|
Aschoff's Rules
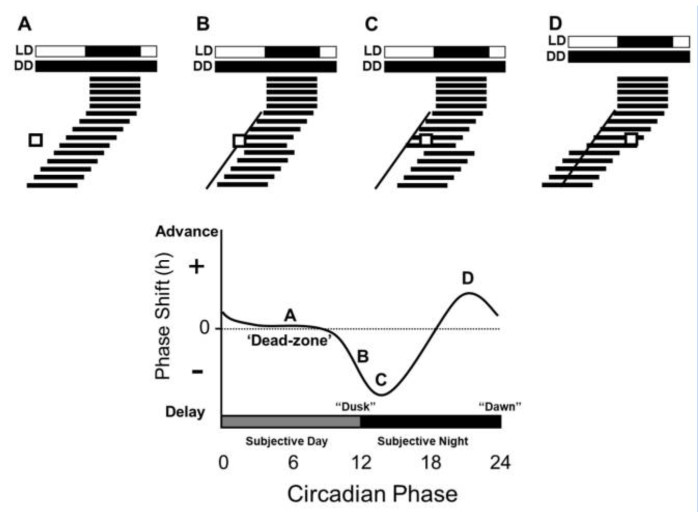
Aschoff's Rules consist of three generalized statements that were first introduced by Jürgen Aschoff. These rules are fundamental in the field of chronobiology as they describe how the circadian rhythms of both Diurnality, diurnal and Nocturnality, nocturnal animals are impacted by varying light conditions.Daan S, Gwinner E (1998). "Jürgen Aschoff (1913–1998)". ''Nature.'' 396 (6710): 418. doi:10.1038/24750. PMID 9853745 The circadian rhythm, regulated by a circadian pacemaker, demonstrates endogenous and entrainable oscillation with a period close to 24 hours. The time required for one Circadian oscillations, circadian oscillation to occur under constant conditions is known as the free-running period (τ). In a natural setting, the circadian rhythm is synchronized with the external environment through Entrainment (chronobiology), entrainment to Zeitgeber signals.Daan, Serge. (1998) "Colin Pittendrigh, Jürgen Aschoff, and the Natural Entrainment of Circadian Systems." ''The Coli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jürgen Aschoff
Jürgen Walther Ludwig Aschoff (January 25, 1913 – October 12, 1998) was a German physician, biologist and behavioral physiologist. Together with Erwin Bünning and Colin Pittendrigh, he is considered to be a co-founder of the field of chronobiology. Aschoff's work in the field of chronobiology introduced ideas of light interactions in the circadian rhythms of nocturnal and diurnal species as summarized by Aschoff's Rules. Life Aschoff was born in Freiburg Im Breisgau, the fifth child of pathologist Ludwig Aschoff (known for discovering the Aschoff-Tawara or atrioventricular node) and his wife Clara. He grew up in the liberal but morally strict world of Prussian academia. After the Abitur at a humanistic high school, he – according to his own statement "lacking a specific interest" – studied medicine at the University of Bonn, where he joined the Burschenschaft (fraternity) Alemannia Bonn. Aschoff's scientific career began in 1938, when he moved to the University of Göttin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (gene)
Period (per) is a gene located on the X chromosome of '' Drosophila melanogaster''. Oscillations in levels of both ''per'' transcript and its corresponding protein PER have a period of approximately 24 hours and together play a central role in the molecular mechanism of the ''Drosophila'' biological clock driving circadian rhythms in eclosion and locomotor activity. Mutations in the per gene can shorten (''perS''), lengthen (''perL''), and even abolish (''per0'') the period of the circadian rhythm. Discovery The period gene and three mutants (''perS'', ''perL'', and ''per0'') were isolated in an EMS mutagenesis screen by Ronald Konopka and Seymour Benzer in 1971. The ''perS'', ''perL'', and ''per0'' mutations were found to not complement each other, so it was concluded that the three phenotypes were due to mutations in the same gene. The discovery of mutants that altered the period of circadian rhythms in eclosion and locomotor activity (''perS'' and ''perL'') indicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Ganglion Cells
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract. A small p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoentrainment (chronobiology)
In chronobiology, photoentrainment refers to the process by which an organism's biological clock, or circadian rhythm, synchronizes to daily cycles of light and dark in the environment. The mechanisms of photoentrainment differ from organism to organism. Photoentrainment plays a major role in maintaining proper timing of physiological processes and coordinating behavior within the natural environment. Studying organisms’ different photoentrainment mechanisms sheds light on how organisms may adapt to anthropogenic changes to the environment. Background 24-hour physiological rhythms, known now as circadian rhythms, were first documented in 1729 by Jean Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan, a French astronomer who observed that mimosa plants (''Mimosa pudica'') would orient themselves to be toward the position of the sun despite being in a dark room. That observation spawned the field of chronobiology, which seeks to understand the mechanisms that underlie endogenously expressed daily rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoreceptor Cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential. There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes: rod cell, rods, cone cell, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form an image of the environment, Visual perception, sight. Rods primarily mediate scotopic vision (dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate photopic vision (bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. The intrinsically photosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Entrainment Through RHT Pathway
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared (with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies), called collectively '' optical radiation''. In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarization. Its speed in vacuum, , is one of the fundamental constants of nature. All electromagnetic radiation exhibits some properties of both particles and waves. Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoentrainment
In chronobiology, photoentrainment refers to the process by which an organism's biological clock, or circadian rhythm, synchronizes to daily cycles of light and dark in the environment. The mechanisms of photoentrainment differ from organism to organism. Photoentrainment plays a major role in maintaining proper timing of physiological processes and coordinating behavior within the natural environment. Studying organisms’ different photoentrainment mechanisms sheds light on how organisms may adapt to anthropogenic changes to the environment. Background 24-hour physiological rhythms, known now as circadian rhythms, were first documented in 1729 by Jean Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan, a French astronomer who observed that mimosa plants (''Mimosa pudica'') would orient themselves to be toward the position of the sun despite being in a dark room. That observation spawned the field of chronobiology, which seeks to understand the mechanisms that underlie endogenously expressed daily rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprachiasmatic Nuclei
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a small region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for regulating sleep cycles in animals. Reception of light inputs from photosensitive retinal ganglion cells allow it to coordinate the subordinate cellular clocks of the body and entrain to the environment. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in an approximately 24-hour cycle. The SCN also interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types, neurotransmitters and peptides, including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide. Disruptions or damage to the SCN has been associated with different mood disorders and sleep disorders, suggesting the significance of the SCN in regulating circadian timing. Neuroanatomy The SCN is situated in the anterior part of the hypothalamus immediately dorsal, or ''superior'' (hence supra) to the optic chiasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanopsin
Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinylidene protein, retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene ''Opn4''. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, both involved in the formation of visual images: rhodopsin and photopsin (types I, II, and III) in the Rod cell, rod and Cone cell, cone photoreceptor cells, respectively. In humans, melanopsin is found in intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs). It is also found in the iris of mice and primates. Melanopsin is also found in rats, amphioxus, and other chordates. ipRGCs are photoreceptor cells which are particularly sensitive to the absorption of short-wavelength (blue) visible light and communicate information directly to the area of the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), also known as the central "body clock", in mammals. Melanopsin plays an important non-image-forming role in the Entrainment (chronobiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinohypothalamic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) is a photic neural input pathway involved in the circadian rhythms of mammals. The origin of the retinohypothalamic tract is the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGC), which contain the photopigment melanopsin. The axons of the ipRGCs belonging to the retinohypothalamic tract project directly, monosynaptically, to the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) via the optic nerve and the optic chiasm. The suprachiasmatic nuclei receive and interpret information on environmental light, dark and day length, important in the entrainment of the "body clock". They can coordinate peripheral "clocks" and direct the pineal gland to secrete the hormone melatonin. Structure The retinohypothalamic tract consists of retinal ganglion cells. A distinct population of ganglion cells, known as intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), is critically responsible for providing non-image-forming visual signals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARNTL
Basic helix-loop-helix ARNT-like protein 1 or aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL), or brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BMAL1'' gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as ''MOP3'', and, less commonly, ''bHLHe5'', ''BMAL'', ''BMAL1C'', ''JAP3'', ''PASD3'', and ''TIC''. ''BMAL1'' encodes a transcription factor with a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and two PAS domains. The human ''BMAL1'' gene has a predicted 24 exons, located on the p15 band of the 11th chromosome. The BMAL1 protein is 626 amino acids long and plays a key role as one of the positive elements in the mammalian auto-regulatory transcription-translation negative feedback loop (TTFL), which is responsible for generating molecular circadian rhythms. Research has revealed that ''BMAL1'' is the only clock gene without which the circadian clock fails to function in humans. ''BMAL1'' has also been identified as a candidate gene for susc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptochrome
Cryptochromes (from the Greek κρυπτός χρώμα, "hidden colour") are a class of flavoproteins found in plants and animals that are sensitive to blue light. They are involved in the circadian rhythms and the sensing of magnetic fields in a number of species. The name ''cryptochrome'' was proposed as a ''portmanteau'' combining the '' chromatic'' nature of the photoreceptor, and the '' cryptogamic'' organisms on which many blue-light studies were carried out. The genes ''CRY1'' and ''CRY2'' encode the proteins CRY1 and CRY2, respectively. Cryptochromes are classified into plant Cry and animal Cry. Animal Cry can be further categorized into insect type (Type I) and mammal-like (Type II). CRY1 is a circadian photoreceptor whereas CRY2 is a clock repressor which represses Clock/Cycle (Bmal1) complex in insects and vertebrates. In plants, blue-light photoreception can be used to cue developmental signals. Besides chlorophylls, cryptochromes are the only proteins known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |