|
Association For Renaissance Martial Arts
Association for Renaissance Martial Arts (ARMA) is a US-based non-profit organization dedicated to the study and practice of historical European martial arts of the 15th to 17th centuries.About This article contains information about the goals and aims of the Association for Renaissance Martial Arts. ARMA was formed in 2001 under director John Clements as a continuation of the Historical Armed Combat Association (HACA, since 1992). As of 2006, the ARMA claimed a number of close to 500 paying members. They also list a number of "Academic Consultants". History The ARMA began in 1992 as the Historical Armed Combat Association (HACA), a group led principally by[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-profit Organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or social benefit, as opposed to an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a Profit (accounting), profit for its owners. A nonprofit organization is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. Depending on the local laws, charities are regularly organized as non-profits. A host of organizations may be non-profit, including some political organizations, schools, hospitals, business associations, churches, foundations, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be Tax exemption, tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greatsword
The English language terminology used in the classification of swords is imprecise and has varied widely over time. There is no historical dictionary for the universal names, classification, or terminology of swords; a sword was simply a single-edged or double-edged knife that grew incrementally longer and more complex with technological advances. Historical terms without a universal consensus of definition (e.g. "arming sword", "broadsword", "long sword", etc.) were used to label weapons of similar appearance but of different historical periods, regional cultures, and fabrication technology. These terms were often described in relation to other unrelated weapons, without regard to their intended use and fighting style. In modern history, many of these terms have been given specific, often arbitrary meanings that are unrelated to any of their historical meanings. Terminology Some of these terms originate contemporaneously with the weapons which they describe. Others are modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
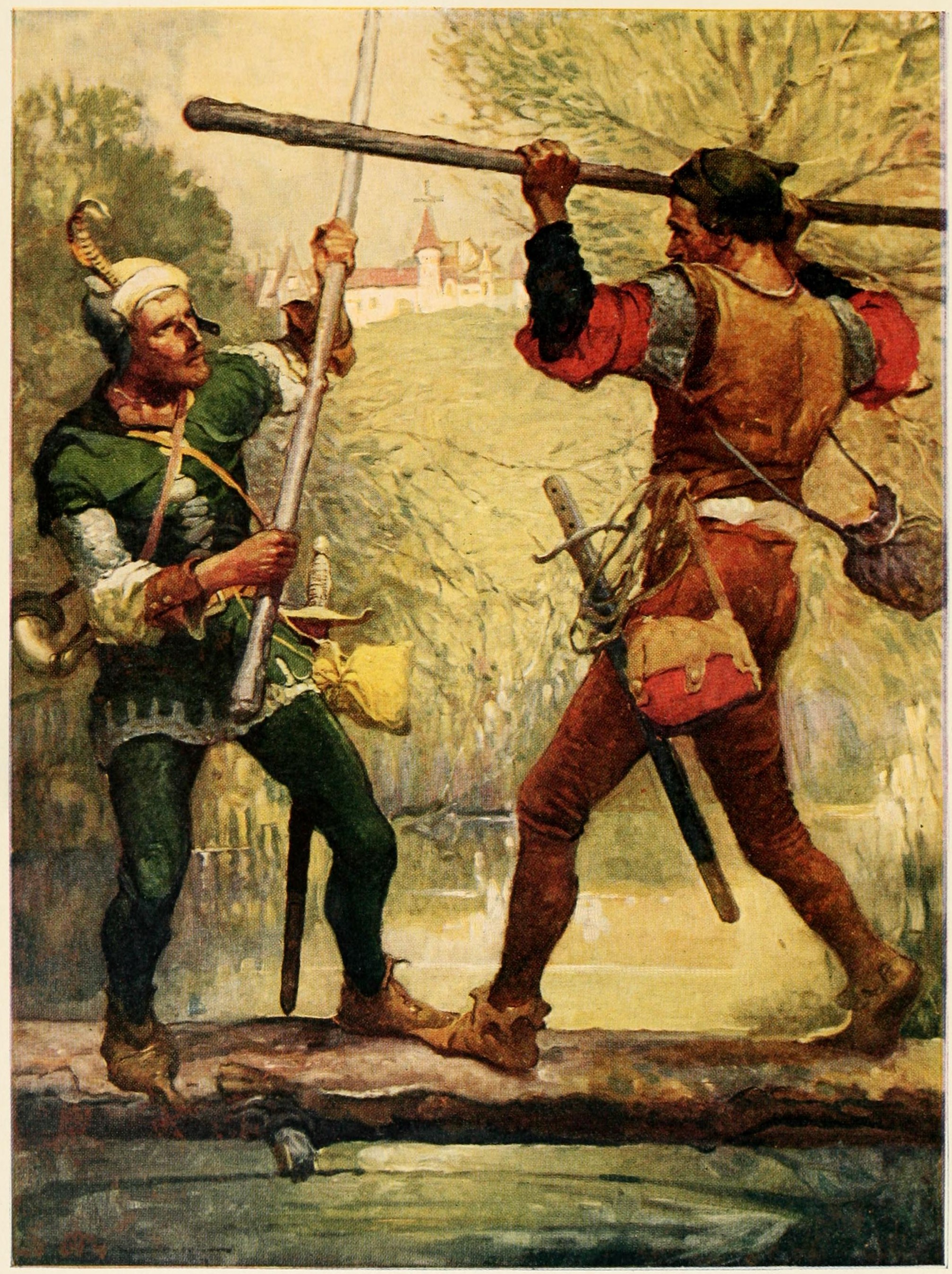
Swordsmanship
Swordsmanship or sword fighting refers to the skills and techniques used in combat and training with any type of sword. The term is modern, and as such was mainly used to refer to smallsword fencing, but by extension it can also be applied to any martial art involving the use of a sword. The formation of the English word "swordsman" is parallel to the Latin word ''gladiator'', a term for the professional fighters who fought against each other and a variety of other foes for the entertainment of spectators in the Roman Empire. The word ''gladiator'' itself comes from the Latin word ''gladius'', which is a type of sword. Europe Classical history The Roman legionary, legionaries and other forces of the Roman military, until the 2nd century A.D., used the gladius as a short thrusting sword effectively with the ''Scutum (shield), scutum'', a type of shield, in battle. According to Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus, Vegetius, the Romans mainly used underhanded stabs and thrusts, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Playing
A Prize Playing was a test of martial skill popular in Renaissance England with the London-based Corporation of Masters of the Noble Science of Defence. It involved several dozen bouts against continually refreshing opponents, with little or no rest in between. This practice was revived after a fashion in the late 17th century in the form of "Prize Fights", whence the term prizefighting for modern professional boxing. Renaissance Prize Playings The time and place for a Prize Playing was determined by the four Ancient Masters of the school. Notices called Bills of Challenge were posted of the event and a wooden scaffolding was erected in a public square. A good number of formalities were observed and at one time rules were endorsed by the Crown. On the appointed day and time, following a procession of drums and flags the Player was paraded to the raised scaffold with much fanfare. The public gathered close to watch, cheer, and throw coins onto the platform; the student would e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company Of Masters
The Company of Maisters of the Science of Defence was an organisation formed in England during the reign of Henry VIII Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ... to regulate the teaching of the ''Arte of Defence'' or ''historical fencing, fencing'', using a range of weapons, including the rapier, quarterstaff, and, most notably, the broadsword. This school of fencing persisted throughout the 16th century but declined after the end of the Tudor period. Tudor England It served to prevent unlicensed instructors from operating, both as a form of quality assurance and as a monopoly to protect the livelihoods of its members. It also regulated the conduct of members to one another, both instructor and student. Like the guilds it resembled, the company certified its members with v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provost (martial Arts)
In the 16th-century, London-based Corporation of Masters of the Noble Science of Defence (or "Company of Masters") Provost was the third of four ranks, the others being Scholar, Free Scholar, and Master. A Free Scholar could not be accredited as a Provost until they had studied under a registered Master for seven years (though this time requirement was occasionally shortened). Acquiring the rank of Provost required a gruelling Prize Playing with a variety of swords and other weapons, followed by a formal oath. Provosts were allowed to accept students and open their own fighting schools. Provost is also used as a rank in Historical European martial arts Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms. While there is limited surviving documentation of the mar ... organisations, such as the Association for Renaissance Martial Arts, and the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminars
A seminar is a form of academic instruction, either at an academic institution or offered by a commercial or professional organization. It has the function of bringing together small groups for recurring meetings, focusing each time on some particular subject, in which everyone present is requested to participate. This is often accomplished through an ongoing Socratic dialogue with a seminar leader or instructor, or through a more formal presentation of research. It is essentially a place where assigned readings are discussed, questions can be raised and debates can be conducted. Etymology The word ''seminar'' was borrowed from German (in which it is capitalized as ), and is ultimately derived from the Latin word , meaning 'seed plot' (an old-fashioned term for ' seedbed'). Its root word is (Latin for 'seed'). Overview In some European universities, a ''seminar'' may be a large lecture course, especially when conducted by a renowned thinker (regardless of the size of the audi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampfringen
''Ringen'' is the German language term for grappling (wrestling). In the context of the German school of historical European martial arts during the Late Middle Ages and the German Renaissance, ''Ringen'' refers to unarmed combat in general, including grappling techniques used as part of swordsmanship. The German tradition has records of a number of master-''Ringer'' of the 15th to 16th centuries specializing in unarmed combat, such as Ott Jud. Medieval and early Renaissance wrestling treatises present both sport and combat techniques together as one art. The distinction is made more frequently by modern practitioners than is present in historical sources, but in a select few examples the terms for sportive grappling or ''geselliges Ringen'' and earnest unarmed combat or ''Kampfringen'' (where ''Kampf'' is the Early Modern German term for "war" or ''battle'') were used to describe specific techniques which were only suitable for one scenario or the other. There are no known s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterstaff
A quarterstaff (plural quarterstaffs or quarterstaves), also short staff or simply staff is a traditional European polearm, which was especially prominent in England during the Early Modern period. The term is generally accepted to refer to a shaft of hardwood from long, sometimes with a metal tip, ferrule, or spike at one or both ends. The term "short staff" compares this to the "long staff" based on the pike with a length in excess of . The height of the staff should be around the same as the user plus their hand set upright on their head (approximately ). Etymology The name "quarterstaff" is first attested in the mid-16th century. The "quarter" possibly refers to the means of production, the staff being made from quartersawn hardwood (as opposed to a staff of lower quality made from conventionally sawn lumber or from a tree branch). OED; English longbows were traditionally made from staves of yew or ash that were split into quarters. If the longbow was not in use, the 'q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polearm
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantly melee weapons, with a subclass of spear-like designs fit for thrusting and/or throwing. Because many polearms were adapted from Garden tool, agricultural implements or other fairly abundant tools, and contained relatively little metal, they were cheap to make and readily available. When belligerents in warfare had a poorer class who could not pay for dedicated military weapons, they would often appropriate tools as cheap weapons. The cost of training was comparatively low, since these conscripted farmers had spent most of their lives using these "weapons" in the fields. This made polearms the favoured weapon of peasant levies and peasant rebellions the world over. Polearms can be divided into three broad categories: those designed for extended rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
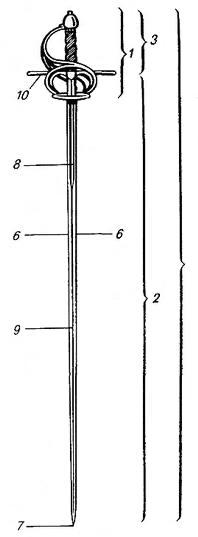
Rapier
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as '' spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It was widely popular in Western Europe throughout the 16th and 17th centuries as a symbol of nobility or gentleman status. It is called because it was carried as an accessory to clothing, generally used for fashion and as a weapon for dueling, self-defense and as a military side arm. Its name is of Spanish origin and appears recorded for the first time in the '' Coplas de la panadera'', by Juan de Mena, written approximately between 1445 and 1450: As fencing spread throughout Western Europe, important sources for rapier fencing arose in Spain, known under the term ("dexterity"), in Italy and France. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct continuation of this tradition of fencing. Rapier fencing form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großes Messer
A messer (German for "knife") is a single-edged sword of the 15th and 16th century, characterised by knife-like hilt construction methods. While the various names are often used synonymously, messers can be divided into several principal groups: A ''Bauernwehr'' ("peasant's knife" or "peasant's sidearm") or ''Hauswehr'' ("home/household knife") is a single-handed knife, used for utility and defence. Typical blade lengths range from lengths up to around . ''Messer'', ''Langes Messer'', and ''Großes Messer'' ("knife", "long knife", and "great knife" respectively) are usually single-handed swords used for self-defence. These blade lengths ranged from about to . Hilts are normally suited to single handed use, but the larger examples may feature extended grips suitable for a second hand-hold. ''Kriegsmesser'' ("war knife") are the largest examples of messer-hilted weapons, ranging from around long with approximately blade, up to around long with blades up to in length. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |