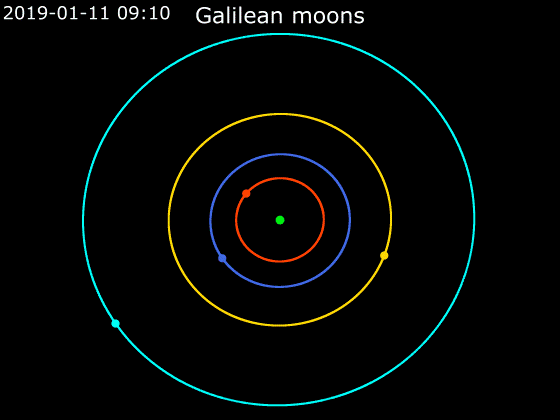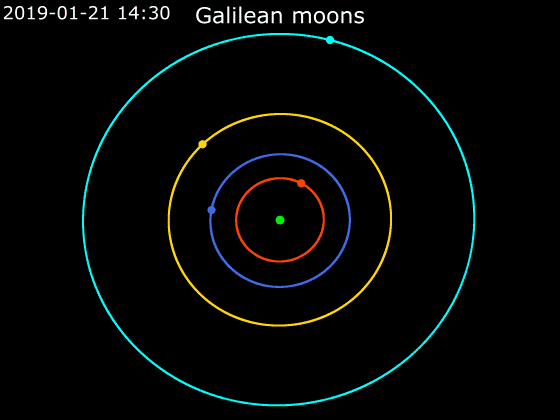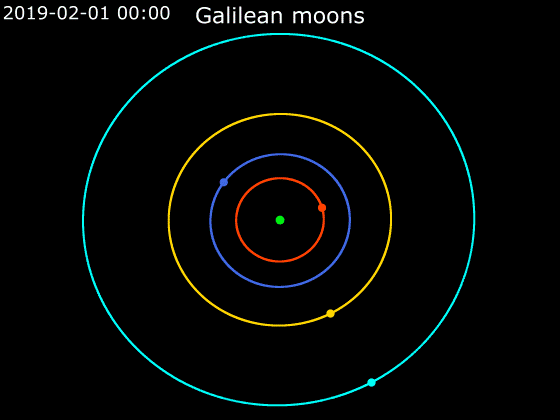
Callisto (moon)
Callisto ( ) is the second-largest moon of Jupiter, after Ganymede. In the Solar System it is the third-largest moon after Ganymede and Saturn's largest moon Titan, and nearly as large as the smallest planet Mercury. Callisto is, with a diameter of , roughly a third larger than Earth's Moon and orbits Jupiter on average at a distance of , which is about five times further out than the Moon orbiting Earth. It is the outermost of the four large Galilean moons of Jupiter, which were discovered in 1610 with one of the first telescopes, and is today visible from Earth with common binoculars. The surface of Callisto is the oldest and most heavily cratered in the Solar System. Its surface is completely covered with impact craters. It does not show any signatures of subsurface processes such as plate tectonics or volcanism, with no signs that geological activity in general has ever occurred, and is thought to have evolved predominantly under the influence of impacts. Promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylene (compound)
Methylene (IUPAC name: methylidene, also called carbene or methene) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (also written and not to be confused with compressed hydrogen, which is also denoted ). It is a colourless gas that fluoresces in the mid-infrared range, and only persists in dilution, or as an adduct. Methylene is the simplest carbene.Roald Hoffman (2005), ''Molecular Orbitals of Transition Metal Complexes''. Oxford. . It is usually detected only at very low temperatures or as a short-lived intermediate in chemical reactions.W. B. DeMore and S. W. Benson (1964), Preparation, properties, and reactivity of methylene'. In ''Advances in Photochemistry'', John Wiley & Sons, 453 pages. Nomenclature The trivial name ''carbene'' is the preferred IUPAC name. The systematic names ''methylidene'' and ''dihydridocarbon'', valid IUPAC names, are constructed according to the substitutive and additive nomenclatures, respectively. ''Methylidene'' is viewed as methane with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by absorption of light or photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule that dissociates into two fragments. Here, “light” is broadly defined as radiation spanning the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV), ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. To break covalent bonds, photon energies corresponding to visible, UV, or VUV light are typically required, whereas IR photons may be sufficiently energetic to detach ligands from coordination complexes or to fragment supramolecular complexes. Photolysis in photosynthesis Photolysis is part of the light-dependent reaction, light phase, photochemical phase, or Hill reaction of photosynthesis. The general reaction of photosynthetic photolysis can be given in terms of photons as: :\ce + 2 \text \longri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of air. Neon was discovered in 1898 alongside krypton and xenon, identified as one of the three remaining rare inert elements in dry air after the removal of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. Its discovery was marked by the distinctive bright red emission spectrum it exhibited, leading to its immediate recognition as a new element. The name ''neon'' originates from the Greek word , a neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is a chemically inert gas; although neon compounds do exist, they are primarily ionic molecules or fragile molecules held together by van der Waals forces. The synthesis of most neon in the cosmos resulted from the nuclear fusion within stars of oxygen and helium through the alpha-capture proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solstice
A solstice is the time when the Sun reaches its most northerly or southerly sun path, excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around 20–22 June and 20–22 December. In many countries, the seasons of the year are defined by reference to the solstices and the equinoxes. The term ''solstice'' can also be used in a broader sense, as the day when this occurs. For locations not too close to the equator or the poles, the dates with the longest and shortest periods of daylight are the summer and winter solstices, respectively. Terms with no ambiguity as to which hemisphere is the context are "June solstice" and "December solstice", referring to the months in which they take place every year. Etymology The word ''solstice'' is derived from the Latin () and (), because at the solstices, the Sun's declination appears to "stand still"; that is, the seasonal movement of the Sun's sun path, daily path (as seen from Earth) paus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MmHg
A millimetre of mercury is a manometric unit of pressure, formerly defined as the extra pressure generated by a column of mercury one millimetre high. Currently, it is defined as exactly , or approximately 1 torr = atmosphere = pascals.Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC of the It is denoted mmHg or mm Hg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |