|
Asaph The Jew
Asaph the Jew ( , ''Asaph HaYehudi''), also known as Asaph ben Berechiah and Asaph the Physician ( ''Asaph HaRofè'') is a figure mentioned in the ancient Jewish medical text the ''Sefer Refuot'' (lit. “Book of Medicines”). Thought by some to have been a History of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Jew and the earliest known Hebrew language, Hebrew medical writer, he is however a rather uncertain figure who some have suggested is identifiable with the legendary mystical vizier Asif ibn Barkhiya of Arabian folklore, associated with King Solomon. Scholars in favor of Asaph’s historicity suggest that he might have lived somewhere between the 3rd and 7th Centuries CE, possibly in Byzantine Palaestina or Mesopotamia. However, the text itself from which Asaph is known seems to place him between Hippocrates and Pedanius Dioscorides, which if chronological would imply that he might have been thought to have been between the 5th Century BCE and 1st Century CE, though this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Refuot
Sefer Refuot (, "The Book of Medicines"), also known as Sefer Asaph ( , , "The Book of Asaph" or "Asaf") , is the earliest-known medical book written in Hebrew. Attributed or dedicated to Asaph the Physician (also known as Asaph ben Berechiah; possibly a Byzantine Jew; or possibly identifiable with Asif ibn Barkhiya, a legendary mystical polymath vizier in Arabic folklore, associated with King Solomon) and one Yoḥanan ben Zabda, who may have lived in Byzantine Palestine or Mesopotamia between the 3rd and 6th Centuries CE (though this is very uncertain, and some have suggested that Asaph and Yoḥanan were both legendary sages in Jewish tradition, to whom the text was dedicated; not its literal authors). The date of the text is uncertain, with most manuscripts coming from the late medieval era; though the lack of Arabian medical knowledge in the book implies it may have originally been written much earlier. Content Sefer Refuot discusses illnesses, treatments and prevention. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
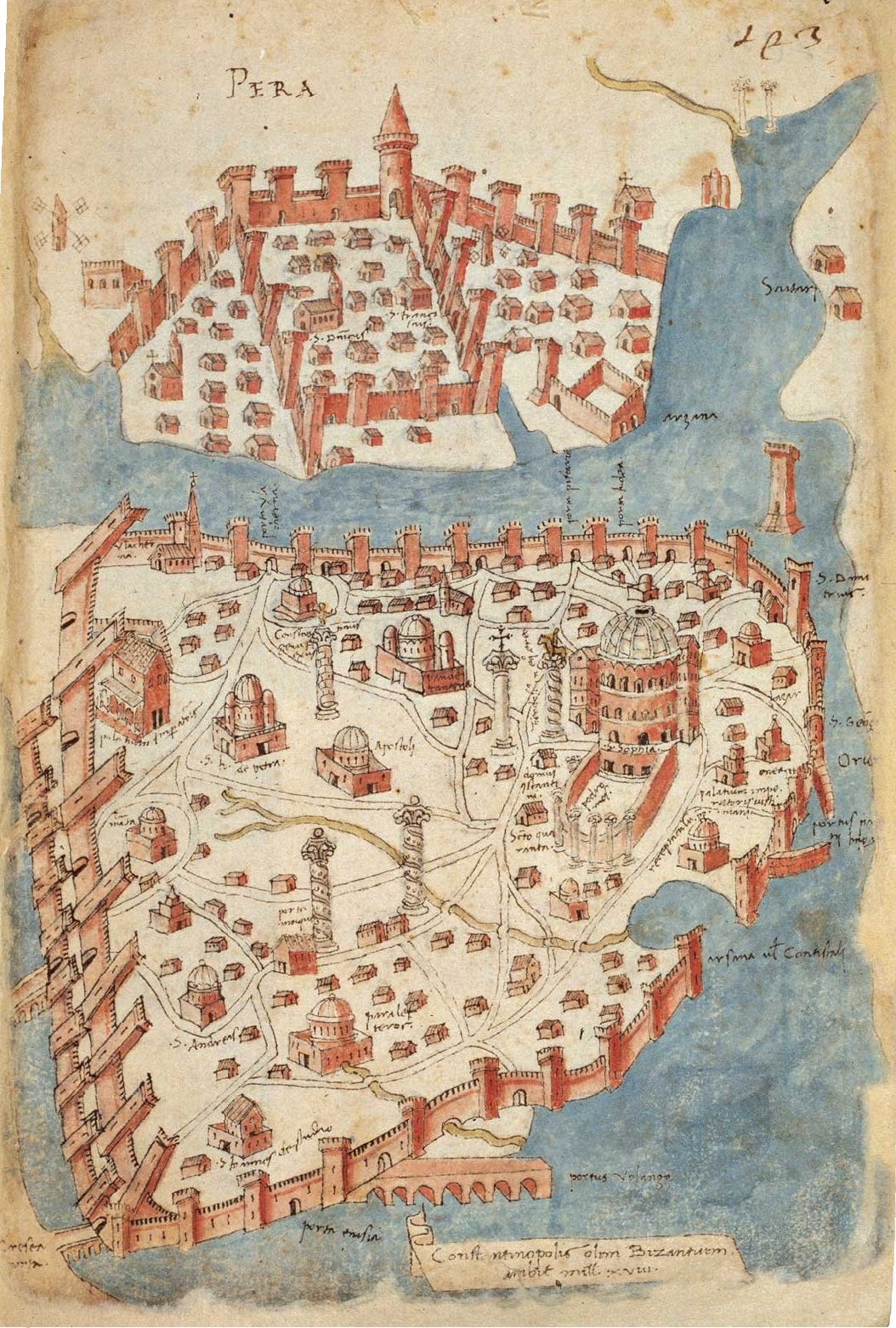
History Of The Jews In The Byzantine Empire
Jews were numerous and had significant roles throughout the history of the Byzantine Empire. Background and legal standing After the decline of the Greek-speaking Hellenistic Judaism in ancient times, the use of the Greek language and the integration of Greek culture into Judaism continued to be an integral part of life in Jewish communities in the Byzantine Empire. The legal standing of the Jews of the Byzantine Empire was unique throughout the empire’s history. They did not belong to the Christian Eastern Orthodox faith, which was the state church of the Byzantine Empire, nor were they, in most circumstances, grouped together with heretics and pagans. They were placed in a legal position somewhere between the two. The place along the spectrum of social freedom in which Byzantine Jews found themselves varied somewhat, though far from drastically, over time. This status was shaped largely by three factors: the theological aim of the state to preserve Jews as a living testame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asif Ibn Barkhiya
Āṣif bin Barkhiyā () is thought to be the Islamic scriptural figure who brought the Queen of Sheba's throne to King Solomon "...in the twinkling of an eye". Credited with the role of court vizier,Richard F. Burton, ''Book of the Thousand Nights and a Night: vol. I'', Kissinger Publishing Co, 2003, p. 42 it is a story occasionally recounted in Middle Eastern lore, but perhaps more so in occult circles. The figure himself is largely unexpounded, as very few references to him are found in classical texts other than through subtle terms in Chapter 27 of the Qur'an. He is, however, apparent in a number of books that deal with Islamic occultism or '' Ruhaniyya'', and in one that appears to be attributed directly to him (titled, ''al-Ajnas''). In like manner, through the ages he was eminently revered by the Quranic exegetical traditions where the powers he possessed were associated to the Ineffable Name of Allah. Narration The Qur'anic narrative is as follows: He said, 'O Council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Solomon
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish '' rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as '' rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is understood to be the highest rank in the feudal order, potentially subject, at least nominally, only to an emperor (harking back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, and the (however misguided) formulation of Humorism, humoral theory. His studies set out the basic ideas of modern-day specialties, including surgery, urology, neurology, acute medicine and Orthopedic surgery, orthopedics. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedanius Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides (, ; 40–90 AD), "the father of pharmacognosy", was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of (in the original , , both meaning "On Medical Material") , a 5-volume Greek encyclopedic pharmacopeia on herbal medicine and related medicinal substances, that was widely read for more than 1,500 years. For almost two millennia Dioscorides was regarded as the most prominent writer on plants and plant drugs. Life A native of Anazarbus, Cilicia, Asia Minor, Dioscorides likely studied medicine nearby at the school in Tarsus, which had a pharmacological emphasis, and he dedicated his medical books to Laecanius Arius, a medical practitioner there. Though he writes he lived a "soldier's life" or "soldier-like life", his pharmacopeia refers almost solely to plants found in the Greek-speaking eastern Mediterranean, making it likely that he served in campaigns, or travelled in a civilian capacity, less widely as supposed. The name Pedanius is Roman, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charaka Samhita
The ''Charaka Samhita'' () is a Sanskrit text on Ayurveda (Indian traditional medicine). Along with the '' Sushruta Samhita'', it is one of the two foundational texts of this field that have survived from ancient India. It is one of the three works that constitute the Brhat Trayi. The text is based on the Agnivesha Samhitā, an older encyclopedic medical compendium by Agniveśa. It was revised by Charaka between 100 BCE and 200 CE and renamed ''Charaka Samhitā''. The pre-2nd century CE text consists of 8 books and 120 chapters. It describes ancient theories on the human body, etiology, symptomology and therapeutics for a wide range of diseases. The ''Charaka Samhita'' also includes sections on the importance of diet, hygiene, prevention, medical education, and the teamwork of a physician, nurse and patient necessary for recovery to health. Authorship The ''Charaka Samhita'' states that the content of the book was first taught by Atreya, and then subsequently codified b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yitzhak Shamir Medical Center
Shamir Medical Center, formerly Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, is a teaching hospital in Be'er Ya'akov, southeast of Tel Aviv, Israel. History The Medical Center was named after Asaph the Jew, author of the Oath of Asaph and an early medical text. The facility was established in 1918 as a military hospital of the British Army in the closing days of the First World War. It was located adjacent to the sprawling British military base in Tzrifin (Sarafand). After the creation of the State of Israel, it was converted to an Israeli hospital. The hospital was renamed after the former Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Shamir in April 2017. Services It is one of Israel's largest hospitals, with over 800 beds. It serves over 370,000 people in Israel's Central District. As a teaching facility, the hospital is part of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine of Tel Aviv University. On its grounds are the first and largest Israeli academic nursing school and the oldest Israeli school of physiotherapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Israeli-occupied territories, It occupies the Occupied Palestinian territories, Palestinian territories of the West Bank in the east and the Gaza Strip in the south-west. Israel also has a small coastline on the Red Sea at its southernmost point, and part of the Dead Sea lies along its eastern border. Status of Jerusalem, Its proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, while Tel Aviv is the country's Gush Dan, largest urban area and Economy of Israel, economic center. Israel is located in a region known as the Land of Israel, synonymous with the Palestine (region), Palestine region, the Holy Land, and Canaan. In antiquity, it was home to the Canaanite civilisation followed by the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Situate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |