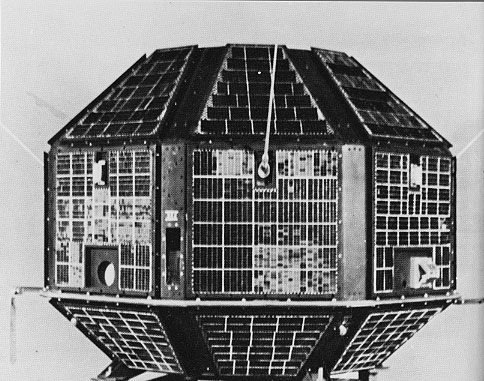
|
Aryabhata (other) , an Indian surname
{{disambig ...
Aryabhata (also Aryabhatta and Aryabhata I; 476 – 550) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer and author of the ''Aryabhatiya''. Aryabhata may also refer to: ;Mathematics * Aryabhata algorithm * Aryabhata equation *Āryabhaṭa numeration * Āryabhaṭa's sine table ;Others *Aryabhata (satellite), the first satellite of India *Aryabhata (crater), lunar crater *Aryabhata II (fl. between and CE), an Indian mathematician *Aryabhata Award, an aerospace award in India See also * * * Arya (other) *Bhat Bhat (also spelled as Bhatt or Butt, ) is a Brahmin surname used in the Indian subcontinent. Bhat and Bhatt are shortened renditions of Bhatta or Brahmabhatta. Etymology The word "Bhat" (, ) means "scholar" in Sanskrit. While the original sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryabhata
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the '' Āryabhaṭīya'' (which mentions that in 3600 '' Kali Yuga'', 499 CE, he was 23 years old) and the ''Arya- siddhanta''. For his explicit mention of the relativity of motion, he also qualifies as a major early physicist. Biography Name While there is a tendency to misspell his name as "Aryabhatta" by analogy with other names having the " bhatta" suffix, his name is properly spelled Aryabhata: every astronomical text spells his name thus, including Brahmagupta's references to him "in more than a hundred places by name". Furthermore, in most instances "Aryabhatta" would not fit the metre either. Time and place of birth Aryabhata mentions in the ''Aryabhatiya'' that he was 23 years old 3,600 years into the '' Kali Yuga'', but this is not to mean that the text was composed at that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryabhatiya
''Aryabhatiya'' (IAST: ') or ''Aryabhatiyam'' ('), a Indian astronomy, Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is the ''Masterpiece, magnum opus'' and only known surviving work of the 5th century Indian mathematics, Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Philosopher of astronomy Roger Billard estimates that the book was composed around 510 CE based on historical references it mentions. Structure and style Aryabhatiya is written in Sanskrit and divided into four sections; it covers a total of 121 verses describing different moralitus via a mnemonic writing style typical for such works in India (see definitions below): # Gitikapada (13 verses): large units of time—Kalpa (aeon), kalpa, manvantara, and Yuga Cycle, yuga—which present a cosmology different from earlier texts such as Lagadha's Vedanga Jyotisha (ca. 1st century BCE). There is also a table of [sine]s (jya), given in a single verse. The duration of the planetary revolutions during a mahayuga is given as 4.32 million years, using the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryabhata Algorithm
In mathematics, the Chinese remainder theorem states that if one knows the remainders of the Euclidean division of an integer ''n'' by several integers, then one can determine uniquely the remainder of the division of ''n'' by the product of these integers, under the condition that the divisors are pairwise coprime (no two divisors share a common factor other than 1). The theorem is sometimes called Sunzi's theorem. Both names of the theorem refer to its earliest known statement that appeared in ''Sunzi Suanjing'', a Chinese manuscript written during the 3rd to 5th century CE. This first statement was restricted to the following example: If one knows that the remainder of ''n'' divided by 3 is 2, the remainder of ''n'' divided by 5 is 3, and the remainder of ''n'' divided by 7 is 2, then with no other information, one can determine the remainder of ''n'' divided by 105 (the product of 3, 5, and 7) without knowing the value of ''n''. In this example, the remainder is 23. Moreove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryabhata Equation
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the ''Āryabhaṭīya'' (which mentions that in 3600 ''Kali Yuga'', 499 CE, he was 23 years old) and the ''Arya-siddhanta''. For his explicit mention of the relativity of motion, he also qualifies as a major early physicist. Biography Name While there is a tendency to misspell his name as "Aryabhatta" by analogy with other names having the "bhatta" suffix, his name is properly spelled Aryabhata: every astronomical text spells his name thus, including Brahmagupta's references to him "in more than a hundred places by name". Furthermore, in most instances "Aryabhatta" would not fit the metre either. Time and place of birth Aryabhata mentions in the ''Aryabhatiya'' that he was 23 years old 3,600 years into the ''Kali Yuga'', but this is not to mean that the text was composed at that time. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |