|
Astronomical Society Of The Pacific
The Astronomical Society of the Pacific (ASP) is an American scientific and educational organization, founded in San Francisco on February 7, 1889, immediately following the solar eclipse of January 1, 1889. Its name derives from its origins on the Pacific Coast, but today it has members all over the country and the world. It has the legal status of a nonprofit organization. It is the largest general astronomy education society in the world, with members from over 40 countries. Education and outreach programs The ASP's mission is to promote public interest in and awareness of astronomy (and increase scientific literacy) through its publications, web site, and many educational and outreach programs. * The NASA Night Sky Network – a community of more than 450 astronomy clubs across the U.S. that share their time and telescopes to engage the public with unique astronomy experiences. The ASP provides training and materials to enhance clubs outreach activities, and inspires more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-profit Organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or social benefit, as opposed to an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a Profit (accounting), profit for its owners. A nonprofit organization is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. Depending on the local laws, charities are regularly organized as non-profits. A host of organizations may be non-profit, including some political organizations, schools, hospitals, business associations, churches, foundations, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be Tax exemption, tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest known trans-Neptunian object by volume by a small margin, but is less massive than Eris (dwarf planet), Eris. Like other Kuiper belt objects, Pluto is made primarily of ice and rock and is much smaller than the inner planets. Pluto has roughly one-sixth the mass of the Moon and one-third its volume. Originally considered a planet, its classification was changed when astronomers adopted a new definition of planet, definition of ''planet''. Pluto has a moderately Orbital eccentricity, eccentric and Inclination, inclined orbit, ranging from from the Sun. Light from the Sun takes 5.5 hours to reach Pluto at its orbital distance of . Pluto's eccentric orbit periodically brings it closer to the Sun than Neptune, but a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothea Klumpke-Roberts
Dorothea Klumpke Roberts (August 9, 1861 in San Francisco – October 5, 1942 in San Francisco) was an American astronomer. She was the Director of the Bureau of Measurements at the Paris Observatory and was made a Chevalier de la Légion d'Honneur, or a Knight of the National Order of the Legion of Honor. Biography Roberts' father, John Gerard Klumpke (1825-1917), was a German immigrant who came to California in 1850 with the Gold Rush and later became a successful realtor in San Francisco. He married Dorothea Mathilda Tolle in 1855, and the couple had five daughters and two sons. Her sisters included Anna Elizabeth Klumpke, painter and companion to the French animal painter Rosa Bonheur; Julia Klumpke, a violinist and composer; Mathilda, an accomplished pianist and pupil of Marmontel; and the neurologist Augusta, who, with her physician husband, Joseph Jules Dejerine, established a clinic and wrote numerous papers. In 1877, Klumpke moved to Paris, France, while her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klumpke-Roberts Award
The Klumpke-Roberts Award, one of seven international and national awards for service to astronomy and astronomy education given by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, was established from a bequest by astronomer An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ... Dorothea Klumpke-Roberts to honor her husband Isaac Roberts and her parents. It recognizes outstanding contributions to the public understanding and appreciation of astronomy. It is open to "individuals involved in science, education, writing/publishing, broadcasting, astronomy popularization, the arts, or other pursuits" from all nations and is the most prestigious award of its kind. Award winners SourceAstronomical Society of the Pacific See also * List of astronomy awards References {{reflist Astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Wolfe Bruce
Catherine Wolfe Bruce (January 22, 1816, New York – March 13, 1900, New York) was a noted American philanthropist and patron of astronomy. Early life Bruce was born on January 22, 1816. She was the daughter of the George Bruce (1781–1866), a famous type founder who was born in Edinburgh, and Catherine Wolfe (1785–1861), the daughter of David Wolfe (1748–1836) of New York City. One of five children,Ogilvie, Marilyn Bailey, and Joy Dorothy Harvey. ''The Biographical Dictionary of Women in Science: Pioneering Lives from Ancient Times to the Mid-20th Century''. New York: Routledge, 2000. her brother was David Wolfe Bruce (1824–1895), who, along with David Wolfe Bishop, inherited the fortune of their cousin, Catharine Lorillard Wolfe. Career She studied painting, learned Latin, German, French and Italian, and was familiar with the literature of those languages. In 1890, she wrote and published a translation of the "'' Dies Irae''." Personal life Due to an ever-increasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Medal
The Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal is awarded every year by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific for outstanding lifetime contributions to astronomy. It is named after Catherine Wolfe Bruce, an American patroness of astronomy, and was first awarded in 1898. List of Bruce Medalists SourceAstronomical Society of the Pacific * 1898 – Simon Newcomb * 1899 – Arthur Auwers * 1900 – David Gill * 1902 – Giovanni V. Schiaparelli * 1904 – William Huggins * 1906 – Hermann Carl Vogel * 1908 – Edward C. Pickering * 1909 – George William Hill * 1911 – Henri Poincaré * 1913 – Jacobus C. Kapteyn * 1914 – Oskar Backlund * 1915 – William Wallace Campbell * 1916 – George Ellery Hale * 1917 – Edward Emerson Barnard * 1920 – Ernest W. Brown * 1921 – Henri A. Deslandres * 1922 – Frank W. Dyson * 1923 – Benjamin Baillaud * 1924 – Arthur Stanley Eddington * 1925 – Henry Norris Russell * 1926 – Robert G. Aitken * 1927 – Herber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logo Of The Astronomical Society Of The Pacific
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name that it represents, as in a wordmark. In the days of hot metal typesetting, a logotype was one word cast as a single piece of type (e.g. "The" in ATF Garamond), as opposed to a ligature, which is two or more letters joined, but not forming a word. By extension, the term was also used for a uniquely set and arranged typeface or colophon. At the level of mass communication and in common usage, a company's logo is today often synonymous with its trademark or brand.Wheeler, Alina. ''Designing Brand Identity'' © 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (page 4) Etymology Douglas Harper's ''Online Etymology Dictionary'' states that the first surviving written record of the term 'logo' dates back to 1937, and that the term was "probably a shortening of logogram". History Numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia Louise Trimble
Virginia Louise Trimble (born November 15, 1943) is an American astronomer specializing in the structure and evolution of stars and galaxies, and the history of astronomy. She has published more than 600 works in Astrophysics, and dozens of other works in the history of other sciences. She is famous for an annual review of astronomy and astrophysics research that was published in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, and often gives summary reviews at astrophysical conferences. In 2018, she was elected a Patron of the American Astronomical Society, for her many years of intellectual, organizational, and financial contributions to the society. Life Trimble "grew up the only child of a chemist father and a mother with a flair for language, within easy driving distance of both UCLA and Caltech." While attending UCLA in 1962, she was the subject of a ''Life'' article titled "Behind a Lovely Face, a 180 I.Q." The following year, she was selected to promote ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Photography
Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors interfaced to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The digitized image is stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. It is a form of digital imaging based on gathering visible light (or for scientific instruments, light in various ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum). Until the advent of such technology, photographs were made by exposing light-sensitive photographic film and paper, which was processed in liquid chemical solutions to develop and stabilize the image. Digital photographs are typically created solely by computer-based photoelectric and mechanical techniques, without wet bath chemical processing. In consumer markets, apart from enthusiast digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLR), most digital cameras now come wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
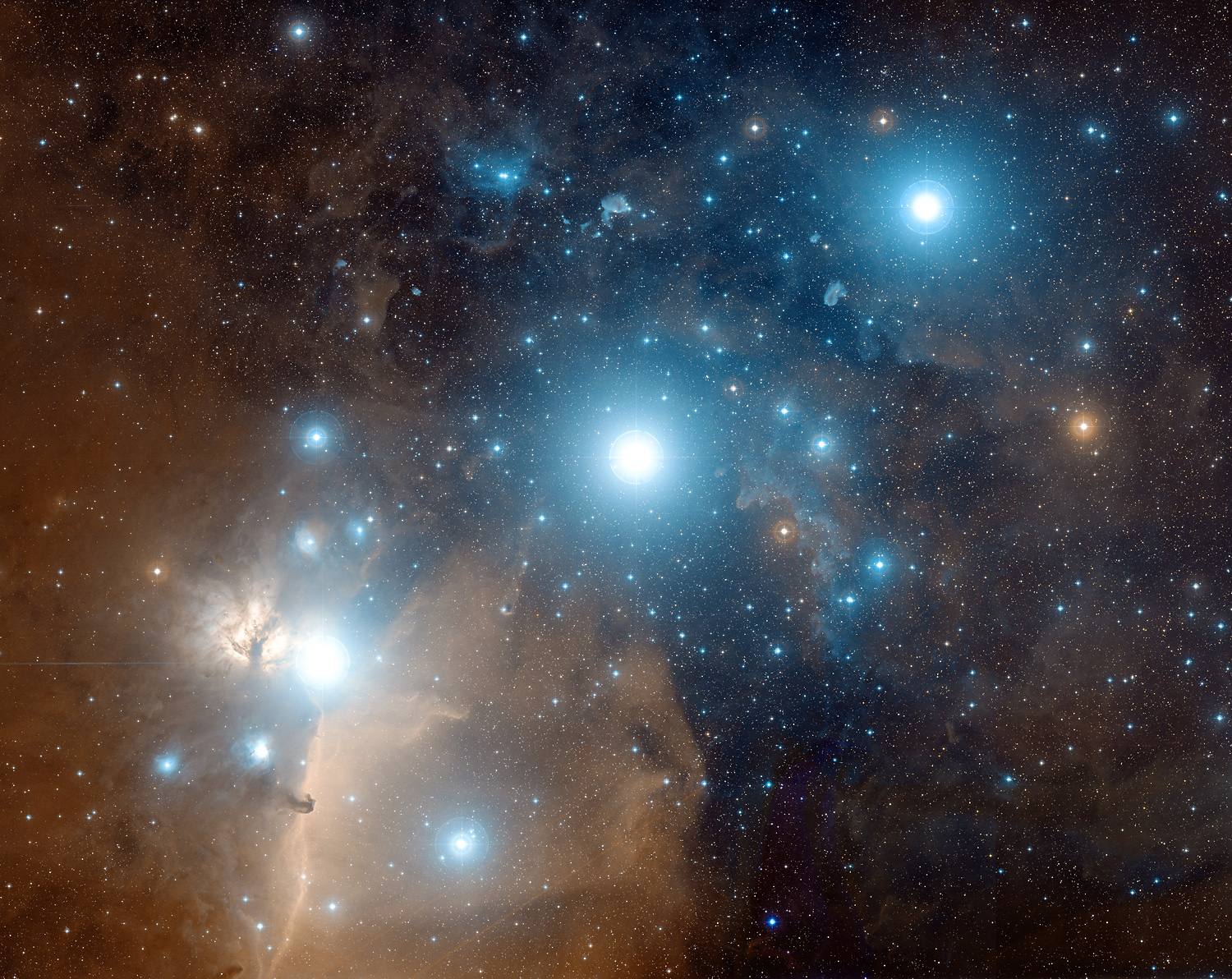
David Malin
David Frederick Malin (born 28 March 1941) is a British-Australian astronomer and photographer. He is principally known for his spectacular colour images of astronomical objects. A galaxy is named after him, Malin 1, which he discovered in 1986 and which is the largest spiral galaxy so far discovered. Career Malin was born in 1941 and raised in Heywood, Greater Manchester, in the north of England. He was trained as a chemist and originally worked as a microscopist. In 1975 he moved to Sydney to take up a job with the Anglo-Australian Observatory (AAO), now the Australian Astronomical Observatory. Whilst working at the AAO, Malin developed several photographic processing techniques to maximise the ability to extract faint and low contrast detail from the non-linear response and high densities of photographic plates. These techniques were initially devised to enhance the scientific return from photography, but Malin is now best known for the series of three-colour wide fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Photographer
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1839, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects outside of the visible spectrum of the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxy, galaxies. This is accomplished through long-exposure photography, long time exposure as both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over long periods of time or using specialized optical filters which limit the photons to a certain wavelength. Photography using extended exposure-times revolutionized the field of professional astronomical research, recording hundreds of thousands of new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |