|
Atlas Of North American English
''The Atlas of North American English: Phonetics, Phonology and Sound Change'' (abbreviated ANAE; formerly, the ''Phonological Atlas of North America'') is a 2006 book that presents an overview of the pronunciation patterns ( accents) in all the major dialect regions of the English language as spoken in urban areas of the United States and Canada. It is the result of a large-scale survey by linguists William Labov, Sharon Ash, and Charles Boberg. Speech data was collected, mainly from 1992 to 1999, by means of telephone interviews with individuals in metropolitan areas in all regions of the U.S. and Canada. Using acoustic analysis of speech from these interviews, ''ANAE'' traces sound changes in progress in North American English, and defines boundaries between dialect regions based on the different sound changes taking place in them. ''The Atlas of North American English'' received the Leonard Bloomfield Book Award at the 2008 meeting of the Linguistic Society of Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accent (sociolinguistics)
In sociolinguistics, an accent is a way of pronouncing a language that is distinctive to a country, area, social class, or individual. An accent may be identified with the locality in which its speakers reside (a regional or geographical accent), the socioeconomic status of its speakers, their ethnicity (an ethnolect), their caste or social class (a social accent), or influence from their first language (a foreign accent). Accents typically differ in quality of voice, pronunciation and distinction of vowels and consonants, stress, and prosody. Although grammar, semantics, vocabulary, and other language characteristics often vary concurrently with accent, the word "accent" may refer specifically to the differences in pronunciation, whereas the word "dialect" encompasses the broader set of linguistic differences. "Accent" is often a subset of "dialect". History As human beings spread out into isolated communities, stresses and peculiarities develop. Over time, they can develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City English
New York City English, or Metropolitan New York English, is a regional dialect of American English spoken primarily in New York City and some of its surrounding metropolitan area. Along with Southern American English, it has been described by sociolinguist William Labov as one of the most widely recognized regional dialects in the United States. Its pronunciation system—the New York accent—is widely represented in American media by many public figures and fictional characters. Major features of the accent include a high, gliding vowel (in words like ''talk'' and ''caught''); a split of the "short a" vowel into two separate sounds; variable dropping of ''r'' sounds; and a lack of the '' cot–caught'', '' Mary–marry–merry'', and '' hurry–furry'' mergers heard in many other American accents. Today, New York City English is associated particularly with urban New Yorkers of lower and middle socioeconomic status who are descended from 19th- and 20th-century European i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialectology
Dialectology (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ''dialektos'', "talk, dialect"; and , ''-logy, -logia'') is the scientific study of dialects: subsets of languages. Though in the 19th century a branch of historical linguistics, dialectology is often now considered a sub-field of, or subsumed by, sociolinguistics. It studies variations in language based primarily on geographic distribution and their associated features. Dialectology deals with such topics as divergence of two local dialects from a common ancestor and Historical_linguistics#Diachronic_and_synchronic_analysis, synchronic variation. Dialectologists are ultimately concerned with grammatical, lexical and phonological features that correspond to regional areas. Thus they usually deal not only with populations that have lived in certain areas for generations, but also with migrant groups that bring their languages to new areas (see language contact). Commonly studied concepts in dialectology include the problem of mutual intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American English Regional Phonology
North American English regional phonology is the study of variations in the pronunciation of spoken North American English (English of the United States and Canada)—what are commonly known simply as "regional accents". Though studies of regional dialects can be based on multiple characteristics, often including characteristics that are phonology, phonemic (sound-based, focusing on major word-differentiating patterns and structures in speech), phonetics, phonetic (sound-based, focusing on any more exact and specific details of speech), lexicon, lexical (vocabulary-based), and syntax, syntactic (grammar-based), this article focuses only on the former two items. North American English includes American English, which has several highly developed and distinct regional varieties, along with the closely related Canadian English, which is more homogeneous geographically. American English (especially Western dialects) and Canadian English have more in common with each other than with Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautosyllabic
Two or more segments are tautosyllabic (with each other) if they occur in the same syllable. For instance, the English word "cat", , is monosyllabic In linguistics, a monosyllable is a word or utterance of only one syllable. It is most commonly studied in the fields of phonology and morphology. The word has originated from the Greek language Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Ind ... and so its three phonemes , and are tautosyllabic. They can also be described as sharing a 'tautosyllabic distribution'. Phonemes that are not tautosyllabic are heterosyllabic. For example, in the English word "mustard" , and are heterosyllabic since they are members of different syllables. See also * Ambisyllabicity, sounds that are arguably shared between two syllables (such as 'rr' in British English "hurry") References * Phonotactics {{phonology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checked Vowel
In phonetics and phonology, checked vowels are those that commonly stand in a stressed closed syllable, while free vowels are those that can stand in either a stressed closed syllable or a stressed open syllable. Usage The terms ''checked vowel'' and ''free vowel'' originated in English phonetics and phonology; they are seldom used for the description of other languages, even though a distinction between vowels that usually have to be followed by a consonant and other vowels is common in most Germanic languages. The terms ''checked vowel'' and ''free vowel'' correspond closely to the terms ''lax vowel'' and ''tense vowel'', respectively, but linguists often prefer to use the terms ''checked'' and ''free'', as there is no clear-cut phonetic definition of vowel tenseness, and, because by most given definitions of tenseness, and are considered lax—even though they behave in American English as free vowels. ''Checked vowels'' is also used to refer to the kind of very short g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western American English
Western American English (also known as Western U.S. English) is a variety of American English that largely unites the entire Western United States as a single dialect region, including the states of California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, and Montana. It also generally encompasses Washington, Oregon, and Idaho, some of whose speakers are classified under Pacific Northwest English. The West was the last area in the United States to be reached during the gradual westward expansion of settlement by English speakers and its history shows considerable mixing and leveling of the linguistic patterns of other regions. Therefore, since the settlement populations are relatively young when compared with other regions, the American West continues to be a dialect region in formation. According to the 2006 '' Atlas of North American English'', as a very broad generalization, Western U.S. accents are differentiated from Southern U.S. accents in maintaining as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland American English
Midland American English is a regional dialect or super-dialect of American English, geographically lying between the traditionally-defined Northern United States, Northern and Southern United States. The boundaries of Midland American English are not entirely clear, being revised and reduced by linguists due to definitional changes and several Midland sub-regions undergoing rapid and diverging pronunciation shifts since the early-middle 20th century onwards. As of the 2000s (decade), early 21st century, these general characteristics of the Midland regional accent are firmly established: fronting (phonetics), fronting of the , , and vowels occurs towards the center or even the front of the mouth; the cot–caught merger is neither fully completed nor fully absent; and æ tensing, short-''a'' tensing evidently occurs strongest before nasal consonants. The currently-documented core of the Midland dialect region spans from central Ohio at its eastern extreme to central Nebraska and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
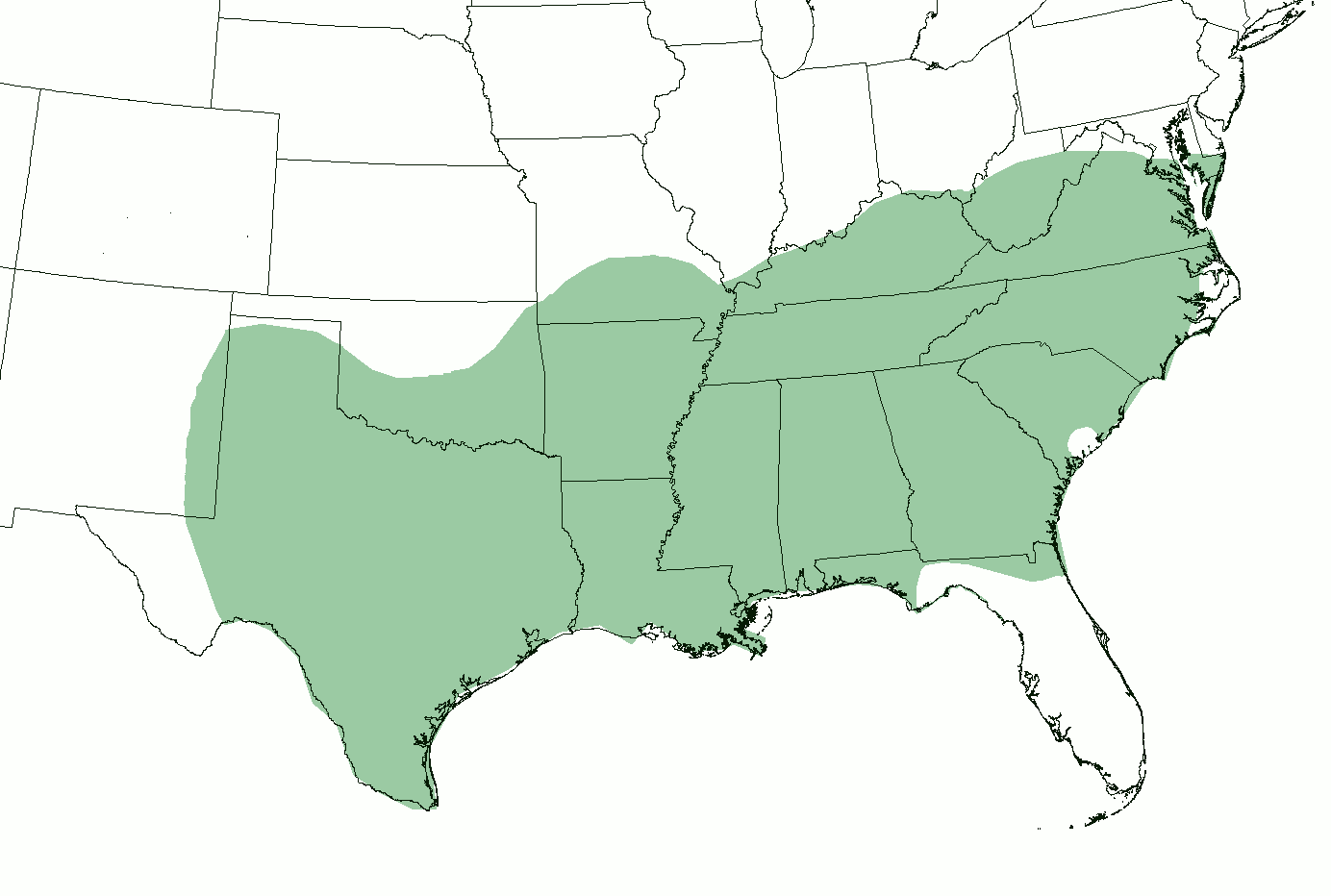
Southern Vowel Shift
In the United States, a Southern accent or simply Southern is the sound system of the modern Southern regional dialect of American English. Most English of the Southern United States, particularly as spoken by white Southerners, underwent several major sound changes from the late 19th century to the middle of the 20th century, during which a rural-originating sound system, including two vowel shifts, expanded geographically through the whole region. This regional accent is fairly unified, contrasting with the more diverse and localized sound systems of the 19th-century Southern dialects. Still, there remains ongoing variation in the Southern accent regarding potential differences based on a speaker's exact sub-region, age, ethnicity, and other social factors. General modern phonology The South as a wide-ranging accent region of the U.S. as distinct from, say, the West or the Northeast, generally includes the pronunciation features below. Southern Vowel Shift The Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, primarily by White Southerners and increasingly concentrated in more rural areas. As of 2000s research, its conservative and innovative (linguistics), most innovative accents include southern Appalachian English, Appalachian and certain Texan English, Texan accents. Such research has described Southern American English as the largest Dialects of North American English, American regional accent group by number of speakers. More formal terms used within American linguistics include ''Southern White Vernacular English'' and ''Rural White Southern English''. However, more commonly in the United States, the variety is recognized as a Southern accent, which technically refers merely to the Southern accent (United States), dialect's sound system, often also simply called Southern. History A diversity of Older Southern Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore English
A Baltimore accent, also known as Baltimorese and sometimes humorously spelled Bawlmerese or Ballimorese, is an accent or sub-variety of Delaware Valley English (a dialect whose largest hub is ) that originates among blue-collar residents of , < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |